Homework Set #6 Due: 3-28-14
... and thus have a wavelength dependent transmission. To avoid this, as well as to avoid loss of energy and stray beams, waveplates are always anti-reflection (AR) coated on both sides. Note that a beam sent through a waveplate and telescope, for example, will lose ~27% of its power if all the surfaces ...
... and thus have a wavelength dependent transmission. To avoid this, as well as to avoid loss of energy and stray beams, waveplates are always anti-reflection (AR) coated on both sides. Note that a beam sent through a waveplate and telescope, for example, will lose ~27% of its power if all the surfaces ...
Laser Refraction and Diffraction
... 5. Let the refractive index of air be na, and use Snell’s law to calculate the refractive index of the glass plate. 6. Repeat Procedures 1 to 5 for 3 to 5 iterations to calculate the refractive indice average and errors. 7. Determine the possible refractive index of a glass plate. B. Slit and gratin ...
... 5. Let the refractive index of air be na, and use Snell’s law to calculate the refractive index of the glass plate. 6. Repeat Procedures 1 to 5 for 3 to 5 iterations to calculate the refractive indice average and errors. 7. Determine the possible refractive index of a glass plate. B. Slit and gratin ...
Supplementary Information (doc 4223K)
... want to achieve giant slow light effect. Gold rectangles have been investigated in many papers, and the group index for gold rectangles is not large. While, few works of slow light effect on triangle are found, and the curiosity on triangles encouraged us to investigate. Secondly, we want to achieve ...
... want to achieve giant slow light effect. Gold rectangles have been investigated in many papers, and the group index for gold rectangles is not large. While, few works of slow light effect on triangle are found, and the curiosity on triangles encouraged us to investigate. Secondly, we want to achieve ...
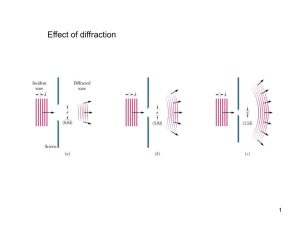
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
... "Diffraction" refers to the spreading of waves and appearance of fringes that occur when a wave front is constricted by an aperture in a screen that is otherwise opaque. The Huygens-Fresnel principle governs diffraction phenomena: "Every unobstructed element of a wavefront acts as a source of spheri ...
... "Diffraction" refers to the spreading of waves and appearance of fringes that occur when a wave front is constricted by an aperture in a screen that is otherwise opaque. The Huygens-Fresnel principle governs diffraction phenomena: "Every unobstructed element of a wavefront acts as a source of spheri ...
12Sept_Synergist Solutions article
... OPCs cannot handle high dust concentrations and are more difficult to calibrate to the particulates being measured. Their measurements are also significantly affected if the sampled flow rate changes. Therefore, flow control is very critical to accurate concentration measurements. The optics in an O ...
... OPCs cannot handle high dust concentrations and are more difficult to calibrate to the particulates being measured. Their measurements are also significantly affected if the sampled flow rate changes. Therefore, flow control is very critical to accurate concentration measurements. The optics in an O ...
Get full text
... In the last two decades many studies have been carried out for the remote sensing of cirrus clouds from ground, airplane, and satellites (Lynch et al., 2002). Both active and passive approaches have been tested. Most of them are exploiting the advantages of the visible, infrared, and microwave range ...
... In the last two decades many studies have been carried out for the remote sensing of cirrus clouds from ground, airplane, and satellites (Lynch et al., 2002). Both active and passive approaches have been tested. Most of them are exploiting the advantages of the visible, infrared, and microwave range ...
Check focal lengths of board ray optics set Equipment o Graph
... you wanted. If you bent it specifically into a parabola, or it’s usually good enough to use a circle, then rays that were coming in parallel to each other can be aimed to converge to a single point or diverge as if from a single point, and rays radiating from a point on an object can be reflected to ...
... you wanted. If you bent it specifically into a parabola, or it’s usually good enough to use a circle, then rays that were coming in parallel to each other can be aimed to converge to a single point or diverge as if from a single point, and rays radiating from a point on an object can be reflected to ...
1 Janaky Narayanan PC 5213 AY 2004
... chemical structure, and finally by its molecular structure. For example, C2H6O is the chemical formula of ethyl alcohol. CH3-CH2-OH is the chemical structure of ethyl alcohol. The molecular structure is determined by the three dimensional arrangement of the atoms in space. The word “conformation” de ...
... chemical structure, and finally by its molecular structure. For example, C2H6O is the chemical formula of ethyl alcohol. CH3-CH2-OH is the chemical structure of ethyl alcohol. The molecular structure is determined by the three dimensional arrangement of the atoms in space. The word “conformation” de ...
Statistical Mechanics
... Course Objectives: Student should be able to understand simple evaluations of nonlinear phenomena in optics. Examples will be directed toward applications within optical communications, and lasers. ...
... Course Objectives: Student should be able to understand simple evaluations of nonlinear phenomena in optics. Examples will be directed toward applications within optical communications, and lasers. ...
Optical losses
... As in the case of most transitive systems, light loss through absorption in an optical fiber tends to be an exponential function of length. Absorption loss is caused by the presence of impurities such as traces of metal ions (e.g., Cu2+, Fe3+) and hydroxyl (OH–) ions. Optical power is absorbed in the ...
... As in the case of most transitive systems, light loss through absorption in an optical fiber tends to be an exponential function of length. Absorption loss is caused by the presence of impurities such as traces of metal ions (e.g., Cu2+, Fe3+) and hydroxyl (OH–) ions. Optical power is absorbed in the ...
Flow Cytometry and Sorting, Part 1
... Sample volume flow rate can be changed by changing speed of motor Control is absolute (under normal conditions) ...
... Sample volume flow rate can be changed by changing speed of motor Control is absolute (under normal conditions) ...
3 The concept of diffraction limit
... transverse directions, become much larger than the |k| and hence the uncertainty in the λi position can be made comparably smaller than the diffraction limiting case of . As the 2π evanescent waves are excited at the boundary of two different media, they have dominance only close to the interface. T ...
... transverse directions, become much larger than the |k| and hence the uncertainty in the λi position can be made comparably smaller than the diffraction limiting case of . As the 2π evanescent waves are excited at the boundary of two different media, they have dominance only close to the interface. T ...
CHEM 210 Chapter 5 Wrap-up
... Calculating Enantiomeric Excess or Optical Purity • It is important to know what this means. Since any R impurity will ‘cancel’ the rotation of an equal amount of S: • A sample with an ee of 50% S is actually 50% pure S and 50% racemic R/S. • The total S enantiomer in the sample is actually ...
... Calculating Enantiomeric Excess or Optical Purity • It is important to know what this means. Since any R impurity will ‘cancel’ the rotation of an equal amount of S: • A sample with an ee of 50% S is actually 50% pure S and 50% racemic R/S. • The total S enantiomer in the sample is actually ...
Chapter2 Interaction Characteristics of Light
... medium to optically rare medium, it will move away from the normal. If the angle of incidence is increased so that the angle of refraction becomes 900 . The phenomena known as total internal reflection will occur ,if angle of incidence is further increased. The light instead of refracting will refle ...
... medium to optically rare medium, it will move away from the normal. If the angle of incidence is increased so that the angle of refraction becomes 900 . The phenomena known as total internal reflection will occur ,if angle of incidence is further increased. The light instead of refracting will refle ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.