PHYS2101: General Physics I
... Analyse problems into components and treat each component using the relevant physical laws. Assess the use of different principles and approaches in solutions of the problems in linear and rotational motions. Experience applications of dynamics and kinematics in common real-life situations. ...
... Analyse problems into components and treat each component using the relevant physical laws. Assess the use of different principles and approaches in solutions of the problems in linear and rotational motions. Experience applications of dynamics and kinematics in common real-life situations. ...
File - PHYSICS PHUN WITH MS.BEGUM
... 12. Mass does not affect motion in a free fall, falls at rate of 10 m/s each second. 13. Once an object is set in motion, no other force is necessary to keep it in motion. 14. When any two objects touch or collide with each other, the force each exerts is the same. 15. Quantities that have both size ...
... 12. Mass does not affect motion in a free fall, falls at rate of 10 m/s each second. 13. Once an object is set in motion, no other force is necessary to keep it in motion. 14. When any two objects touch or collide with each other, the force each exerts is the same. 15. Quantities that have both size ...
Forces - faculty at Chemeketa
... energy now and there couldn’t be any energy before the big bang. The total energy apparently increased thus violating the first law of thermodynamics. For this alleged violation to be true, we must know both the total energy of the universe both before and after the big bang and show that they are d ...
... energy now and there couldn’t be any energy before the big bang. The total energy apparently increased thus violating the first law of thermodynamics. For this alleged violation to be true, we must know both the total energy of the universe both before and after the big bang and show that they are d ...
amanda`sNewton`s First Law
... being moved or, if the object is moving, to resist a change in speed or direction until an outside force acts on the object. ...
... being moved or, if the object is moving, to resist a change in speed or direction until an outside force acts on the object. ...
Review Forces Part 2
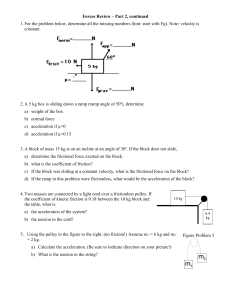
... 2. A 5 kg box is sliding down a ramp (ramp angle of 50º), determine a) weight of the box b) normal force c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. ...
... 2. A 5 kg box is sliding down a ramp (ramp angle of 50º), determine a) weight of the box b) normal force c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. ...
10 Motion Trial Test
... ticker tape used to record the motion of a student pulling the tape through a ticker timer. The marked interval represents a time interval of 0.1 seconds. (a) What is the average speed (in cm/s) shown a during the marked interval? (b) Is the speed throughout the marked interval constant, increasing ...
... ticker tape used to record the motion of a student pulling the tape through a ticker timer. The marked interval represents a time interval of 0.1 seconds. (a) What is the average speed (in cm/s) shown a during the marked interval? (b) Is the speed throughout the marked interval constant, increasing ...
Name: Date:______ Period: ______ Study Guide Answers Motion
... Be able to define and understand Motion- One objects distance from another is changing Reference point- A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion. Velocity- speed in a given direction ...
... Be able to define and understand Motion- One objects distance from another is changing Reference point- A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion. Velocity- speed in a given direction ...
Simple Harmonic Motion and Elastic Energy
... motion. The spring force is a restoring force always directed toward the equilibrium position. The Acceleration of an object in simple harmonic motion (SHM) is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium and oppositely directed. a=-(k/m)x is the result of applying Newton’s second law to a mass ...
... motion. The spring force is a restoring force always directed toward the equilibrium position. The Acceleration of an object in simple harmonic motion (SHM) is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium and oppositely directed. a=-(k/m)x is the result of applying Newton’s second law to a mass ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... 6.2 Newton’s second law Newton’s first law tells us that motion cannot change without a net force. According to Newton’s second law, the amount of acceleration depends on both the force and the mass. ...
... 6.2 Newton’s second law Newton’s first law tells us that motion cannot change without a net force. According to Newton’s second law, the amount of acceleration depends on both the force and the mass. ...
Projectile Motion
... Object that is launched by a force and continues to move by its own inertia Only force acting on object is gravity Trajectory- the path of a projectile (parabola) ...
... Object that is launched by a force and continues to move by its own inertia Only force acting on object is gravity Trajectory- the path of a projectile (parabola) ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... body diagram for the crate. b) The truck starts to accelerate with an acceleration ac. Draw the free body diagram for the crate, if the crate does not slip. ...
... body diagram for the crate. b) The truck starts to accelerate with an acceleration ac. Draw the free body diagram for the crate, if the crate does not slip. ...
Physics Challenge Question 1: Solutions
... Even though this is just an estimate (our escape velocity equation isn’t entirely correct for light beams), it still shows just how extremely compact black holes are: The mass of our sun (about 700,000 km in radius) has been squeezed into a radius of just 3 km! ...
... Even though this is just an estimate (our escape velocity equation isn’t entirely correct for light beams), it still shows just how extremely compact black holes are: The mass of our sun (about 700,000 km in radius) has been squeezed into a radius of just 3 km! ...
ACCELERATION WORD PROBLEMS
... b. Should your answer be positive or negative? Explain your reasoning. ...
... b. Should your answer be positive or negative? Explain your reasoning. ...