Verify the dependence of electrostatic force on the distance at both
... way as Coulomb did1 or a simple scales, as it is described in [2]. However, our experiment was inspired mainly by [3] where the author used electronic scales. We present the variant of such experiment enabling rather simple and fast measurement we developed for our new Interactive Physics Laboratory ...
... way as Coulomb did1 or a simple scales, as it is described in [2]. However, our experiment was inspired mainly by [3] where the author used electronic scales. We present the variant of such experiment enabling rather simple and fast measurement we developed for our new Interactive Physics Laboratory ...
Homework Set 25B PH 112 – 10 Q1. A student asked, “Since electric
... A total electric charge of 3.50 nC is distributed uniformly over the surface of a metal sphere with a radius of 24.0 cm. If the potential is zero at infinity, find the value of the potential at the following distances from the center of the sphere: (A) ...
... A total electric charge of 3.50 nC is distributed uniformly over the surface of a metal sphere with a radius of 24.0 cm. If the potential is zero at infinity, find the value of the potential at the following distances from the center of the sphere: (A) ...
Electrostatics Test Review
... a. Electric field lines start at negative charges and end at positive charges or at infinity. b. Electric field lines start at positive charges and end at negative charges or at infinity. c. Electric field lines can cross each other. d. Electric field lines show the direction in which a positive cha ...
... a. Electric field lines start at negative charges and end at positive charges or at infinity. b. Electric field lines start at positive charges and end at negative charges or at infinity. c. Electric field lines can cross each other. d. Electric field lines show the direction in which a positive cha ...
Presentation_30
... Electromagnetism Review • E fields are created by: (1) electric charges (2) time changing B fields • B fields are created by (1) moving electric charges (NOT magnetic charges) (2) time changing E fields ...
... Electromagnetism Review • E fields are created by: (1) electric charges (2) time changing B fields • B fields are created by (1) moving electric charges (NOT magnetic charges) (2) time changing E fields ...
What Now??? - UCF Physics
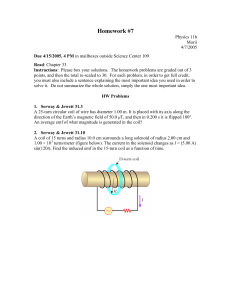
... Figure 31-36 shows two parallel loops of wire having a common axis. The smaller loop (radius r) is above the larger loop (radius R) by a distance x >> R. Consequently, the magnetic field due to the current i in the larger loop is nearly constant throughout the smaller loop. Suppose that x is increa ...
... Figure 31-36 shows two parallel loops of wire having a common axis. The smaller loop (radius r) is above the larger loop (radius R) by a distance x >> R. Consequently, the magnetic field due to the current i in the larger loop is nearly constant throughout the smaller loop. Suppose that x is increa ...
In pptx
... The electrostatic potential energy of a point charge q2 when it is brought from infinity to a distance r away from another point charge q1 is U = keq1q2/r The principal of superposition holds. To find the total electrostatic potential energy of a collection of point charges, sum over all pairs. For ...
... The electrostatic potential energy of a point charge q2 when it is brought from infinity to a distance r away from another point charge q1 is U = keq1q2/r The principal of superposition holds. To find the total electrostatic potential energy of a collection of point charges, sum over all pairs. For ...
Chapter 22: Electromagnetic Induction
... Relative motion between magnet and coil produce an induced current The coil behaves as if it were a source of emf, known as induced emf Changing magnetic field induces an emf, and emf leads to an induced current The phenomenon of producing an induced emf with the aid of a magnetic field is called el ...
... Relative motion between magnet and coil produce an induced current The coil behaves as if it were a source of emf, known as induced emf Changing magnetic field induces an emf, and emf leads to an induced current The phenomenon of producing an induced emf with the aid of a magnetic field is called el ...
Chapter 14
... The force on each segment is given by F=IlB. Using the right-hand rule, you can verify that the loop will tend to rotate in the direction indicated. The forces on the two ends of the loop produce no torque about center of the loop, because their lines of action pass through the center of the l ...
... The force on each segment is given by F=IlB. Using the right-hand rule, you can verify that the loop will tend to rotate in the direction indicated. The forces on the two ends of the loop produce no torque about center of the loop, because their lines of action pass through the center of the l ...
Chapter 17
... The electric force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation, r, between the charges. The electric force is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges, |q1| and |q2| It is attractive if the charges are of opposite sign and repulsive if the charges have the same sign ...
... The electric force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation, r, between the charges. The electric force is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges, |q1| and |q2| It is attractive if the charges are of opposite sign and repulsive if the charges have the same sign ...
Magnetism - Practice - Little Miami Schools
... Sir William Gilbert lived in England in the 1500s. He is remembered today for his investigations into electricity and magnetism. In fact, he is sometimes credited with founding the science of magnetism. He published descriptions of his many investigations in a book called De Magnete or “On the Magne ...
... Sir William Gilbert lived in England in the 1500s. He is remembered today for his investigations into electricity and magnetism. In fact, he is sometimes credited with founding the science of magnetism. He published descriptions of his many investigations in a book called De Magnete or “On the Magne ...
Spherical and Cylindrical Capacitors
... ◦ The change in Electric Potential, or Voltage, is equal to the integral of the Electric Field from inner to outer radius ...
... ◦ The change in Electric Potential, or Voltage, is equal to the integral of the Electric Field from inner to outer radius ...
Document
... 1. Where is the magnitude of the magnetic field around a permanent magnet greatest? a. The magnitude is greatest close to the poles. b. The magnitude is greatest far from the poles. c. The magnitude is equal at all points on the field. d. The magnitude is greatest halfway between poles. 2. One usefu ...
... 1. Where is the magnitude of the magnetic field around a permanent magnet greatest? a. The magnitude is greatest close to the poles. b. The magnitude is greatest far from the poles. c. The magnitude is equal at all points on the field. d. The magnitude is greatest halfway between poles. 2. One usefu ...