cross-sectional-anatomy-liver-part-2
... into anterior and posterior segments. Middle hepatic vein divides the liver into right and left lobes (or right and left hemi liver). This plane runs from the inferior vena cava to the gallbladder fossa. Left hepatic vein divides the left lobe into a medial and lateral part. Portal vein divides th ...
... into anterior and posterior segments. Middle hepatic vein divides the liver into right and left lobes (or right and left hemi liver). This plane runs from the inferior vena cava to the gallbladder fossa. Left hepatic vein divides the left lobe into a medial and lateral part. Portal vein divides th ...
- erc
... • Breaks down toxic substances. • Stores iron for the body. • Stores glycogen (converted glucose). • Metabolizes carbohydrates. • Metabolizes proteins. ...
... • Breaks down toxic substances. • Stores iron for the body. • Stores glycogen (converted glucose). • Metabolizes carbohydrates. • Metabolizes proteins. ...
The Small and Large Intestines
... A collection of protein enzymes including trypsin Lipase: fats Nucleases: nucleic acids Bicarbonate keeps the pH slightly alkaline Neutralizes the chyme upon entry to the small int. ...
... A collection of protein enzymes including trypsin Lipase: fats Nucleases: nucleic acids Bicarbonate keeps the pH slightly alkaline Neutralizes the chyme upon entry to the small int. ...
Digestive System
... Nucleases break down nucleotides Enzymes are secreted into the duodenum Alkaline fluid introduced with enzymes neutralizes acidic chyme coming from stomach Hormones produced by the pancreas ...
... Nucleases break down nucleotides Enzymes are secreted into the duodenum Alkaline fluid introduced with enzymes neutralizes acidic chyme coming from stomach Hormones produced by the pancreas ...
Cat Dissection of the Digestive System
... 4. Mesentery/Mesocolon—The mesentery/mesocolon looks like “cobwebs” connecting the organs to other organs and the abdominal wall. Identify the mesentery and mesocolon. 5. Lesser Omentum—Identify the lesser curvature of the stomach and its associated lesser omentum. ...
... 4. Mesentery/Mesocolon—The mesentery/mesocolon looks like “cobwebs” connecting the organs to other organs and the abdominal wall. Identify the mesentery and mesocolon. 5. Lesser Omentum—Identify the lesser curvature of the stomach and its associated lesser omentum. ...
The Digestive System
... is called a **bolus ** and it enters the pharynx or throat The Pharynx carries food from the mouth to the esophagus. When bolus is swallowed, muscle action causes epiglottis to close over larynx Prevents bolus from entering respiratory tract ...
... is called a **bolus ** and it enters the pharynx or throat The Pharynx carries food from the mouth to the esophagus. When bolus is swallowed, muscle action causes epiglottis to close over larynx Prevents bolus from entering respiratory tract ...
Chemical Digestion and Enzymes
... The major nutrients taken in by the body through eating are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and nucleic acids. These large macromolecules need to be broken down by the digestive system into their simpler building blocks. In order to breakdown these nutrient they under go a chemical reaction called HYD ...
... The major nutrients taken in by the body through eating are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and nucleic acids. These large macromolecules need to be broken down by the digestive system into their simpler building blocks. In order to breakdown these nutrient they under go a chemical reaction called HYD ...
Digestive Ch23-part 2
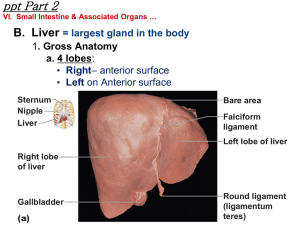
... • Falciform Ligament: separates Right & Left lobes anteriorly and suspends liver from diaphragm • Round ligament (ligamentum teres) – remnant of umbilical vein ...
... • Falciform Ligament: separates Right & Left lobes anteriorly and suspends liver from diaphragm • Round ligament (ligamentum teres) – remnant of umbilical vein ...
Biology 233
... hepatic artery – supplies oxygenated blood to liver cells bile duct – collects bile secreted by liver cells hepatic portal vein – carries venous blood from GI tract to liver cells ...
... hepatic artery – supplies oxygenated blood to liver cells bile duct – collects bile secreted by liver cells hepatic portal vein – carries venous blood from GI tract to liver cells ...
Digestive System—This system consists of several organs that work
... mesentery/mesocolon looks like “cobwebs” connecting the organs to other organs and the abdominal wall. Identify the mesentery and mesocolon. 5. Lesser Omentum—Identify the lesser curvature of the stomach and its associated lesser omentum. ...
... mesentery/mesocolon looks like “cobwebs” connecting the organs to other organs and the abdominal wall. Identify the mesentery and mesocolon. 5. Lesser Omentum—Identify the lesser curvature of the stomach and its associated lesser omentum. ...
Liver - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... • Peyer's patches protect especially distal part against bacteria – May protrude into submucosa ...
... • Peyer's patches protect especially distal part against bacteria – May protrude into submucosa ...
DIGESTIVE AND EXCRETORY SYSTEMS
... product is passed along its length until it is removed from the body through the rectum. ...
... product is passed along its length until it is removed from the body through the rectum. ...
Digestive (GI) System Flashcards
... 94. This is the largest internal organ of the body, located on the right side, below the diaphragm, and extends below the costal margin (can palpate). It has many functions and is the most complex organ except the brain, and as over 500 known functions. 95. What are the two main sources of blood for ...
... 94. This is the largest internal organ of the body, located on the right side, below the diaphragm, and extends below the costal margin (can palpate). It has many functions and is the most complex organ except the brain, and as over 500 known functions. 95. What are the two main sources of blood for ...
Animal & Human Nutrition
... hepatic artery (what type of blood does this carry? From where does it come?) hepatic vein (what type of blood does this carry? From where does it come?) ...
... hepatic artery (what type of blood does this carry? From where does it come?) hepatic vein (what type of blood does this carry? From where does it come?) ...
Digestion
... Largest gland in the body (1.4 kg) four lobes main function is to filter and process nutrients in the blood ...
... Largest gland in the body (1.4 kg) four lobes main function is to filter and process nutrients in the blood ...
Introduction to Gastrointestinal tract
... Largest gland of human body Largest internal organ Weighs 1.4 – 1.6 kg Rests on diaphragm on the right side of abdomen. ...
... Largest gland of human body Largest internal organ Weighs 1.4 – 1.6 kg Rests on diaphragm on the right side of abdomen. ...
Digestion Quest - Guido de Bres Christian High School
... Esophagus, pharynx, stomach, large intestine, small intestine. ...
... Esophagus, pharynx, stomach, large intestine, small intestine. ...
Aubrey
... The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. Weighing about 3 pounds, the liver is reddish-brown in color and feels rubbery to the touch. Normally you can't feel the liver, because it's protected by the rib cage. The liver has two large sections, called the right and t ...
... The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. Weighing about 3 pounds, the liver is reddish-brown in color and feels rubbery to the touch. Normally you can't feel the liver, because it's protected by the rib cage. The liver has two large sections, called the right and t ...
19 Digestive System
... This is the shortest region, only one foot long. It receives chyme from the stomach. This is where the vast majority of digestion begins. There are two ducts at the beginning of the duodenum from the pancreas and gallbladder. It is the site of action of liver and pancreas secretions. ...
... This is the shortest region, only one foot long. It receives chyme from the stomach. This is where the vast majority of digestion begins. There are two ducts at the beginning of the duodenum from the pancreas and gallbladder. It is the site of action of liver and pancreas secretions. ...
Digestive PPT
... This is the shortest region, only one foot long. It receives chyme from the stomach. This is where the vast majority of digestion begins. There are two ducts at the beginning of the duodenum from the pancreas and gallbladder. It is the site of action of liver and pancreas secretions. ...
... This is the shortest region, only one foot long. It receives chyme from the stomach. This is where the vast majority of digestion begins. There are two ducts at the beginning of the duodenum from the pancreas and gallbladder. It is the site of action of liver and pancreas secretions. ...
Lipid Transportu - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Fat (lipid) makes up 37% of the calories in the American diet Fat is energy rich and provides 9 kcal/gm Dietary lipids are 90% triacylglycerols, but also include cholesterol esters, phospholipids, essential unsaturated fatty acids and fat soluble vitamins Normally essentially all (98%) of the fat c ...
... Fat (lipid) makes up 37% of the calories in the American diet Fat is energy rich and provides 9 kcal/gm Dietary lipids are 90% triacylglycerols, but also include cholesterol esters, phospholipids, essential unsaturated fatty acids and fat soluble vitamins Normally essentially all (98%) of the fat c ...
Liver

The liver is a vital organ of vertebrates and some other animals. In the human it is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. The liver has a wide range of functions, including detoxification of various metabolites, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.The liver is a gland and plays a major role in metabolism with numerous functions in the human body, including regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification. It is an accessory digestive gland and produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion via the emulsification of lipids. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver. The liver's highly specialized tissue consisting of mostly hepatocytes regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecules, many of which are necessary for normal vital functions. Estimates regarding the organ's total number of functions vary, but textbooks generally cite it being around 500.Terminology related to the liver often starts in hepar- or hepat- from the Greek word for liver, hēpar (ἧπαρ, root hepat-, ἡπατ-).There is currently no way to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although liver dialysis techniques can be used in the short term. Liver transplantation is the only option for complete liver failure.