Notes for Newton`s Laws
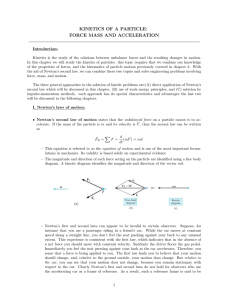
... Step 1 We introduce the concept of Force and define it in terms of the acceleration experienced by a particular standard object. Step 2 We develop a procedure for assigning a Mass to an object so that we may understand the fact that different particles of the same kind experience different accelerat ...
... Step 1 We introduce the concept of Force and define it in terms of the acceleration experienced by a particular standard object. Step 2 We develop a procedure for assigning a Mass to an object so that we may understand the fact that different particles of the same kind experience different accelerat ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion – The Law of Inertia
... two ropes, how would the tension force in both supporting ropes compare with her weight? The tension force in each rope equals half her weight. ...
... two ropes, how would the tension force in both supporting ropes compare with her weight? The tension force in each rope equals half her weight. ...
chapter 2 - temsscience7
... W = (60 kg) (9.8 m /s ) W = 588 N From the list of Conversion Factors on the inside cover of the text we obtain the conversion that tells us that 1 lb = 4.448 N, so we can convert 588 N to pounds by multiplying the right hand side of the equation by unity expressed in the form 1 = 1 lb / 4.448 N W = ...
... W = (60 kg) (9.8 m /s ) W = 588 N From the list of Conversion Factors on the inside cover of the text we obtain the conversion that tells us that 1 lb = 4.448 N, so we can convert 588 N to pounds by multiplying the right hand side of the equation by unity expressed in the form 1 = 1 lb / 4.448 N W = ...
Inertia And Force Diagrams
... “An energy field created by all living things. It surrounds us, penetrates us, and binds the galaxy together.” ...
... “An energy field created by all living things. It surrounds us, penetrates us, and binds the galaxy together.” ...
AP-1 Cutnell 06-10 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m above the initial position. Find the speed of the bullet. ...
... A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m above the initial position. Find the speed of the bullet. ...
Dynamics Problem Set
... 7. A truck skidding on wet asphalt has a mass of 2000 kg. The total force of kinetic friction of the asphalt on the tires is 1000 N [back]. Calculate the deceleration of the truck. 8. A net force of 2.2 × 102 N [W] applied to an object increases its velocity from 8.0 m/s [W] to 24 m/s [W] in 5.4 s. ...
... 7. A truck skidding on wet asphalt has a mass of 2000 kg. The total force of kinetic friction of the asphalt on the tires is 1000 N [back]. Calculate the deceleration of the truck. 8. A net force of 2.2 × 102 N [W] applied to an object increases its velocity from 8.0 m/s [W] to 24 m/s [W] in 5.4 s. ...
Name of Model - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 4. The international space station orbits earth once every 90 minutes. a. Name the force that allows the ISS to orbit earth. The force of gravity of the earth on the space station. b. Explain why the space station doesn't crash to earth due to the force on it. Because the space station keeps moving ...
... 4. The international space station orbits earth once every 90 minutes. a. Name the force that allows the ISS to orbit earth. The force of gravity of the earth on the space station. b. Explain why the space station doesn't crash to earth due to the force on it. Because the space station keeps moving ...
Force
... result in an object with mass accelerating. The standard unit of force is a Newton (N) which is the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/sec2. Force has both magnitude and direction and therefore it is a vector quantity. Typically directions noted as forward, up, or to ...
... result in an object with mass accelerating. The standard unit of force is a Newton (N) which is the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/sec2. Force has both magnitude and direction and therefore it is a vector quantity. Typically directions noted as forward, up, or to ...
What is a Force? (PowerPoint)
... Before we go any further we need to talk about types of forces. There are many types of forces but we will only touch on seven in detail. There are two others I’d like to mention: Nuclear force: The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of a ...
... Before we go any further we need to talk about types of forces. There are many types of forces but we will only touch on seven in detail. There are two others I’d like to mention: Nuclear force: The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of a ...
Unit 3.2 Force & Motion
... then speeds up in the opposite direction. C. Hesoo moves in one direction, remains at rest, and then moves in the opposite direction D. Hesoo has no acceleration ...
... then speeds up in the opposite direction. C. Hesoo moves in one direction, remains at rest, and then moves in the opposite direction D. Hesoo has no acceleration ...
Rotational or Angular Motion
... The net torque now adds to zero—and the board does not rotate. The board is in rotational equilibrium. Note: This will only be true if the board is uniform and the pivot is at the center of the board, so that the gravitational force is causing no torque on the board. ...
... The net torque now adds to zero—and the board does not rotate. The board is in rotational equilibrium. Note: This will only be true if the board is uniform and the pivot is at the center of the board, so that the gravitational force is causing no torque on the board. ...
Problems
... constant 5 000 N/m and pushed downward, so that the spring is compressed by 0.100 m. After the block is released from rest it travels upward and then leaves the spring. To what maximum height above the point of release does it rise 10- A force acting on a particle moving in the xy plane is given ...
... constant 5 000 N/m and pushed downward, so that the spring is compressed by 0.100 m. After the block is released from rest it travels upward and then leaves the spring. To what maximum height above the point of release does it rise 10- A force acting on a particle moving in the xy plane is given ...