NewtonsLaws - University of Colorado Boulder
... exactly like a compressed spring. The heavier the book, the more the table-spring compresses, and the more it pushes upward on the book. Rules for drawing "Free-body diagram" or force diagram : 0) Draw a blob representing the object. 1) Draw only the forces acting on the object (not the forces which ...
... exactly like a compressed spring. The heavier the book, the more the table-spring compresses, and the more it pushes upward on the book. Rules for drawing "Free-body diagram" or force diagram : 0) Draw a blob representing the object. 1) Draw only the forces acting on the object (not the forces which ...
Motion/Force/Machines (Fifth Grade)
... Earth’s gravity has less effect on objects as they get farther away from Earth. the weight of the object is less when orbiting the Earth the space shuttle’s engines cause too much vibration for objects to remain still ...
... Earth’s gravity has less effect on objects as they get farther away from Earth. the weight of the object is less when orbiting the Earth the space shuttle’s engines cause too much vibration for objects to remain still ...
AP Physics D: Mechanics Midterm Review Problems
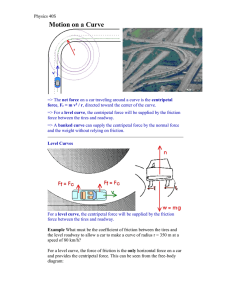
... 7. A train slows down at a constant rate as it rounds a sharp circular horizontal turn. Its initial speed is not known. It takes 15.5 s to slow down from 88 km/h to 33 km/h. The radius of the curve is 165 m. a. As the train goes around the turn, what is the magnitude of the tangential component of t ...
... 7. A train slows down at a constant rate as it rounds a sharp circular horizontal turn. Its initial speed is not known. It takes 15.5 s to slow down from 88 km/h to 33 km/h. The radius of the curve is 165 m. a. As the train goes around the turn, what is the magnitude of the tangential component of t ...
mapping fields
... The force required to change the motion of an object. The energy required to change the motion of an object. The resistance to changes in motion of an object. The momentum of an object in motion. ...
... The force required to change the motion of an object. The energy required to change the motion of an object. The resistance to changes in motion of an object. The momentum of an object in motion. ...
magnetic_induction
... truck is increasing the magnetic permeability of the coil of wire.” Another question to ask the students is “Why don’t most pedal bikes trigger a traffic light detection system?”. ...
... truck is increasing the magnetic permeability of the coil of wire.” Another question to ask the students is “Why don’t most pedal bikes trigger a traffic light detection system?”. ...
Physics 211 Lab #2 – Forces
... very different stance. The power of Newton’s theories was revealed through their ability to make detailed mathematical predictions about the motion of objects. These predictions have consistently been verified experimentally. Newton hypothesized that forces cause a change in motion, not motion itsel ...
... very different stance. The power of Newton’s theories was revealed through their ability to make detailed mathematical predictions about the motion of objects. These predictions have consistently been verified experimentally. Newton hypothesized that forces cause a change in motion, not motion itsel ...
Electromagnets Goal: To understand that electricity can form a
... deflected when brought into the vicinity of a current carrying wire. Thus, currents create magnetic fields. At the same time, when an electrical current is passed through a coil of wire a magnetic field is created. So put simply, electricity generates m ...
... deflected when brought into the vicinity of a current carrying wire. Thus, currents create magnetic fields. At the same time, when an electrical current is passed through a coil of wire a magnetic field is created. So put simply, electricity generates m ...
Slide 1
... A capacitor is a device designed to provide capacitance in an electric circuit by supplying it with the ability to store energy in an electric field between two conducting bodies (eg. two pieces of charged metal). In its most basic form, a capacitor consists of two conducting plates separated by an ...
... A capacitor is a device designed to provide capacitance in an electric circuit by supplying it with the ability to store energy in an electric field between two conducting bodies (eg. two pieces of charged metal). In its most basic form, a capacitor consists of two conducting plates separated by an ...