Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
... The solenoid s magnetic field is the vector sum of the fields produced by the individual turns (windings) that make up the solenoid. at points inside the solenoid and reasonably far from the wire, the magnetic field is approximately parallel to the (central) solenoid axis. In the limiting case of a ...
... The solenoid s magnetic field is the vector sum of the fields produced by the individual turns (windings) that make up the solenoid. at points inside the solenoid and reasonably far from the wire, the magnetic field is approximately parallel to the (central) solenoid axis. In the limiting case of a ...
Electro-Statics Think then MC
... 1 A charged object shoots straight up away from another charged object and reaches its highest point. 2 A charged object is high above the ground in an electric field. The field pulls the charged particle downward. We see the system’s energy when it is halfway down to the ground.. 3 A charged object ...
... 1 A charged object shoots straight up away from another charged object and reaches its highest point. 2 A charged object is high above the ground in an electric field. The field pulls the charged particle downward. We see the system’s energy when it is halfway down to the ground.. 3 A charged object ...
Review (Faraday`s law, magnetic field, Gauss`s law
... A moving charge will interact with other magnetic poles. This is because it has a magnetic field of its own. The field for a moving charge is given by the Biot-Savart Law: B= ...
... A moving charge will interact with other magnetic poles. This is because it has a magnetic field of its own. The field for a moving charge is given by the Biot-Savart Law: B= ...
Force Quiz - VCC Library - Vancouver Community College
... 9) D. The teams were standing up because forces were in balance, but when the rope broke, one of the forces (tension) acting on each team as a system disappeared, and they move in the direction the remaining forces dictate. 10) C. F = m·a, so if m = 0, there’s no force. Light changes direction when ...
... 9) D. The teams were standing up because forces were in balance, but when the rope broke, one of the forces (tension) acting on each team as a system disappeared, and they move in the direction the remaining forces dictate. 10) C. F = m·a, so if m = 0, there’s no force. Light changes direction when ...
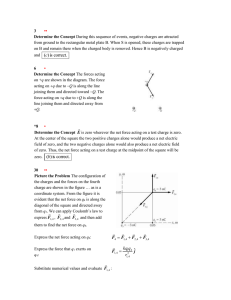
There are only two charges, positive and negative.
... Ex. 7 - In figure 18.18a the charges on the two metal spheres and the ebonite rod create an electric field E at the spot indicated. The field has a magnitude of 2.0 N/C and is directed as in the drawing. Determine the force on a charge placed at that spot, if the charge has a value of (a) q0 = +18 ...
... Ex. 7 - In figure 18.18a the charges on the two metal spheres and the ebonite rod create an electric field E at the spot indicated. The field has a magnitude of 2.0 N/C and is directed as in the drawing. Determine the force on a charge placed at that spot, if the charge has a value of (a) q0 = +18 ...
Chapter 8 Section 3
... of wire in a magnetic field Wire coil is wrapped around an iron core and placed between the poles of a permanent magnet. http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph11e/generator_e.htm ...
... of wire in a magnetic field Wire coil is wrapped around an iron core and placed between the poles of a permanent magnet. http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph11e/generator_e.htm ...























