Conservation of Momentum in One Dimension
... When impulse and momentum were introduced, we used an example of a batted ball to discuss the impulse and momentum change that occurred with the ball. At the time, we did not consider what had happened to the bat. According to Newton’s third law, however, when the bat exerted a force on the ball, th ...
... When impulse and momentum were introduced, we used an example of a batted ball to discuss the impulse and momentum change that occurred with the ball. At the time, we did not consider what had happened to the bat. According to Newton’s third law, however, when the bat exerted a force on the ball, th ...
Work and Simple Machines Info
... The very tip of a screw is usually shaped like a triangle, which makes it a tiny wedge. Higher up on the screw are the threads. The threads of a screw are actually one long spiral, reaching from the bottom of the screw to the top. If this spiral was unwound, it would simply be an inclined plane. Thi ...
... The very tip of a screw is usually shaped like a triangle, which makes it a tiny wedge. Higher up on the screw are the threads. The threads of a screw are actually one long spiral, reaching from the bottom of the screw to the top. If this spiral was unwound, it would simply be an inclined plane. Thi ...
Lesson 06: Temperature and Kinetic Energy
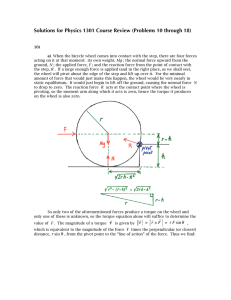
... The important concept to master in these problems is breaking the force into two components. One component must point in the direction of the motion of the block. The second component must be perpendicular to the first component. The two components must add up (as vectors) to the original force vect ...
... The important concept to master in these problems is breaking the force into two components. One component must point in the direction of the motion of the block. The second component must be perpendicular to the first component. The two components must add up (as vectors) to the original force vect ...
Work, Power, Energy
... E) It is gaining heat energy, gaining kinetic energy, and losing potential energy 22. Base your answer to the following question on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum. At the bottom of the of the swing, the tension in ...
... E) It is gaining heat energy, gaining kinetic energy, and losing potential energy 22. Base your answer to the following question on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum. At the bottom of the of the swing, the tension in ...
Fictive forces
... Let us introduce a general, mathematical description of an accelerated and rotated coordinate system, so that we may relate the acceleration in the accelerated system to real and fictive forces. The system S is an inertial system, and the system S 0 is both translated and rotated relative to S as il ...
... Let us introduce a general, mathematical description of an accelerated and rotated coordinate system, so that we may relate the acceleration in the accelerated system to real and fictive forces. The system S is an inertial system, and the system S 0 is both translated and rotated relative to S as il ...
force on a current in a magnetic field
... Thus the cube pictured in Problem 1 is in the quadrant of 3-dimensional space where all coordinates are positive. Do not be put off by the orientation of the axes in the figure: axes can be shown in any orientation as long as they show a right-handed coordinate system. 2. To begin the problem, do as ...
... Thus the cube pictured in Problem 1 is in the quadrant of 3-dimensional space where all coordinates are positive. Do not be put off by the orientation of the axes in the figure: axes can be shown in any orientation as long as they show a right-handed coordinate system. 2. To begin the problem, do as ...
rate of change
... The Lagrangian term dt is the rate of change experienced by a given tagged water parcel. The Eulerian term t is the local rate of change at a fixed point. du ...
... The Lagrangian term dt is the rate of change experienced by a given tagged water parcel. The Eulerian term t is the local rate of change at a fixed point. du ...
相對論簡介
... – Within the framework of classical mechanics, all clocks run at the same rate – The time at which an event occurs for an observer in S is the same as the time for the same event in S’ – This turns out to be incorrect when v is comparable to the speed of light ...
... – Within the framework of classical mechanics, all clocks run at the same rate – The time at which an event occurs for an observer in S is the same as the time for the same event in S’ – This turns out to be incorrect when v is comparable to the speed of light ...
Inertial and Non-Inertial Frames of Reference - K
... If you were observing the motion from the road (which is an inertial frame of reference) the ball just continues to move forward at the speed it was already going, and it’s motion is easily explained by the law of inertia. To an observer in the inertial frame of reference (the ground) the bus experi ...
... If you were observing the motion from the road (which is an inertial frame of reference) the ball just continues to move forward at the speed it was already going, and it’s motion is easily explained by the law of inertia. To an observer in the inertial frame of reference (the ground) the bus experi ...
Newton 3 notes
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion • Consider a system comprised of both the orange and the apple – The apple is no longer external to the system. – Force pair is internal to system, which doesn’t cause acceleration. – Action and reaction within the system cancel. – With no external forces, there is no a ...
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion • Consider a system comprised of both the orange and the apple – The apple is no longer external to the system. – Force pair is internal to system, which doesn’t cause acceleration. – Action and reaction within the system cancel. – With no external forces, there is no a ...
Introductory_Physics_Notes_May_1_2008.doc
... equations, and relationships for an introductory Physics course. My objective is to provide the student with an outline of the very essentials which are to serve as a guide to my lectures and any of the very well written texts that are available and to keep the focus on the core ideas as it is easy ...
... equations, and relationships for an introductory Physics course. My objective is to provide the student with an outline of the very essentials which are to serve as a guide to my lectures and any of the very well written texts that are available and to keep the focus on the core ideas as it is easy ...
Physics Physics 8E Volume 2 -Cutenll and Johnson (2009) (www
... characteristics of a moving charged object within a charged parallel plate capacitor. This simulation file name is “#15 Charge and Cap”. A positively charged particle is moving horizontally when it enters the region between the plates of a capacitor as the simulation illustrates. (a) Draw (sketch) t ...
... characteristics of a moving charged object within a charged parallel plate capacitor. This simulation file name is “#15 Charge and Cap”. A positively charged particle is moving horizontally when it enters the region between the plates of a capacitor as the simulation illustrates. (a) Draw (sketch) t ...
Momentum - Mindset Learn
... Impulse is the change in momentum. Impulse = ∆p. Impulse is also given by the product of the resultant force and the period of time the force is acting on an object: F∆t = ∆p. Thus the unit of measurement of impulse can also be expressed as N∙s. The mass of an object is usually intact and does not c ...
... Impulse is the change in momentum. Impulse = ∆p. Impulse is also given by the product of the resultant force and the period of time the force is acting on an object: F∆t = ∆p. Thus the unit of measurement of impulse can also be expressed as N∙s. The mass of an object is usually intact and does not c ...
Investigation 3
... We know that energy cannot be created or destroyed, and we also know that it can be converted from one form to another (e.g., kinetic energy to potential energy and vice versa). Suppose a 1 kg ball is at the top of a 40 meter high cliff. In the first case, at position A, we drop the ball and in the ...
... We know that energy cannot be created or destroyed, and we also know that it can be converted from one form to another (e.g., kinetic energy to potential energy and vice versa). Suppose a 1 kg ball is at the top of a 40 meter high cliff. In the first case, at position A, we drop the ball and in the ...