Balancing Forces
... Students often want to include both internal and external forces in their diagrams. For example, a soda bottle may have a large internal pressure resisted by the walls, but neither of these are external forces that would cause the soda bottle to move. Since this model only deals with external forces ...
... Students often want to include both internal and external forces in their diagrams. For example, a soda bottle may have a large internal pressure resisted by the walls, but neither of these are external forces that would cause the soda bottle to move. Since this model only deals with external forces ...
Solution to the Static Charge Distribution on a Thin Wire Using the
... Just as differential equations are a common class of mathematical tools for electromagnetic systems, integral equations can likewise provide valuable insight into practical engineering problems. By analogy, finite-difference methods serve as a popular tool for numerically solving differential equati ...
... Just as differential equations are a common class of mathematical tools for electromagnetic systems, integral equations can likewise provide valuable insight into practical engineering problems. By analogy, finite-difference methods serve as a popular tool for numerically solving differential equati ...
Static Equilibrium (print version)
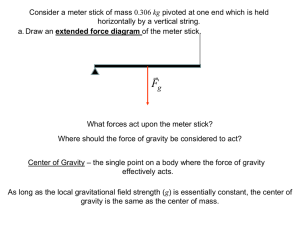
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
Rotational Equilibrium and Dynamics1 Net torque: Add up individual
... a. Remember to resolve into components for forces acting at an angle 2. Add up all forces acting on the object Second condition of equilibrium 1. Choose an axis for the object to rotate around (torque). a. The axis chosen doesn’t matter, so choose an axis that will help you! An unknown force that ac ...
... a. Remember to resolve into components for forces acting at an angle 2. Add up all forces acting on the object Second condition of equilibrium 1. Choose an axis for the object to rotate around (torque). a. The axis chosen doesn’t matter, so choose an axis that will help you! An unknown force that ac ...
Magnetic diffusion and the motion of field lines
... they can disappear either at a neutral sheet or at infinity, let us now turn to diffusion in two dimensions. The simplest approach mathematically is to consider one-dimensional solutions of 2D fields of the form Bðr, tÞh^ having circular field lines, for which the diffusive limit of the induction eq ...
... they can disappear either at a neutral sheet or at infinity, let us now turn to diffusion in two dimensions. The simplest approach mathematically is to consider one-dimensional solutions of 2D fields of the form Bðr, tÞh^ having circular field lines, for which the diffusive limit of the induction eq ...
Is the electrostatic force between a point charge and a neutral
... grounded rather than neutral: in that case, a positively charged point charge will only induce negative charges on the metallic object, leading to an attractive force. Given all of this evidence, one might think that the force is always attractive. Surprisingly, this is not the case. In this paper, ...
... grounded rather than neutral: in that case, a positively charged point charge will only induce negative charges on the metallic object, leading to an attractive force. Given all of this evidence, one might think that the force is always attractive. Surprisingly, this is not the case. In this paper, ...