Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics
... 3. Suppose the global isolated system is initially divided by internal constraints into subsystems that are separately at equilibrium: if we lift one (or more) constraint the final entropy, after the re-establisment of equilibrium, must be greater or equal to the initial i are such entropy. The new ...
... 3. Suppose the global isolated system is initially divided by internal constraints into subsystems that are separately at equilibrium: if we lift one (or more) constraint the final entropy, after the re-establisment of equilibrium, must be greater or equal to the initial i are such entropy. The new ...
File
... by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively) the signs of both Ho and So, and calculation or estimation of Go when needed. LO 5.14 The student is able to determine whether a chemical or physical process is thermodynamically favorable by calculating the change in standard Gibbs fre ...
... by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively) the signs of both Ho and So, and calculation or estimation of Go when needed. LO 5.14 The student is able to determine whether a chemical or physical process is thermodynamically favorable by calculating the change in standard Gibbs fre ...
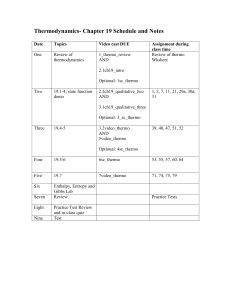
Chapter Two The Thermodynamic Laws
... It is impossible for any system to operate in such a way that the sole result would be an energy transfer by heat from a cooler to a hotter body. Another statement by Clausius is: "Heat cannot of itself pass from a colder to a hotter body." This statement implies an inequality of the heat transfer b ...
... It is impossible for any system to operate in such a way that the sole result would be an energy transfer by heat from a cooler to a hotter body. Another statement by Clausius is: "Heat cannot of itself pass from a colder to a hotter body." This statement implies an inequality of the heat transfer b ...
q 2 - q 1
... But if q ≠ 0 and W ≠ 0 , is there a definite maximum amount of work which the system can do during its change of state ? the answer to this question requires an examination of the nature of process . ...
... But if q ≠ 0 and W ≠ 0 , is there a definite maximum amount of work which the system can do during its change of state ? the answer to this question requires an examination of the nature of process . ...