Chapter 7
... Since a current carrying wire may experience a force when placed in a magnetic field, it is not surprising that a moving charge that is not confine within a wire may also experience a force due to magnetic field. F= B I L sin F=B ...
... Since a current carrying wire may experience a force when placed in a magnetic field, it is not surprising that a moving charge that is not confine within a wire may also experience a force due to magnetic field. F= B I L sin F=B ...
03.EFieldNotesAndProblems
... 1. Arrows represent the direction of the electric field 2. Field lines always point ___________________ to the surface of the charge 3. The ______________ of the electric field is represented by how close together the lines are 4. Arrows point _____________ negative charges (representing the attract ...
... 1. Arrows represent the direction of the electric field 2. Field lines always point ___________________ to the surface of the charge 3. The ______________ of the electric field is represented by how close together the lines are 4. Arrows point _____________ negative charges (representing the attract ...
Magnetic field Conductor
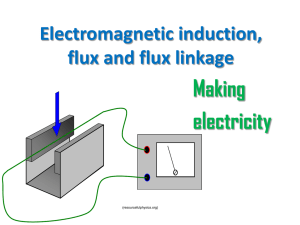
... Electromagnetic Induction 1) When a conductor cuts or it is cut by magnetic flux, an emf is induced in the conductor. 2) The magnitude of the induced emf is proportional to the rate at which the conductor cuts or is cut by the magnetic flux ELE101/102 ...
... Electromagnetic Induction 1) When a conductor cuts or it is cut by magnetic flux, an emf is induced in the conductor. 2) The magnitude of the induced emf is proportional to the rate at which the conductor cuts or is cut by the magnetic flux ELE101/102 ...
Review: Momentum and Impulse, Conservation of Momentum
... Know how work on a charge in an electric field affects PE. Know how to draw electric field lines correctly. Know what charge is used to test an electric field. ...
... Know how work on a charge in an electric field affects PE. Know how to draw electric field lines correctly. Know what charge is used to test an electric field. ...
DC Motors DC Motors
... for institutions. These notes can be freely copied for classroom use only. ...
... for institutions. These notes can be freely copied for classroom use only. ...
Science Study Guide
... Magnets can make objects move without direct contact between the object and the magnet. ● Magnets pull on (attract) objects made of iron or have iron in them. Materials can be identified using magnets, and mixtures of materials can be separated using magnets. ● Magnets can pull (attract) or push (re ...
... Magnets can make objects move without direct contact between the object and the magnet. ● Magnets pull on (attract) objects made of iron or have iron in them. Materials can be identified using magnets, and mixtures of materials can be separated using magnets. ● Magnets can pull (attract) or push (re ...
SCCS General Physics Chapter 5 STUDY GUIDE Name
... Practice problems: 1. To get a cart to move, two farmers pull on ropes attached to the cart, as shown below. One farmer pulls with a force of 50.0 N in a direction 35.0 east of north, while the other exerts a force of 30.0 N in a direction 25.0 west of north. What are the magnitude and the directi ...
... Practice problems: 1. To get a cart to move, two farmers pull on ropes attached to the cart, as shown below. One farmer pulls with a force of 50.0 N in a direction 35.0 east of north, while the other exerts a force of 30.0 N in a direction 25.0 west of north. What are the magnitude and the directi ...
F x
... torque on an object (or on a system) are zero. The object is either at rest or its center of mass is moving at constant velocity. ...
... torque on an object (or on a system) are zero. The object is either at rest or its center of mass is moving at constant velocity. ...
The Electrical Conductivity of a Partially Ionized Argon
... partially ionized plasma there are two well-known limiting cases. For the case where the ionization is so weak that the electron-ion collisions can be ignored in relation to the collisions between electrons and neutral particles a complete theory of mobility of electrons in electric and magnetic fie ...
... partially ionized plasma there are two well-known limiting cases. For the case where the ionization is so weak that the electron-ion collisions can be ignored in relation to the collisions between electrons and neutral particles a complete theory of mobility of electrons in electric and magnetic fie ...
Sources of Magnetic Fields (7/11)
... A positive point charge is moving directly toward point P. The magnetic field that the point charge produces at point P A. points from the charge toward point P. B. points from point P toward the charge. C. is perpendicular to the line from the point charge to point P. ...
... A positive point charge is moving directly toward point P. The magnetic field that the point charge produces at point P A. points from the charge toward point P. B. points from point P toward the charge. C. is perpendicular to the line from the point charge to point P. ...