RP 3P1 Force and Motion - NC Science Wiki
... The two kinds of forces we are commonly aware of are gravitational and electromagnetic. Everything in the universe exerts gravitational forces on everything else, although the effects are readily noticeable only when at least one very large mass is involved (such as a star or planet). Gravity is the ...
... The two kinds of forces we are commonly aware of are gravitational and electromagnetic. Everything in the universe exerts gravitational forces on everything else, although the effects are readily noticeable only when at least one very large mass is involved (such as a star or planet). Gravity is the ...
oscillations
... In this section we show that the projection of uniform circular motion on a diameter of the circle follows simple harmonic motion. A simple experiment (Fig. 14.9) helps us visualize this connection. Tie a ball to the end of a string and make it move in a horizontal plane about a fixed point with a c ...
... In this section we show that the projection of uniform circular motion on a diameter of the circle follows simple harmonic motion. A simple experiment (Fig. 14.9) helps us visualize this connection. Tie a ball to the end of a string and make it move in a horizontal plane about a fixed point with a c ...
COM and Momentum
... Q33) An object of mass 3m, initially at rest, explodes breaking into two fragments with masses m and 2m. Which one of the following statements concerning the fragments after the explosion is true? 1) They may fly off at right angles. 2) They may fly off in the same direction. 3) The larger fragment ...
... Q33) An object of mass 3m, initially at rest, explodes breaking into two fragments with masses m and 2m. Which one of the following statements concerning the fragments after the explosion is true? 1) They may fly off at right angles. 2) They may fly off in the same direction. 3) The larger fragment ...
mi08
... which means that the force is the rate of change of the momentum with time. If the mass is constant then this reduces to Fnet = ma, because the change in velocity with time is the ________. But sometimes the mass changes, for example a vehicle which burns fuel changes mass as it uses the fuel. If no ...
... which means that the force is the rate of change of the momentum with time. If the mass is constant then this reduces to Fnet = ma, because the change in velocity with time is the ________. But sometimes the mass changes, for example a vehicle which burns fuel changes mass as it uses the fuel. If no ...
Chapter 2
... The units used to describe speed are usually miles/hour (mi/h), kilometers/hour (km/h), or meters/second (m/s). Let’s go back to your car that is moving over a straight highway and imagine you are driving to cover equal distances in equal periods of time (figure 2.2). If you use a stopwatch to measu ...
... The units used to describe speed are usually miles/hour (mi/h), kilometers/hour (km/h), or meters/second (m/s). Let’s go back to your car that is moving over a straight highway and imagine you are driving to cover equal distances in equal periods of time (figure 2.2). If you use a stopwatch to measu ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... the charges are moving towards each other, which of the following statements is correct? (a) W+ is positive and W– is negative. (b) W+ is negative and W– is positive. (c) *Both W+ and W– are positive. (d) Both W+ and W– are negative. (e) Without knowing the coordinate system, the sign of the work ca ...
... the charges are moving towards each other, which of the following statements is correct? (a) W+ is positive and W– is negative. (b) W+ is negative and W– is positive. (c) *Both W+ and W– are positive. (d) Both W+ and W– are negative. (e) Without knowing the coordinate system, the sign of the work ca ...
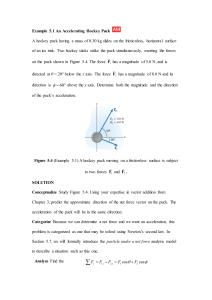
Example 5.1 An Accelerating Hockey Puck A hockey puck having a
... Figure 5.11 (Example 5.6) (a) A car on a frictionless incline. (b) The free-body diagram for the car. The black dot represents the position of the center of mass of the car. We will learn about center of mass in Chapter 9. Categorize We categorize the car as a particle under a net force because it a ...
... Figure 5.11 (Example 5.6) (a) A car on a frictionless incline. (b) The free-body diagram for the car. The black dot represents the position of the center of mass of the car. We will learn about center of mass in Chapter 9. Categorize We categorize the car as a particle under a net force because it a ...
Problem 7.54 A Ball Hits a Wall Elastically
... Hint 2. Determine which physical laws and principles apply Which of the following physical laws or principles can best be used to analyze the collision between the object and the pendulum bob? Which can best be used to analyze the resulting swing? A. Newton's first law B. Newton's second law C. Newt ...
... Hint 2. Determine which physical laws and principles apply Which of the following physical laws or principles can best be used to analyze the collision between the object and the pendulum bob? Which can best be used to analyze the resulting swing? A. Newton's first law B. Newton's second law C. Newt ...
Phys 21 Rotational Inertia and Torque
... pulley, and show how equations (4) and (5) are derived. Explain your steps. 2) (Optional) In the discussion section, derive (6) and (7). Explain your steps. 3) Explain why the acceleration is greater when you attach the string to a larger radius. 4) Your two experimental results should each give the ...
... pulley, and show how equations (4) and (5) are derived. Explain your steps. 2) (Optional) In the discussion section, derive (6) and (7). Explain your steps. 3) Explain why the acceleration is greater when you attach the string to a larger radius. 4) Your two experimental results should each give the ...
ppt - Full-Time Faculty - California State University, Fullerton
... T.L. Williams, G. Bowtell, and N.A. Curtin. Predicting force generation by lamprey muscle during applied sinusoidal movement using a simple dynamic model. J. Exp. Biol. ...
... T.L. Williams, G. Bowtell, and N.A. Curtin. Predicting force generation by lamprey muscle during applied sinusoidal movement using a simple dynamic model. J. Exp. Biol. ...
Anonymous-VibrationTheoryFundamentals.pdf
... also harmonic, with a maximum value of x0ω2. A vibrating system is said to have one degree of freedom if its geometrical position can be expressed at any instant in time by one number only. For example, a piston moving in a cylinder can be specified by giving the distance from the cylinder end, thus ...
... also harmonic, with a maximum value of x0ω2. A vibrating system is said to have one degree of freedom if its geometrical position can be expressed at any instant in time by one number only. For example, a piston moving in a cylinder can be specified by giving the distance from the cylinder end, thus ...
10 Simple Harmonic Motion
... position at any time. Because of the oscillatory nature of the vibrating mass, we can express the displacement x from equilibrium position at any time t as ...
... position at any time. Because of the oscillatory nature of the vibrating mass, we can express the displacement x from equilibrium position at any time t as ...
CP Physics Final Exam Review 2
... e. None of the above statements are absolutely true. 2. A plastic rod is charged up by rubbing a wool cloth, and brought to an initially neutral metallic sphere that is insulated from ground. The sphere is a. is repelled by the rod. b. is attracted to the rod. c. feels no force due to the rod. 3. A ...
... e. None of the above statements are absolutely true. 2. A plastic rod is charged up by rubbing a wool cloth, and brought to an initially neutral metallic sphere that is insulated from ground. The sphere is a. is repelled by the rod. b. is attracted to the rod. c. feels no force due to the rod. 3. A ...
narayana - Docslide.net
... Every body continues to remain in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless an external force is applied on it i.e. If a particle is at rest, it will remain at rest and if it is moving with constant speed, it will continue to move in the same direction with same constant speed unless an external ...
... Every body continues to remain in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless an external force is applied on it i.e. If a particle is at rest, it will remain at rest and if it is moving with constant speed, it will continue to move in the same direction with same constant speed unless an external ...