Physics Challenge 2012
... This question asks you to use unfamiliar equations and concepts to solve a problem. You will not have met some of the concepts in your normal physics course. All of the information you need to solve the problem is given in the question. A student was interested to work out if the copper cable connec ...
... This question asks you to use unfamiliar equations and concepts to solve a problem. You will not have met some of the concepts in your normal physics course. All of the information you need to solve the problem is given in the question. A student was interested to work out if the copper cable connec ...
Wikipedia and Coriolis Force
... reluctantly. They even recognize that it is real and frame independent, but they adamantly refuse to recognize the primary Newton’s first law effect that causes it. They’ll accept its reality if it is described as being an effect of inertia, but under no circumstances will they acknowledge that this ...
... reluctantly. They even recognize that it is real and frame independent, but they adamantly refuse to recognize the primary Newton’s first law effect that causes it. They’ll accept its reality if it is described as being an effect of inertia, but under no circumstances will they acknowledge that this ...
VCE Physics
... Where, u = initial velocity (ms-1) v = final velocity (ms-1) a = acceleration (ms-2) s = displacement (m) t = time (s) THESE EQUATION CAN ONLY BE USED IF THE ACCELERATION IS ______________________ When using the equations, always ________ out the information given and note what you need to find, the ...
... Where, u = initial velocity (ms-1) v = final velocity (ms-1) a = acceleration (ms-2) s = displacement (m) t = time (s) THESE EQUATION CAN ONLY BE USED IF THE ACCELERATION IS ______________________ When using the equations, always ________ out the information given and note what you need to find, the ...
GE6253-Engineering Mechanics - Valliammai Engineering College
... 1. Two cylinders, having weight WA = 2000N and WB = 1000 N are resting on smooth inclined planes having inclination 60* and 45ᵒ with the horizontal respectively as shown in figure. They are connected by a weightless bar AB with hinge connections. The bar AB makes 15 ᵒ angle with the horizontal. Find ...
... 1. Two cylinders, having weight WA = 2000N and WB = 1000 N are resting on smooth inclined planes having inclination 60* and 45ᵒ with the horizontal respectively as shown in figure. They are connected by a weightless bar AB with hinge connections. The bar AB makes 15 ᵒ angle with the horizontal. Find ...
Energy3
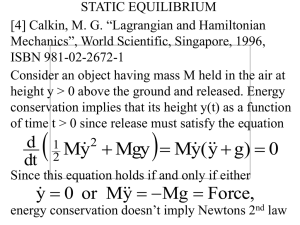
... We made the painful observation, that conservation of energy by itself does not suffice to explain the real world in which things happen: rain falls from the sky and objects move when they are pushed Definition A virtual displacement r of an object is any change of its position that can be imagined ...
... We made the painful observation, that conservation of energy by itself does not suffice to explain the real world in which things happen: rain falls from the sky and objects move when they are pushed Definition A virtual displacement r of an object is any change of its position that can be imagined ...
CP-S-HW-ch-5-detailed
... magnitude (speed) and direction. The work–energy theorem shows that the magnitude or speed is unchanged when Wnet 0 , but makes no statement about the direction of the velocity. Therefore, choice (d) is correct but choice (c) is not necessarily true. 12. A block of mass m is dropped from the fourt ...
... magnitude (speed) and direction. The work–energy theorem shows that the magnitude or speed is unchanged when Wnet 0 , but makes no statement about the direction of the velocity. Therefore, choice (d) is correct but choice (c) is not necessarily true. 12. A block of mass m is dropped from the fourt ...
normal force measurement on the rheolyst series AR1000-N
... the same flow pattern and therefore achieving good miscibility can sometimes be difficult. The type of flow pattern obtained in a given situation will depend upon the dominance of either the elastic or inertial forces. The Normal Force Transducer: The normal force transducer on the TA Instruments AR ...
... the same flow pattern and therefore achieving good miscibility can sometimes be difficult. The type of flow pattern obtained in a given situation will depend upon the dominance of either the elastic or inertial forces. The Normal Force Transducer: The normal force transducer on the TA Instruments AR ...
AP Physics B Exam Cram Sheet - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... Remember to distinguish between what causes a field and what a field does to a charged particle. For our purposes, an object cannot be affected by its own field. Fields exert forces. It’s what they do. It’s what they are. It’s their job. Forces and potential energies are associated with particles. F ...
... Remember to distinguish between what causes a field and what a field does to a charged particle. For our purposes, an object cannot be affected by its own field. Fields exert forces. It’s what they do. It’s what they are. It’s their job. Forces and potential energies are associated with particles. F ...
AP Physics B Exam Cram Sheet
... Remember to distinguish between what causes a field and what a field does to a charged particle. For our purposes, an object cannot be affected by its own field. Fields exert forces. It’s what they do. It’s what they are. It’s their job. Forces and potential energies are associated with particles. F ...
... Remember to distinguish between what causes a field and what a field does to a charged particle. For our purposes, an object cannot be affected by its own field. Fields exert forces. It’s what they do. It’s what they are. It’s their job. Forces and potential energies are associated with particles. F ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... III. Kinetics of Particles: Force, Mass, and Acceleration A. Newton’s Second Law of Motion B. Systems of Units C. Equations of Motion. Dynamic Equilibrium D. Systems of Particles. D’Alembert’s Principle E. Motion of the Mass Center of a System of Particles F. Rectilinear Motion of a Particle G. Cu ...
... III. Kinetics of Particles: Force, Mass, and Acceleration A. Newton’s Second Law of Motion B. Systems of Units C. Equations of Motion. Dynamic Equilibrium D. Systems of Particles. D’Alembert’s Principle E. Motion of the Mass Center of a System of Particles F. Rectilinear Motion of a Particle G. Cu ...
Period 5 Activity Sheet: Forces and Newton’s Laws
... 1) Your instructor will demonstrate two toy cars moving up an incline. Explain the differences in the motion of the cars as they go up the incline. 2) Balance a meter stick on two fingers. Start with one finger under each end of the meter stick. Slowly slide your fingers together while balancing the ...
... 1) Your instructor will demonstrate two toy cars moving up an incline. Explain the differences in the motion of the cars as they go up the incline. 2) Balance a meter stick on two fingers. Start with one finger under each end of the meter stick. Slowly slide your fingers together while balancing the ...
MS Word
... You have now developed a model of how things move by considering work done on an object and the change in energy of the object. In the cases studied so far, you've only needed to concern yourself about constant forces (or in some cases, average forces, for which we don't have detailed information ab ...
... You have now developed a model of how things move by considering work done on an object and the change in energy of the object. In the cases studied so far, you've only needed to concern yourself about constant forces (or in some cases, average forces, for which we don't have detailed information ab ...
Dynamics 2
... string or rope is much less than the masses of the objects that it connects. In such cases, we can adopt the following massless string approximation: ...
... string or rope is much less than the masses of the objects that it connects. In such cases, we can adopt the following massless string approximation: ...