Projectile motion
... The initial velocity is affecting both the projectiles in a vacuum and with air resistance. As the magnitude of the initial velocity increases, both the maximum height reached and the final horizontal d ...
... The initial velocity is affecting both the projectiles in a vacuum and with air resistance. As the magnitude of the initial velocity increases, both the maximum height reached and the final horizontal d ...
Force and Motion
... Define and give example of Force Define and give example of balanced force Define and give example of unbalanced force Define and give example of Net Force Newton’s 2nd law of Motion Montage Title, credits, music, and editing. ...
... Define and give example of Force Define and give example of balanced force Define and give example of unbalanced force Define and give example of Net Force Newton’s 2nd law of Motion Montage Title, credits, music, and editing. ...
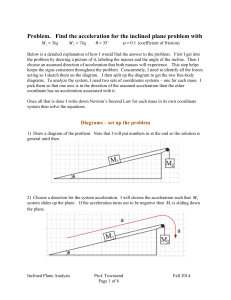
Problem. Find the acceleration for the inclined plane problem with
... acting so I sketch them on the diagram. I then split up the diagram to get the two free-body diagrams. To analyze the system, I need two sets of coordinates systems – one for each mass. I pick them so that one axis is in the direction of the assumed acceleration then the other coordinate has no acce ...
... acting so I sketch them on the diagram. I then split up the diagram to get the two free-body diagrams. To analyze the system, I need two sets of coordinates systems – one for each mass. I pick them so that one axis is in the direction of the assumed acceleration then the other coordinate has no acce ...
2.2.1 In Class or Homework Exercise 1. If you are in a car that is
... (a) Using Newton’s laws of motion, explain what happens. Your body is initially at rest; it therefore needs a force to accelerate it forward (1st Law). The back of the seat applies this force to your body, but your head is above the seat. In order for your head to accelerate forward at the same rate ...
... (a) Using Newton’s laws of motion, explain what happens. Your body is initially at rest; it therefore needs a force to accelerate it forward (1st Law). The back of the seat applies this force to your body, but your head is above the seat. In order for your head to accelerate forward at the same rate ...
Uniform Motion - Virtual Homeschool Group
... action then it deflects the motion into an arc. If force is at an arbitrary angle then both timing and path of action are affected. Force (up & left) Moving this way ...
... action then it deflects the motion into an arc. If force is at an arbitrary angle then both timing and path of action are affected. Force (up & left) Moving this way ...
A 75.0-kg skier starts from rest and slides down a
... by friction, we use the Work-Kinetic Energy Principle: Wnet = ∆K ...
... by friction, we use the Work-Kinetic Energy Principle: Wnet = ∆K ...
Problem Set 4 - Cabrillo College
... Q4.8: Internal injuries in vehicular accidents may be due to what is called the "third collision." The first collision is the vehicle hitting the external object. The second collision is the person hitting something on the inside of the car, such as the dashboard or windshield. This may cause extern ...
... Q4.8: Internal injuries in vehicular accidents may be due to what is called the "third collision." The first collision is the vehicle hitting the external object. The second collision is the person hitting something on the inside of the car, such as the dashboard or windshield. This may cause extern ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they ...
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they ...
Forces
... Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (cont.) • Newton’s third law of motion says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of the same size but in the opposite direction on the first object. • E ...
... Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (cont.) • Newton’s third law of motion says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of the same size but in the opposite direction on the first object. • E ...
Slide 1
... A person is pulling a crate of mass M along the floor with a constant force F over a distance d. The coefficient of friction is . (a) Find the work done by the force F on the crate. (b) Same if F changes as F0(1+x2/d2). (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the crate. (d) Find the net ...
... A person is pulling a crate of mass M along the floor with a constant force F over a distance d. The coefficient of friction is . (a) Find the work done by the force F on the crate. (b) Same if F changes as F0(1+x2/d2). (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the crate. (d) Find the net ...
Forces
... • Terminal velocity is the constant velocity of a falling object when the force air resistance equals the force of gravity -the doesn’t mean the objects stop in mid air…it just means it doesn’t accelerate anymore • Mass does NOT matter, all objects fall at the same rate ...
... • Terminal velocity is the constant velocity of a falling object when the force air resistance equals the force of gravity -the doesn’t mean the objects stop in mid air…it just means it doesn’t accelerate anymore • Mass does NOT matter, all objects fall at the same rate ...
Unbalanced Force = Net Force
... A force is a push or a pull that is capable of changing the velocity of a mass. Forces are measured in “Newtons” or “N”, in honor of Sir Isaac Newton. According to Mr. Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is “net force” acting upon it. A net force is the sum of all forces acting on an obj ...
... A force is a push or a pull that is capable of changing the velocity of a mass. Forces are measured in “Newtons” or “N”, in honor of Sir Isaac Newton. According to Mr. Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is “net force” acting upon it. A net force is the sum of all forces acting on an obj ...
inertia and mechanisms
... accelerate them than objects with small masses. This is why, for example, large vehicles need larger engines than small vehicles. The reluctance of a body to speed up or slow down is in direct proportion to the mass and the effect is known as inertia. Newton showed that the relationship between Forc ...
... accelerate them than objects with small masses. This is why, for example, large vehicles need larger engines than small vehicles. The reluctance of a body to speed up or slow down is in direct proportion to the mass and the effect is known as inertia. Newton showed that the relationship between Forc ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-4
... 7. In the Bohr Model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves around the proton at a speed of 2.2 x 106 m/s in a circle of radius 5.3 x 10-11 m. ...
... 7. In the Bohr Model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves around the proton at a speed of 2.2 x 106 m/s in a circle of radius 5.3 x 10-11 m. ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... 4.2 Newton’s Laws of Motion (Weight) Relation Between Mass and Weight ...
... 4.2 Newton’s Laws of Motion (Weight) Relation Between Mass and Weight ...
A standard definition of static equilibrium is - cal
... In other words, for stationary objects or objects moving with constant velocity, the resultant force acting on the object is zero. The object is said to be in equilibrium. If a resultant force acts on an object then that object can be brought into equilibrium by applying an additional force that ex ...
... In other words, for stationary objects or objects moving with constant velocity, the resultant force acting on the object is zero. The object is said to be in equilibrium. If a resultant force acts on an object then that object can be brought into equilibrium by applying an additional force that ex ...
FREE Sample Here
... I suggest not making a big deal about the unfamiliar unit of force—the newton. I simply state that it is the unit of force used by physicists, and if students find themselves uncomfortable with it, simply think of “pounds” in its place. Relative magnitudes, rather than actual magnitudes, are the emp ...
... I suggest not making a big deal about the unfamiliar unit of force—the newton. I simply state that it is the unit of force used by physicists, and if students find themselves uncomfortable with it, simply think of “pounds” in its place. Relative magnitudes, rather than actual magnitudes, are the emp ...
FREE Sample Here
... Another confusion comes from students thinking about wind directions – an easterly wind comes from the east, and therefore heads west (this in itself is confusing), whereas physicists always label vectors according to the direction they are going (so a wind blowing to the west would be represented b ...
... Another confusion comes from students thinking about wind directions – an easterly wind comes from the east, and therefore heads west (this in itself is confusing), whereas physicists always label vectors according to the direction they are going (so a wind blowing to the west would be represented b ...