Notes for Mid
... 3) additional applications include the inclined plane problem which will be done below in the force section. ...
... 3) additional applications include the inclined plane problem which will be done below in the force section. ...
MATH10222, Chapter 4: Frames of Reference 1 Motion relative to a
... acted upon by a gravitational acceleration. This is commonly the case in non-inertial frames of reference where the ‘observer’ and the particle are both in free fall. For example, consider a particle P of mass m in a uniform gravitational field. The force acting on P comes from its weight F = −mgk i ...
... acted upon by a gravitational acceleration. This is commonly the case in non-inertial frames of reference where the ‘observer’ and the particle are both in free fall. For example, consider a particle P of mass m in a uniform gravitational field. The force acting on P comes from its weight F = −mgk i ...
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MECHANICS
... Rigid body – collection of particles, whose relative distances are constant. ...
... Rigid body – collection of particles, whose relative distances are constant. ...
Yr 10 Terms and definitions
... The force of gravity on an object Friction A force that acts against (opposes) or prevents motion Spring balance An instrument to measure weight Balanced forces The forces in one direction equal the forces in other direction (left and right or up and down) and they cause no change in the motion of t ...
... The force of gravity on an object Friction A force that acts against (opposes) or prevents motion Spring balance An instrument to measure weight Balanced forces The forces in one direction equal the forces in other direction (left and right or up and down) and they cause no change in the motion of t ...
Section 12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... 12. Is the following sentence true or false? If the same force acts upon two objects with different masses, the acceleration will be greater false for the object with greater mass. ...
... 12. Is the following sentence true or false? If the same force acts upon two objects with different masses, the acceleration will be greater false for the object with greater mass. ...
212 Lecture 12
... A block of mass M is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface. A bullet of mass m is fired at the block with a muzzle velocity (speed) v. The bullet lodges in the block, and the block ends up with a speed V. In terms of m, M, and V : What is the momentum of the bullet with speed v ? v ...
... A block of mass M is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface. A bullet of mass m is fired at the block with a muzzle velocity (speed) v. The bullet lodges in the block, and the block ends up with a speed V. In terms of m, M, and V : What is the momentum of the bullet with speed v ? v ...
Lecture 4 - Purdue Physics
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • An object’s velocity (a vector) does not change if and only if the net force acting on the object is zero. • In other words, if there is no net force on an object, its speed and direction of motion do not change (including if it is at rest). • Also called “the law ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • An object’s velocity (a vector) does not change if and only if the net force acting on the object is zero. • In other words, if there is no net force on an object, its speed and direction of motion do not change (including if it is at rest). • Also called “the law ...
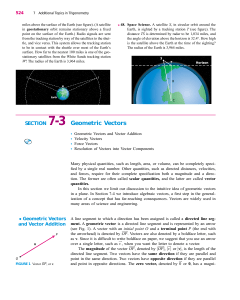
SECTION 7-3 Geometric Vectors
... A vector that represents the direction and magnitude of an applied force is called a force vector. If an object is subjected to two forces, then the sum of these two forces, the resultant force, is a single force. If the resultant force replaced the original two forces, it would act on the object in ...
... A vector that represents the direction and magnitude of an applied force is called a force vector. If an object is subjected to two forces, then the sum of these two forces, the resultant force, is a single force. If the resultant force replaced the original two forces, it would act on the object in ...
APB SHM pendulum Unit 5 packet 2010 KEY
... b. Assume that the spring constant is 500 N/m. A 2.0-kg mass is attached to the lower end of the spring and released from rest. Determine the frequency of oscillation of the mass. f= 1/T but T=2π 2π √ (m/k) = 2π √ (2/500) = 0.4 sec ……..so T = 2.5 Hz c. Suppose that the spring is now used in a spring ...
... b. Assume that the spring constant is 500 N/m. A 2.0-kg mass is attached to the lower end of the spring and released from rest. Determine the frequency of oscillation of the mass. f= 1/T but T=2π 2π √ (m/k) = 2π √ (2/500) = 0.4 sec ……..so T = 2.5 Hz c. Suppose that the spring is now used in a spring ...
2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected
... object’s state of motion, that is, changing its velocity. Any particular force may not actually change an object’s state of motion, as there may be other forces that prevent it from doing so. However, if the net force—the vector sum of all forces acting on the object—is not zero, the velocity will i ...
... object’s state of motion, that is, changing its velocity. Any particular force may not actually change an object’s state of motion, as there may be other forces that prevent it from doing so. However, if the net force—the vector sum of all forces acting on the object—is not zero, the velocity will i ...
Chapter 2 - OnCourse
... Velocity if energy is conserved 1. When calculating PE el the x is defined as a. The stretched length of the spring b. The unstretched length of the spring c. The difference between the stretched and unstretched length of the spring d. The difference between the compressed length and stretched lengt ...
... Velocity if energy is conserved 1. When calculating PE el the x is defined as a. The stretched length of the spring b. The unstretched length of the spring c. The difference between the stretched and unstretched length of the spring d. The difference between the compressed length and stretched lengt ...
Gravity: a force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass
... Free fall- when gravity is the only force acting on an object (free fall acceleration is directed toward center of earth) ...
... Free fall- when gravity is the only force acting on an object (free fall acceleration is directed toward center of earth) ...
Newton`s First Law
... Notes for Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s First Law (law of inertia) An object at _____________ tends to stay at _____________ and an object in _____________ tends to stay in _____________ unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... Notes for Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s First Law (law of inertia) An object at _____________ tends to stay at _____________ and an object in _____________ tends to stay in _____________ unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...