Chapter 10 Elasticity & Oscillations
... by a 67 kilometres per hour (42 mph) wind. The bridge collapse had lasting effects on science and engineering. In many undergraduate physics texts the event is presented as an example of elementary forced resonance with the wind providing an external periodic frequency that matched the natural struc ...
... by a 67 kilometres per hour (42 mph) wind. The bridge collapse had lasting effects on science and engineering. In many undergraduate physics texts the event is presented as an example of elementary forced resonance with the wind providing an external periodic frequency that matched the natural struc ...
Lecture 6
... Particle is said to be in EQUILIBRIUM if: It remains at rest (v=0) if originally at rest. (Static Equilibrium) It has a constant velocity if originally in motion. To maintain EQUILIBRIUM, it is necessary to satisfy Newton’s first law of motion. Resultant force acting on a particle require to ...
... Particle is said to be in EQUILIBRIUM if: It remains at rest (v=0) if originally at rest. (Static Equilibrium) It has a constant velocity if originally in motion. To maintain EQUILIBRIUM, it is necessary to satisfy Newton’s first law of motion. Resultant force acting on a particle require to ...
momentum - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
... Angular Momentum (Cont.) • Just as the linear momentum of an object changes when an impulse acts on it, the angular momentum of an object changes when an angular impulse acts on it. • Thus, the angular impulse on the object is equal to the change in the object’s angular momentum, which is called the ...
... Angular Momentum (Cont.) • Just as the linear momentum of an object changes when an impulse acts on it, the angular momentum of an object changes when an angular impulse acts on it. • Thus, the angular impulse on the object is equal to the change in the object’s angular momentum, which is called the ...
Word doc
... Fig 2. Muscle as a simple “system” with two inputs (one at mechanical port) and one output. ...
... Fig 2. Muscle as a simple “system” with two inputs (one at mechanical port) and one output. ...
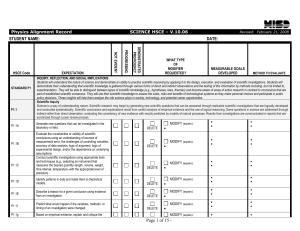
HSCE Code
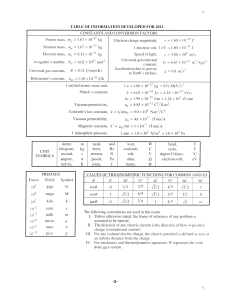
... Gravitation is an attractive force that a mass exerts on every other mass. The strength of the gravitational force between two masses is proportional to the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
... Gravitation is an attractive force that a mass exerts on every other mass. The strength of the gravitational force between two masses is proportional to the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
AP Phys B FRQ - Blue Valley Schools
... A particle with unknown mass and charge moves with constant speed v = 1.9 x 106 mIs as it passes undeflected through a pair of parallel plates, as shown above. The plates are separated by a distance d = 6.0 x I o- m, and a constant potential difference V is maintained between them. A uniform magneti ...
... A particle with unknown mass and charge moves with constant speed v = 1.9 x 106 mIs as it passes undeflected through a pair of parallel plates, as shown above. The plates are separated by a distance d = 6.0 x I o- m, and a constant potential difference V is maintained between them. A uniform magneti ...
Frictional Force—Introduction
... never be constant if we consider the speed of light or sound as constant. In a unidimensional spacetime, time is measured as the relative velocity of the reference with which it is measured. When we travel through time we always travel through time only, when we travel through space, we travel throu ...
... never be constant if we consider the speed of light or sound as constant. In a unidimensional spacetime, time is measured as the relative velocity of the reference with which it is measured. When we travel through time we always travel through time only, when we travel through space, we travel throu ...
Ferrier_kinematics5
... • Use linear algebra + systematic approach • Obtain an expression for the pose of the end-effector as a function of joint variables qi (angles/displacements) and link geometry (link lengths and relative orientations) Pe = f(q1,q2,,qn ;l1,ln,1,n) ME/ECE 439 2007 ...
... • Use linear algebra + systematic approach • Obtain an expression for the pose of the end-effector as a function of joint variables qi (angles/displacements) and link geometry (link lengths and relative orientations) Pe = f(q1,q2,,qn ;l1,ln,1,n) ME/ECE 439 2007 ...
Physics Essentials For Dummies
... What what’s all about? Everything. That’s the whole point. Physics is present in every action around you. And because physics has no limits, it gets into some tricky places, which means that it can be hard to follow. It can be even worse when you’re reading some dense textbook that’s hard to follow. ...
... What what’s all about? Everything. That’s the whole point. Physics is present in every action around you. And because physics has no limits, it gets into some tricky places, which means that it can be hard to follow. It can be even worse when you’re reading some dense textbook that’s hard to follow. ...
lecture3_stress1
... If s1 = 40 MPa and s3 = 20 MPa, all paired values of sN & sS exist for points on the perimeter of the circle. Use angle q=30°, with a radius on a unit circle, its 2 q equals 60°. q is the angle between the greatest principal stress (s1) and the dip of the plane Where the radius intersects the perime ...
... If s1 = 40 MPa and s3 = 20 MPa, all paired values of sN & sS exist for points on the perimeter of the circle. Use angle q=30°, with a radius on a unit circle, its 2 q equals 60°. q is the angle between the greatest principal stress (s1) and the dip of the plane Where the radius intersects the perime ...