Paradoxes Come from the Concept of Magnetism as a
... Now let’s see what happens in S’, where the particle is at rest and the wire is moving past to left with the speed v. For simplicity, we set the velocity v0 of the particle is the same as the velocity v of the conduction electrons. Because the particle is now at rest, there is no magnetic force on i ...
... Now let’s see what happens in S’, where the particle is at rest and the wire is moving past to left with the speed v. For simplicity, we set the velocity v0 of the particle is the same as the velocity v of the conduction electrons. Because the particle is now at rest, there is no magnetic force on i ...
Introduction to Forces forcesppt15-16
... Newton’s 3 Laws 1st : An object in motion stays in motion. An object at rest stays at rest-until an outside force acts upon it 2nd : F=ma 3rd : For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction ...
... Newton’s 3 Laws 1st : An object in motion stays in motion. An object at rest stays at rest-until an outside force acts upon it 2nd : F=ma 3rd : For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction ...
Electric Motors
... (A generator takes a manual force (a person turning a crankshaft) and moves a conductor through a magnetic field to produce an electric current.) ...
... (A generator takes a manual force (a person turning a crankshaft) and moves a conductor through a magnetic field to produce an electric current.) ...
Document
... (a) IDENTIFY: Apply Eq.(27.2) to relate the magnetic force F to the directions of v and B. The electron has negative charge so F is opposite to the direction of v B. For motion in an arc of a circle the acceleration is toward the center of the arc so F must be in this direction. a v2 / R. SET UP ...
... (a) IDENTIFY: Apply Eq.(27.2) to relate the magnetic force F to the directions of v and B. The electron has negative charge so F is opposite to the direction of v B. For motion in an arc of a circle the acceleration is toward the center of the arc so F must be in this direction. a v2 / R. SET UP ...
1. Motors use the effect of forces on current-carrying
... because the magnetic field created by the moving charged particle interacts with the existing field Account for the motor effect due to the force acting on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field ...
... because the magnetic field created by the moving charged particle interacts with the existing field Account for the motor effect due to the force acting on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field ...
Even if the forces acting on a body are balanced in
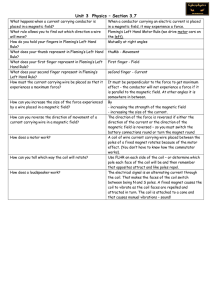
... When a conductor carrying an electric current is placed in a magnetic field, it may experience a force. Fleming’s Left Hand Motor Rule (we drive motor cars on the left). Mutually at right angles thuMb - Movement First finger - Field seCond finger - Current It must be perpendicular to the force to ge ...
... When a conductor carrying an electric current is placed in a magnetic field, it may experience a force. Fleming’s Left Hand Motor Rule (we drive motor cars on the left). Mutually at right angles thuMb - Movement First finger - Field seCond finger - Current It must be perpendicular to the force to ge ...
Electric field
... For the charge distributions shown on the spherical conductors below, which field lines are most reasonable? ...
... For the charge distributions shown on the spherical conductors below, which field lines are most reasonable? ...
Using Electricity and Magnetism
... The magnetic field produced by a current has three characteristics. The field can be turned on or off, have its direction reversed, or have its strength changed. ...
... The magnetic field produced by a current has three characteristics. The field can be turned on or off, have its direction reversed, or have its strength changed. ...