Chapter 23 Energy is conserved, so the change in potential energy
... 30. By energy conservation, all of the initial potential energy of the charges will change to kinetic energy when the charges are very far away from each other. By momentum conservation, since the initial momentum is zero and the charges have identical masses, the charges will have equal speeds in o ...
... 30. By energy conservation, all of the initial potential energy of the charges will change to kinetic energy when the charges are very far away from each other. By momentum conservation, since the initial momentum is zero and the charges have identical masses, the charges will have equal speeds in o ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... uniform circular motion. Question: Why is uniform circular motion accelerated motion? Answer: Although the speed is constant, the velocity is not constant since an object in uniform circular motion is continually changing direction. ...
... uniform circular motion. Question: Why is uniform circular motion accelerated motion? Answer: Although the speed is constant, the velocity is not constant since an object in uniform circular motion is continually changing direction. ...
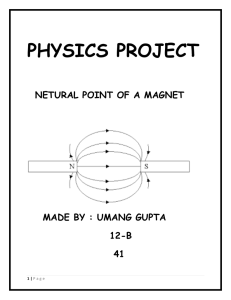
Neutral point of a Magnet
... Stretch sheet of paper over the drawing board. Fix it with pins Place the compass needle over the plain sheet of paper so as to determine the geographic North and South. This can be done by rotating the drawing ...
... Stretch sheet of paper over the drawing board. Fix it with pins Place the compass needle over the plain sheet of paper so as to determine the geographic North and South. This can be done by rotating the drawing ...
Science department Grade 7 Final revision sheet quarter 3
... Fill in each blank with the term that best completes the following sentences. 1. A(n) ________________________ allows electrical charges to move freely. 2. The amount of work required to move a unit electric charge between two points is called ________________________. 3. A(n) ______________________ ...
... Fill in each blank with the term that best completes the following sentences. 1. A(n) ________________________ allows electrical charges to move freely. 2. The amount of work required to move a unit electric charge between two points is called ________________________. 3. A(n) ______________________ ...
Dipole Force
... Assume an electron (mass m=9.109e-31 kg, charge q=-1.602e-19 C) is initially located in the plane at (x0,y0) and released with an initial velocity (vx0, vy0). a) Write a routine to determine the position as a function of time for the electron. You should be solving for x(t), y(t), vx(t), and vy(t). ...
... Assume an electron (mass m=9.109e-31 kg, charge q=-1.602e-19 C) is initially located in the plane at (x0,y0) and released with an initial velocity (vx0, vy0). a) Write a routine to determine the position as a function of time for the electron. You should be solving for x(t), y(t), vx(t), and vy(t). ...
Slide 1
... • Properties of magnetic fields – Outside the magnet the lines start from the north pole and end at the south pole – Inside the magnet they continue from the south pole to the north ...
... • Properties of magnetic fields – Outside the magnet the lines start from the north pole and end at the south pole – Inside the magnet they continue from the south pole to the north ...
physics-p5-what-you-should
... component (or device), work is done by the power supply, and energy is transferred from it to the component and/or its surroundings I can recall that power (in watts, W) is a measure of the rate at which an electrical power supply transfers energy to an appliance or device and/or its surroundings I ...
... component (or device), work is done by the power supply, and energy is transferred from it to the component and/or its surroundings I can recall that power (in watts, W) is a measure of the rate at which an electrical power supply transfers energy to an appliance or device and/or its surroundings I ...
(unbent) area of the net, how many fish per hour will be caught with
... There is nothing in Coulomb’s law that argues against a “fish picture” of electric fields. If we count fish flowing from a + charge, we should get the same number of fish if we capture them 1 m away, or 10 m away. Coulomb’s law says we do. (In fact, all of electromagnetic theory and experiment is c ...
... There is nothing in Coulomb’s law that argues against a “fish picture” of electric fields. If we count fish flowing from a + charge, we should get the same number of fish if we capture them 1 m away, or 10 m away. Coulomb’s law says we do. (In fact, all of electromagnetic theory and experiment is c ...
Newton`s Laws PPT for HTML
... Frictional Force Tensional Force Air Resistance Force Spring Force Buoyant Force Action-at-a-distance forces are types of forces in which the two interacting objects are not in physical contact with each other, yet are able to exert a push or pull despite a physical separation. Gravitational Force E ...
... Frictional Force Tensional Force Air Resistance Force Spring Force Buoyant Force Action-at-a-distance forces are types of forces in which the two interacting objects are not in physical contact with each other, yet are able to exert a push or pull despite a physical separation. Gravitational Force E ...
PPT
... equipotentials; lines (and equipotentials) never cross each other… Electric potential, work and potential energy: work to bring a charge somewhere is W = –qV (signs!). Potential energy of a system = negative work done to build it. Conductors: field and potential inside conductors, and on the surface ...
... equipotentials; lines (and equipotentials) never cross each other… Electric potential, work and potential energy: work to bring a charge somewhere is W = –qV (signs!). Potential energy of a system = negative work done to build it. Conductors: field and potential inside conductors, and on the surface ...
CTWeek2 - University of Colorado Boulder
... with k > 0 and N(t=0) = No > 0. What is the behavior of N(t) as t goes to infinity? A) N(t) decays to zero. B) N(t) doesn’t change. C) N(t) diverges (approaches infinity). D) The behavior of N(t) can’t be determined from the information given. ...
... with k > 0 and N(t=0) = No > 0. What is the behavior of N(t) as t goes to infinity? A) N(t) decays to zero. B) N(t) doesn’t change. C) N(t) diverges (approaches infinity). D) The behavior of N(t) can’t be determined from the information given. ...