Heat and Thermodynamics
... The internal energy U might be thought of as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in temperature or volume. But if the process changes the volume, as in a chemical reaction which produces a gaseous product, then work must be done to produce the change in volume. For a co ...
... The internal energy U might be thought of as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in temperature or volume. But if the process changes the volume, as in a chemical reaction which produces a gaseous product, then work must be done to produce the change in volume. For a co ...
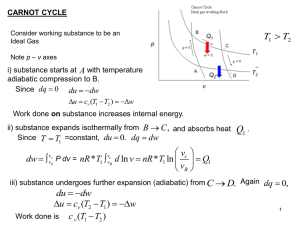
Carnot Cycle - University of Wyoming
... • A disorderly arrangement is much more probable than an orderly one if the laws of nature are allowed to act without interference – This comes from a statistical mechanics development ...
... • A disorderly arrangement is much more probable than an orderly one if the laws of nature are allowed to act without interference – This comes from a statistical mechanics development ...
Thermodynamics and the aims of statistical mechanics
... An absolutely central concept is thermal equilibrium. Equilibrium is any state a system is in once it has stopped exchanging heat with its surroundings; or, if it has no surroundings (= is isolated), once it has settled down to a macroscopically unchanging state. (Feynman: “equilibrium is when all t ...
... An absolutely central concept is thermal equilibrium. Equilibrium is any state a system is in once it has stopped exchanging heat with its surroundings; or, if it has no surroundings (= is isolated), once it has settled down to a macroscopically unchanging state. (Feynman: “equilibrium is when all t ...
PPT
... There exists a function called entropy S, of the extensive variables of a system, defined for all equilibrium states, such that the values assumed by the extensive variables are those that maximize S (at equilibrium) From the viewpoint of classical thermodynamics, entropy is defined as ...
... There exists a function called entropy S, of the extensive variables of a system, defined for all equilibrium states, such that the values assumed by the extensive variables are those that maximize S (at equilibrium) From the viewpoint of classical thermodynamics, entropy is defined as ...
ch06A-2013
... Entropy Rate Balance for Control Volumes Comment: The value of the entropy production for a single component such as the throttling valve considered here often does not have much significance by itself. The significance of the entropy production of any component is normally determined through compa ...
... Entropy Rate Balance for Control Volumes Comment: The value of the entropy production for a single component such as the throttling valve considered here often does not have much significance by itself. The significance of the entropy production of any component is normally determined through compa ...
Thermodynamics
... A state variable describes the state of a system at time t, but it does not reveal how the system was put into that state. Examples of state variables: pressure, temperature, volume, number of moles, and internal energy. Thermal processes can change the state of a system. We assume that thermal proc ...
... A state variable describes the state of a system at time t, but it does not reveal how the system was put into that state. Examples of state variables: pressure, temperature, volume, number of moles, and internal energy. Thermal processes can change the state of a system. We assume that thermal proc ...