Mechanics
... Fig. 1. Let a horizontal force P act on the block. It is observed that, as P is increased from zero slowly, the block initially does not move. However, as P reaches a certain critical value, the block just about exhibits a tendency to move. Any further attempt to increase P results in acceleration o ...
... Fig. 1. Let a horizontal force P act on the block. It is observed that, as P is increased from zero slowly, the block initially does not move. However, as P reaches a certain critical value, the block just about exhibits a tendency to move. Any further attempt to increase P results in acceleration o ...
CHAPTER Work and Energy
... (a) The change in U does not depend on speed, only on difference in elevation. 50 · Which of the following statements is true? (a) The kinetic and potential energies of an object must always be positive quantities. (b) The kinetic and potential energies of an object must always be negative quantitie ...
... (a) The change in U does not depend on speed, only on difference in elevation. 50 · Which of the following statements is true? (a) The kinetic and potential energies of an object must always be positive quantities. (b) The kinetic and potential energies of an object must always be negative quantitie ...
Stacey Carpenter - University of Hawaii System
... Weight is a force. It is mass and acceleration multiplied. But where does the acceleration come from? Gravity. Just like all mass has inertia, all mass has gravity. All objects are attracted to each other by gravity. It is the force of gravity between Earth's mass and the mass of your body that caus ...
... Weight is a force. It is mass and acceleration multiplied. But where does the acceleration come from? Gravity. Just like all mass has inertia, all mass has gravity. All objects are attracted to each other by gravity. It is the force of gravity between Earth's mass and the mass of your body that caus ...
2.016 Hydrodynamics Added Mass
... where m is the system mass, b is the linear damping coefficient, k is the spring coefficient, f(t) is the force acting on the mass, and x is the displacement of the mass. The natural frequency ω of the system is simply ...
... where m is the system mass, b is the linear damping coefficient, k is the spring coefficient, f(t) is the force acting on the mass, and x is the displacement of the mass. The natural frequency ω of the system is simply ...
Gravitation Introduction we are going to identify one of the forces
... That means acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the distance between the centre of the earth and the object. The radius of the earth decreases as we move from the equator to the poles as the earth is not a perfect sphere and hence the acceleration due to gravity will also vary. I ...
... That means acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the distance between the centre of the earth and the object. The radius of the earth decreases as we move from the equator to the poles as the earth is not a perfect sphere and hence the acceleration due to gravity will also vary. I ...
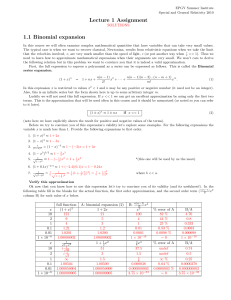
Circumference = 2π × radius = 2π × 60 = 376m time
... Defining positive forces as acting from left to right: Resultant = 6 + (−2) = 4N in direction of 6N force ...
... Defining positive forces as acting from left to right: Resultant = 6 + (−2) = 4N in direction of 6N force ...
Kinematics Multiples
... This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you look at the graph closely, you will see that the FORCE of spring 2 increases with displacement faster than the force for spring 1. ...
... This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you look at the graph closely, you will see that the FORCE of spring 2 increases with displacement faster than the force for spring 1. ...
Forces - faculty at Chemeketa
... A ball on a string is swung in a vertical circle. The string happens to break when it is parallel to the ground and the ball is moving up. Which trajectory does the ball follow? ...
... A ball on a string is swung in a vertical circle. The string happens to break when it is parallel to the ground and the ball is moving up. Which trajectory does the ball follow? ...
What is the work done by the two x
... What is the work done by the two forces together in moving the object a distance Δx to the right as shown in the diagram? The magnitude of each force is F and the directions of the two forces are 90o apart. ...
... What is the work done by the two forces together in moving the object a distance Δx to the right as shown in the diagram? The magnitude of each force is F and the directions of the two forces are 90o apart. ...
Ch 8 Momentum
... A person slaps her leg with her hand, bringing her hand to rest in 2.50 milliseconds from an initial speed of 4.00 m/s. (a) What is the average force exerted on the leg, taking the effective ...
... A person slaps her leg with her hand, bringing her hand to rest in 2.50 milliseconds from an initial speed of 4.00 m/s. (a) What is the average force exerted on the leg, taking the effective ...
Writing Prompts
... What makes a net force balance or unbalanced? 5.1.1 The student will use analytical techniques appropriate to the study of physics. 5.1.3 The student will analyze and explain how Newton’s Laws describe changes in an object’s motion. ...
... What makes a net force balance or unbalanced? 5.1.1 The student will use analytical techniques appropriate to the study of physics. 5.1.3 The student will analyze and explain how Newton’s Laws describe changes in an object’s motion. ...
3.6MB Word - Clydeview Academy
... Each time this repeats some energy is lost as heat (and sound), so the ball does not rise to the same height as before. The gradient of the graph is negative and constant – which shows that acceleration due to gravity is constant at -9.8 ms-2. The area under the graph represents the displacement dur ...
... Each time this repeats some energy is lost as heat (and sound), so the ball does not rise to the same height as before. The gradient of the graph is negative and constant – which shows that acceleration due to gravity is constant at -9.8 ms-2. The area under the graph represents the displacement dur ...
A particle of mass `m` is attached to a thin uniform rod of length `a` at
... PREVIOUS EAMCET QUESTIONS DEMO ...
... PREVIOUS EAMCET QUESTIONS DEMO ...