36125651 Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition – Statistical
... Instructor: Prof. Mayer Aladjem, http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~aladjem THIS COURSE IS INTENDED TO BE LARGELY SELF-CONTAINED PREREQUISITES: basic undergraduate mathematical courses. This course is suitable for all fields of specialization of Electrical & Computer Engineering. This course will cover the th ...
... Instructor: Prof. Mayer Aladjem, http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~aladjem THIS COURSE IS INTENDED TO BE LARGELY SELF-CONTAINED PREREQUISITES: basic undergraduate mathematical courses. This course is suitable for all fields of specialization of Electrical & Computer Engineering. This course will cover the th ...
Data Preprocessing Why Data Preprocessing? Major Tasks in Data
... • Given c, optimization of the mj ’s is easy; mj is just the mean of the data vectors assigned to class j • Optimiztion over c: cannot compute all possible groupings, use the k-means algorithm to find a local optimum ...
... • Given c, optimization of the mj ’s is easy; mj is just the mean of the data vectors assigned to class j • Optimiztion over c: cannot compute all possible groupings, use the k-means algorithm to find a local optimum ...
Predictive systems for computer-aided diagnosis in radiology
... Introduction Intracranial hemorrhages, clinical scales ...
... Introduction Intracranial hemorrhages, clinical scales ...
Package `glmmTMB`
... ~. will set the right-hand side of the zero-inflation formula identical to the righthand side of the main (conditional effects) formula; terms can also be added or subtracted. Offset terms will automatically be dropped from the conditional effects formula. The zero-inflation model uses a logit link. ...
... ~. will set the right-hand side of the zero-inflation formula identical to the righthand side of the main (conditional effects) formula; terms can also be added or subtracted. Offset terms will automatically be dropped from the conditional effects formula. The zero-inflation model uses a logit link. ...
on p (D+ YA+)
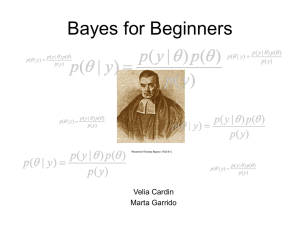
... The likelihood is the probability of the data given the parameter and represents the data now available. The posterior represents what is thought given both prior information and the data just seen. It relates the conditional density of a parameter (posterior probability) with its unconditional dens ...
... The likelihood is the probability of the data given the parameter and represents the data now available. The posterior represents what is thought given both prior information and the data just seen. It relates the conditional density of a parameter (posterior probability) with its unconditional dens ...
Dynamic Data Assimilation
... random forcing • Complete characterization of the state of a stochastic system is given the time evolution of its probability density in the state space Rn • Solution to the evolution of the probability density of xt when there is randomness only in the initial condition is given by the Liouville’s ...
... random forcing • Complete characterization of the state of a stochastic system is given the time evolution of its probability density in the state space Rn • Solution to the evolution of the probability density of xt when there is randomness only in the initial condition is given by the Liouville’s ...
X-mHMM: An Efficient Algorithm for Training Mixtures of HMMs when
... etc.), spectral models, observable operator models, or Hidden Markov Models (HMMs). In this paper we restrict ourselves to the case when the sequences are generated by HMMs where the observations take on values in a finite space, though we note in passing that our algorithm can be extended naturally ...
... etc.), spectral models, observable operator models, or Hidden Markov Models (HMMs). In this paper we restrict ourselves to the case when the sequences are generated by HMMs where the observations take on values in a finite space, though we note in passing that our algorithm can be extended naturally ...
Bootstrapping - University of Notre Dame
... solution will give an approximate answer to the problem The accuracy can be improved by increasing the number of scenarios selected ...
... solution will give an approximate answer to the problem The accuracy can be improved by increasing the number of scenarios selected ...
ICDM10Ozone-5minsver2
... Broad-area: Environmental Pollution Detection and Protection Drawback of alternative approaches Simulation: consume high computational power; customized for a particular location, so solutions not portable to different places Physical model approach: hard to come up with good equations when ther ...
... Broad-area: Environmental Pollution Detection and Protection Drawback of alternative approaches Simulation: consume high computational power; customized for a particular location, so solutions not portable to different places Physical model approach: hard to come up with good equations when ther ...
Privacy Preserving Data Mining: Additive Data Perturbation
... • Knowing perturbed data, and noise distribution • No other prior knowledge ...
... • Knowing perturbed data, and noise distribution • No other prior knowledge ...
Knowledge Engineering for Very Large Decision
... causal graph is usually the easiest for an expert or a user to understand and conceptualize. In our experience, though, the above statement holds only for medical experts who are already somewhat familiar with directed graphs. We have noticed that during initial modeling sessions medical experts ten ...
... causal graph is usually the easiest for an expert or a user to understand and conceptualize. In our experience, though, the above statement holds only for medical experts who are already somewhat familiar with directed graphs. We have noticed that during initial modeling sessions medical experts ten ...
An Overview of Text Mining
... • How can valid inference links be found without succumbing to combinatorial explosion of possibilities? – Need better models of lexical relationships and semantic constraints (very hard) ...
... • How can valid inference links be found without succumbing to combinatorial explosion of possibilities? – Need better models of lexical relationships and semantic constraints (very hard) ...