ppt document
... directions of both the waving Electric and the waving Magnetic Fields, and that the direction of the waving Electric Field must be perpendicular to the direction of the waving Magnetic Field. This is stated in the following: S = (1/mo)E x B where S is called the Poynting vector and gives the Intensi ...
... directions of both the waving Electric and the waving Magnetic Fields, and that the direction of the waving Electric Field must be perpendicular to the direction of the waving Magnetic Field. This is stated in the following: S = (1/mo)E x B where S is called the Poynting vector and gives the Intensi ...
Module P4.3 Electromagnetic forces
... The force on a current can produce a torque, and this is utilized in meters and motors. Magnetic fields due to currents also give rise to forces between current carrying wires, and lead to the basic definition of the ampere. In Section 3 our attention turns to individual charged particles in magneti ...
... The force on a current can produce a torque, and this is utilized in meters and motors. Magnetic fields due to currents also give rise to forces between current carrying wires, and lead to the basic definition of the ampere. In Section 3 our attention turns to individual charged particles in magneti ...
AP® Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism: Syllabus 2
... instructional time engaged in laboratory work. SC11—A hands-on laboratory component is required. SC12—Each student should complete a lab notebook or portfolio of lab reports. ...
... instructional time engaged in laboratory work. SC11—A hands-on laboratory component is required. SC12—Each student should complete a lab notebook or portfolio of lab reports. ...
Physical science - State of New Jersey
... Experimental evidence should allow students to support claims about how an electric current can produce a magnetic field, and how a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current. Claims should be supported and modeled mathematically when appropriate. Students should choose and interpret un ...
... Experimental evidence should allow students to support claims about how an electric current can produce a magnetic field, and how a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current. Claims should be supported and modeled mathematically when appropriate. Students should choose and interpret un ...
VP_Erod_many_loc_S2012Mason
... p f = pi Fnet t to update the momentum, then updating the position ( rf = ri vavg t ), in a loop, where ...
... p f = pi Fnet t to update the momentum, then updating the position ( rf = ri vavg t ), in a loop, where ...
Faraday Rotation
... and ethanol). The Verdet constants we measured were too high compared to the accepted values. One of these reasons was the temperature increase in the water caused by the solenoid heating up. Bubbles can be formed that reflect the laser during the experiment increasing the effective length of the li ...
... and ethanol). The Verdet constants we measured were too high compared to the accepted values. One of these reasons was the temperature increase in the water caused by the solenoid heating up. Bubbles can be formed that reflect the laser during the experiment increasing the effective length of the li ...
Properties Of Conductors
... Click here for Animation Induced Charges in a conductor: The above properties of a conductor influence the behaviour of a conductor placed in an electric field. Consider, for instance, what happens when a charge is brought near an uncharged conductor. The conductor is placed in the electric field o ...
... Click here for Animation Induced Charges in a conductor: The above properties of a conductor influence the behaviour of a conductor placed in an electric field. Consider, for instance, what happens when a charge is brought near an uncharged conductor. The conductor is placed in the electric field o ...
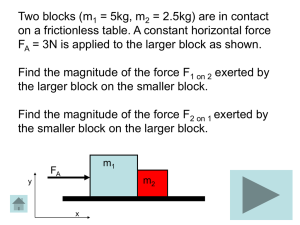
Tutorial_blocks
... 8. Recall from using Newton’s 3rd Law in question 3 that |F2 on 1| = |F1 on 2|, so the magnitude of F2 on 1 is also 1 N. Let’s check that this is true using the correct equations that we found in the previous questions to solve for the magnitude of the normal force (F2 on 1) exerted on the larger b ...
... 8. Recall from using Newton’s 3rd Law in question 3 that |F2 on 1| = |F1 on 2|, so the magnitude of F2 on 1 is also 1 N. Let’s check that this is true using the correct equations that we found in the previous questions to solve for the magnitude of the normal force (F2 on 1) exerted on the larger b ...
Unit_3_Part_2_Centripetal_Acceleration_Notes
... Uniform Circular Motion describes the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path. The direction is not constant, so the object does not have a constant velocity. Therefore, it must be accelerating and there must be a force causing this acceleration. Examples of objects that ...
... Uniform Circular Motion describes the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path. The direction is not constant, so the object does not have a constant velocity. Therefore, it must be accelerating and there must be a force causing this acceleration. Examples of objects that ...