Tutorial_blocks
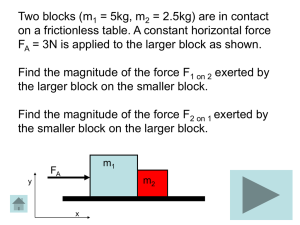
... 8. Recall from using Newton’s 3rd Law in question 3 that |F2 on 1| = |F1 on 2|, so the magnitude of F2 on 1 is also 1 N. Let’s check that this is true using the correct equations that we found in the previous questions to solve for the magnitude of the normal force (F2 on 1) exerted on the larger b ...
... 8. Recall from using Newton’s 3rd Law in question 3 that |F2 on 1| = |F1 on 2|, so the magnitude of F2 on 1 is also 1 N. Let’s check that this is true using the correct equations that we found in the previous questions to solve for the magnitude of the normal force (F2 on 1) exerted on the larger b ...
Unit_3_Part_2_Centripetal_Acceleration_Notes
... Uniform Circular Motion describes the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path. The direction is not constant, so the object does not have a constant velocity. Therefore, it must be accelerating and there must be a force causing this acceleration. Examples of objects that ...
... Uniform Circular Motion describes the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path. The direction is not constant, so the object does not have a constant velocity. Therefore, it must be accelerating and there must be a force causing this acceleration. Examples of objects that ...
Chapter 23
... Coulomb’s Law cont. • Here the q's represent two charges, r is the distance separating them, and k is a constant equal to 8.99x109 N m2 / C2 . • The electrostatic force is directed along the line joining the charges, and it is attractive if the charges have unlike signs and repulsive if the charges ...
... Coulomb’s Law cont. • Here the q's represent two charges, r is the distance separating them, and k is a constant equal to 8.99x109 N m2 / C2 . • The electrostatic force is directed along the line joining the charges, and it is attractive if the charges have unlike signs and repulsive if the charges ...
Electric Potential due to a Charged Conductor
... Therefore, the electric potential is constant everywhere inside the conductor and equal to the value at the surface. ...
... Therefore, the electric potential is constant everywhere inside the conductor and equal to the value at the surface. ...
Inward Diffusion and Acceleration of Particles
... Charged particles in a magnetosphere are spontaneously attracted to a planet while increasing their kinetic energy via inward diffusion process. A constraint on particles’ micro-scale adiabatic invariants restricts the class of motions available to the system, giving rise to a proper frame on which ...
... Charged particles in a magnetosphere are spontaneously attracted to a planet while increasing their kinetic energy via inward diffusion process. A constraint on particles’ micro-scale adiabatic invariants restricts the class of motions available to the system, giving rise to a proper frame on which ...
ppt - RHIG - Wayne State University
... degree of difficulty inherent in solving the 2nd order differential equation F = m a. – Function of position only – Function of speed, or velocity – Separable and non-separable forces ...
... degree of difficulty inherent in solving the 2nd order differential equation F = m a. – Function of position only – Function of speed, or velocity – Separable and non-separable forces ...
Einstein`s Electrodynamic Pathway to Special Relativity
... propagating retardation times by projected retardation times? Promising, BUT… H = H’ still precludes magnetic fields induced by charge currents. ...
... propagating retardation times by projected retardation times? Promising, BUT… H = H’ still precludes magnetic fields induced by charge currents. ...