Polarization of light II
... 1. Place the glass slab on a rotational table table horizontally as shown in fig 3 (transfer fig 3. from Module 17, lecture 4, fig 2). Alternatively it can be placed on a trotractor. and align it with the laser beam for normal incidence. The normal incidence can be ensured by tracing the reflected b ...
... 1. Place the glass slab on a rotational table table horizontally as shown in fig 3 (transfer fig 3. from Module 17, lecture 4, fig 2). Alternatively it can be placed on a trotractor. and align it with the laser beam for normal incidence. The normal incidence can be ensured by tracing the reflected b ...
DEVELOPMENT OF CAROTENOID PIGMENTS
... Xanthophyll and carotene are usually associated in plants and are present before the formation of chlorophyll. Their formulae suggest genetic relationship. Xanthophyll can be reduced to carotene and the transformation is reversible. Together they may represent a respiratory mechanism similar to the ...
... Xanthophyll and carotene are usually associated in plants and are present before the formation of chlorophyll. Their formulae suggest genetic relationship. Xanthophyll can be reduced to carotene and the transformation is reversible. Together they may represent a respiratory mechanism similar to the ...
setting up of a total internal reflection fluorescent microscope
... background noise [1]. TIRF utilizes the evanescent field created when a beam of light strikes an interface between two media to excite fluorescent dyes in the specimen. The phenomenon of total internal reflection occurs in which light is reflected but not refracted from a medium boundary and provide ...
... background noise [1]. TIRF utilizes the evanescent field created when a beam of light strikes an interface between two media to excite fluorescent dyes in the specimen. The phenomenon of total internal reflection occurs in which light is reflected but not refracted from a medium boundary and provide ...
optics - einstein classes
... As focal-length of a spherical mirror f (= R/2) depends only on the radius of mirror and is independent of wavelength of light and refreactive index of medium. Hence the focal length of a spherical mirror in air or water and for red or blue light is same. This is also why the image formed by mirrors ...
... As focal-length of a spherical mirror f (= R/2) depends only on the radius of mirror and is independent of wavelength of light and refreactive index of medium. Hence the focal length of a spherical mirror in air or water and for red or blue light is same. This is also why the image formed by mirrors ...
Polarization rotation of slow light with orbital angular momentum in
... The amount of such a dragging is determined by the difference in the group velocity and the speed of light. For fast light there is no dragging, but for slow light a substantial dragging is possible. ...
... The amount of such a dragging is determined by the difference in the group velocity and the speed of light. For fast light there is no dragging, but for slow light a substantial dragging is possible. ...
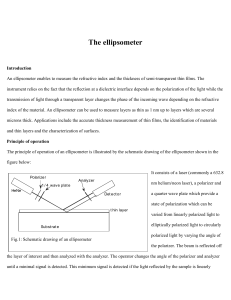
ellip
... of the analyzer and the half wavelength thickness when using a He/Ne laser and an incident angle of 70 degrees. The refractive indices from this table can be used to generate the Y - D curves for any material combination. In addition the minimum/maximum value of A1 can be used to help identify an un ...
... of the analyzer and the half wavelength thickness when using a He/Ne laser and an incident angle of 70 degrees. The refractive indices from this table can be used to generate the Y - D curves for any material combination. In addition the minimum/maximum value of A1 can be used to help identify an un ...
Mirages with atmospheric gravity waves
... We calculate mirage images by tracing a bundle of light rays projected from the observer's eye. The atmosphere is modeled as a set of concentric spherical shells. The temperature profile, required by the program as input data, specifies a set of elevations and their temperatures. These elevations de ...
... We calculate mirage images by tracing a bundle of light rays projected from the observer's eye. The atmosphere is modeled as a set of concentric spherical shells. The temperature profile, required by the program as input data, specifies a set of elevations and their temperatures. These elevations de ...
Presentation - University of Arizona
... Cardinal points and planes-continue Nodal planes have the characteristic of identity angular magnification. When the optical system is in air, nodal points/planes coincide with the principal points/planes. Principal points/planes can be described using Newtonian equations or Gaussian equations w ...
... Cardinal points and planes-continue Nodal planes have the characteristic of identity angular magnification. When the optical system is in air, nodal points/planes coincide with the principal points/planes. Principal points/planes can be described using Newtonian equations or Gaussian equations w ...
1 - Hodge Hill College
... Different cancer tumours are treated with different intensities of gamma radiation and so doctors place the source at different distances from the tumour. Intensity is also affected by the medium the radiation is travelling through. The denser the medium, the weaker the radiation gets. ...
... Different cancer tumours are treated with different intensities of gamma radiation and so doctors place the source at different distances from the tumour. Intensity is also affected by the medium the radiation is travelling through. The denser the medium, the weaker the radiation gets. ...
Wavefront Technology
... used to describe surfaces). These mathematical models are adequate for describing the wavefront measurements of the eye, because they are defined based on a circular form. The shape of the wavefront is described in the x and y coordinates while the third dimension, height is described in the z axis. ...
... used to describe surfaces). These mathematical models are adequate for describing the wavefront measurements of the eye, because they are defined based on a circular form. The shape of the wavefront is described in the x and y coordinates while the third dimension, height is described in the z axis. ...
Info Note 804: UV-VIS Nomenclature and Units
... the solution's concentration. Thus UV/VIS spectroscopy can be used to determine the concentration of a solution. It is necessary to know how quickly the absorbance changes with concentration. This can be taken from references (tables of molar extinction coefficients), or more accurately, determined ...
... the solution's concentration. Thus UV/VIS spectroscopy can be used to determine the concentration of a solution. It is necessary to know how quickly the absorbance changes with concentration. This can be taken from references (tables of molar extinction coefficients), or more accurately, determined ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.