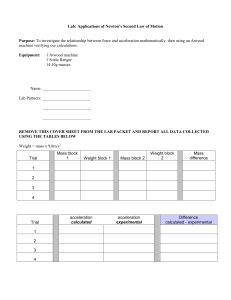
Chapter 06 Momentum
... We have already established that in order to change the momentum of an object, an unbalanced force must be applied. If you are riding in a car, and you push against the inside of the door; does the car accelerate in the direction of your force? No, Newton’s third law says that your force on the door ...
... We have already established that in order to change the momentum of an object, an unbalanced force must be applied. If you are riding in a car, and you push against the inside of the door; does the car accelerate in the direction of your force? No, Newton’s third law says that your force on the door ...
Chapter 5 HW – Conservation of Energy… and Springs
... 14. A force of 18 N stretches a spring 0.25 m from its equilibrium position. a) How much work was done by the spring? b) What is the spring constant? c) What force would be required to stretch the spring 0.50 m? d) What force would it take to stretch it to 0.75 m? e) How much work is done on the sp ...
... 14. A force of 18 N stretches a spring 0.25 m from its equilibrium position. a) How much work was done by the spring? b) What is the spring constant? c) What force would be required to stretch the spring 0.50 m? d) What force would it take to stretch it to 0.75 m? e) How much work is done on the sp ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation The greatest moments in
... FG = Gm1m2/r2 FG = (6.67 x 10-11 N∙m2/kg2)(6.0 x 1024 kg)(2.0 x 1030 kg)/(1.5 x 1011m)2 FG = 36 x 1021N FG = 3.6 x 1022N towards each other’s center ...
... FG = Gm1m2/r2 FG = (6.67 x 10-11 N∙m2/kg2)(6.0 x 1024 kg)(2.0 x 1030 kg)/(1.5 x 1011m)2 FG = 36 x 1021N FG = 3.6 x 1022N towards each other’s center ...
+ v 2 - Cloudfront.net
... where M is the total mass, and ri are the position vectors of the masses mi. Differentiating, where the v vectors are velocity vectors. This leads to ...
... where M is the total mass, and ri are the position vectors of the masses mi. Differentiating, where the v vectors are velocity vectors. This leads to ...
Science
... move. A student justifies this by answering that the two opposite and equal forces cancel each other. Comment on this logic and explain why the truck does not move. Answer: The logic is that Action and Reaction always act on different bodies, so they can not cancel each other. When we push a massive ...
... move. A student justifies this by answering that the two opposite and equal forces cancel each other. Comment on this logic and explain why the truck does not move. Answer: The logic is that Action and Reaction always act on different bodies, so they can not cancel each other. When we push a massive ...
Ch 4 - iPride22.org
... – Start movement, stop movement, or change the direction of movement – Cause an object in motion to speed up or slow down ...
... – Start movement, stop movement, or change the direction of movement – Cause an object in motion to speed up or slow down ...
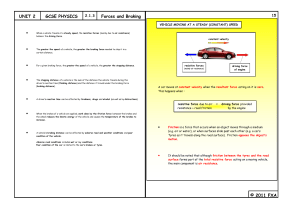
GCSE P2 2.1.3 Forces and Braking
... and the wheel discs reduces the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle and causes the temperature of the brakes to increase. Friction is a force that occurs when an object moves through a medium (e.g. air or water), or when surfaces (e.g. the brake pads and the wheel discs) slide over each other. The ...
... and the wheel discs reduces the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle and causes the temperature of the brakes to increase. Friction is a force that occurs when an object moves through a medium (e.g. air or water), or when surfaces (e.g. the brake pads and the wheel discs) slide over each other. The ...
Work and Energy
... at maximum displacement Force is maximum at maximum displacement Velocity is greatest at equilibrium (all energy is ...
... at maximum displacement Force is maximum at maximum displacement Velocity is greatest at equilibrium (all energy is ...
Widener University
... In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron (mass 9.11 x 10 -31 kg) revolves in a circular orbit about the nucleus. The orbit radius is 5.3 x 10-11 m and the electron circles 6.6 x 1015 times per second. a) Find the speed v of the electron as it travels in its orbit. b) Find the acceleratio ...
... In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron (mass 9.11 x 10 -31 kg) revolves in a circular orbit about the nucleus. The orbit radius is 5.3 x 10-11 m and the electron circles 6.6 x 1015 times per second. a) Find the speed v of the electron as it travels in its orbit. b) Find the acceleratio ...