Acquired Abilities - United States Naval Academy
... Define magnetic field and find the magnetic force on moving charges and currents. Use the Biot-Savart Law and Ampere’s Law to find the magnetic field for simple current configurations. State Faraday’s Law and use it to solve problems and discuss generators and power transmission. Define self inducta ...
... Define magnetic field and find the magnetic force on moving charges and currents. Use the Biot-Savart Law and Ampere’s Law to find the magnetic field for simple current configurations. State Faraday’s Law and use it to solve problems and discuss generators and power transmission. Define self inducta ...
Gravitational Relativity
... Permeability (the magnetic parameter) is therefore a dependent function of permittivity (the electric parameter) of electromagnetic fields. 9. Mechanical properties of matter are electromagnetic phenomena, or more strictly electric phenomena, since magnetism is a dependent phenomenon of electric fi ...
... Permeability (the magnetic parameter) is therefore a dependent function of permittivity (the electric parameter) of electromagnetic fields. 9. Mechanical properties of matter are electromagnetic phenomena, or more strictly electric phenomena, since magnetism is a dependent phenomenon of electric fi ...
Action and Reaction Pairs
... While driving down the road, a firefly strikes the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the ...
... While driving down the road, a firefly strikes the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the ...
Chapter2A 07_08
... v is the electric charge density per unit volume; and J is the current density per unit area. These equations hold in any material, including free space (vacuum), and at any spatial location (x,y,z). His equations, which he deduced from experimental observations reported by Gauss, Ampere, Farad ...
... v is the electric charge density per unit volume; and J is the current density per unit area. These equations hold in any material, including free space (vacuum), and at any spatial location (x,y,z). His equations, which he deduced from experimental observations reported by Gauss, Ampere, Farad ...
lesson homework Tuesday may 1st
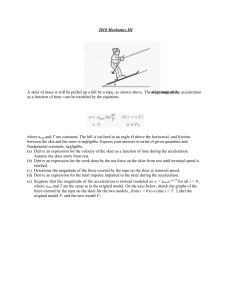
... where r is the distance from the center of the cloud. Express all algebraic answers in terms of Q, R, and fundamental constants (a) Determine the following as a function of r for r > R. i. The magnitude E of the electric field ii. The electric potential V (b) A proton is placed at point P shown abov ...
... where r is the distance from the center of the cloud. Express all algebraic answers in terms of Q, R, and fundamental constants (a) Determine the following as a function of r for r > R. i. The magnitude E of the electric field ii. The electric potential V (b) A proton is placed at point P shown abov ...
Force
... the ball. The ball now heads up, away from you. By bumping the ball, you are applying a force and the ball changes direction. ...
... the ball. The ball now heads up, away from you. By bumping the ball, you are applying a force and the ball changes direction. ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION - Corner Brook Regional High
... • the direction of the induced current in the second coil will depend on whether or not the switch in the first coil is opening or closing. • This is because as the switch opens, the magnetic field around the first coil is "collapsing", and as the switch closes the magnetic field around the first co ...
... • the direction of the induced current in the second coil will depend on whether or not the switch in the first coil is opening or closing. • This is because as the switch opens, the magnetic field around the first coil is "collapsing", and as the switch closes the magnetic field around the first co ...
Electric Fields and Force
... Two equally charged lightweight balls, q, are suspended from strings that are each 10.0 cm long. They repel each other and have a separation distance between the charged particles is 14.00 cm. Assume the mass of each of the lightweight balls is 0.575 g. What is the charge on each of the balls? ...
... Two equally charged lightweight balls, q, are suspended from strings that are each 10.0 cm long. They repel each other and have a separation distance between the charged particles is 14.00 cm. Assume the mass of each of the lightweight balls is 0.575 g. What is the charge on each of the balls? ...