Motion and Forces Study Guide
... the teacher in class if there are any questions. Motion is change in position over a period of time. Frame of referenceWhenever you describe something that is moving, you are comparing it with something that is assumed to be stationary, or not moving. The background or object that is used for compar ...
... the teacher in class if there are any questions. Motion is change in position over a period of time. Frame of referenceWhenever you describe something that is moving, you are comparing it with something that is assumed to be stationary, or not moving. The background or object that is used for compar ...
Friday`s Slides
... An object travels from point A to point B while two constant forces of equal magnitude, and , are exerted on it. Think about the work done by each force and the net work. Is the magnitude of the velocity of the object at point B greater than, less than, or equal to the velocity of the object at poin ...
... An object travels from point A to point B while two constant forces of equal magnitude, and , are exerted on it. Think about the work done by each force and the net work. Is the magnitude of the velocity of the object at point B greater than, less than, or equal to the velocity of the object at poin ...
Performance Benchmark E
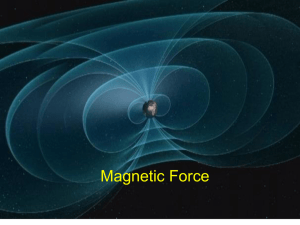
... Electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of the universe. It is a force that involves the interactions between electrically charged particles that occur due to their charge and for the emission and absorption of photons. An electromagnetic force generates an electromagnetic field, ...
... Electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of the universe. It is a force that involves the interactions between electrically charged particles that occur due to their charge and for the emission and absorption of photons. An electromagnetic force generates an electromagnetic field, ...
Newton`s 1st and 2nd Laws
... What are the options for what an object might be doing if the forces on the object are not balanced (i.e. there is a net force)? ...
... What are the options for what an object might be doing if the forces on the object are not balanced (i.e. there is a net force)? ...
Assignment 1
... Show that (0, 0) is a center if and only if a + d = 0, ad − bc > 0. Show that the phase trajectories are then given by cx2 + 2dxy − by 2 = constant. 4. The relativistic linear harmonic oscillator is given by the equation of motion d m0 c2 (p ) + kx = 0, (k > 0, v = ẋ) dt 1 − v 2 /c2 ...
... Show that (0, 0) is a center if and only if a + d = 0, ad − bc > 0. Show that the phase trajectories are then given by cx2 + 2dxy − by 2 = constant. 4. The relativistic linear harmonic oscillator is given by the equation of motion d m0 c2 (p ) + kx = 0, (k > 0, v = ẋ) dt 1 − v 2 /c2 ...
Sources of Magnetic Fields (Currents)
... Magnetic fields are due to currents The Biot-Savart Law for wire element and moving charge Calculating field at the centers of current loops Field due to a long straight wire Force between two parallel wires carrying currents Ampere’s Law Solenoids and toroids Field on the axis of a current loop (di ...
... Magnetic fields are due to currents The Biot-Savart Law for wire element and moving charge Calculating field at the centers of current loops Field due to a long straight wire Force between two parallel wires carrying currents Ampere’s Law Solenoids and toroids Field on the axis of a current loop (di ...
Chapter 29
... Faraday’s law for a coil • A commercial alternator uses many loops of wire wound around a barrel-like structure called an armature. • The resulting induced emf is far larger than would be possible with a single loop of wire. • If a coil has N identical turns and if the flux varies at the same rate ...
... Faraday’s law for a coil • A commercial alternator uses many loops of wire wound around a barrel-like structure called an armature. • The resulting induced emf is far larger than would be possible with a single loop of wire. • If a coil has N identical turns and if the flux varies at the same rate ...
Magnetism
... If a current-carrying wire is bent into a loop, the magnetic field lines bunch up. If you add another loop and another, the magnetic field becomes more and more concentrated. This coil is called an electromagnet. ...
... If a current-carrying wire is bent into a loop, the magnetic field lines bunch up. If you add another loop and another, the magnetic field becomes more and more concentrated. This coil is called an electromagnet. ...