Practical Aspects of Mirror Usage in Optical Systems for
... versions employed a layer of metallic ...
... versions employed a layer of metallic ...
Template BR_Rec_2002.dot
... power-control loops. Proper performance can be verified by test transmission of the SDI checkfield signals specified in SMPTE RP 178 “1996 – Serial Digital Interface Check field for 10-Bit 4:2:2 Component and 4 fsc Composite Digital Signals” for SDTV and SMPTE RP 198 “Bit-Serial Digital Check field ...
... power-control loops. Proper performance can be verified by test transmission of the SDI checkfield signals specified in SMPTE RP 178 “1996 – Serial Digital Interface Check field for 10-Bit 4:2:2 Component and 4 fsc Composite Digital Signals” for SDTV and SMPTE RP 198 “Bit-Serial Digital Check field ...
Portable Ultrafast Blue Light Sources Designed With Frequency
... market leader in providing femtosecond pulses in the near-infrared, their impractical size, cost, and power requirements render such sources impractical for space-limited on-site applications in biomedical and clinical laboratories. Consequently, we have recently demonstrated how small-scale femtose ...
... market leader in providing femtosecond pulses in the near-infrared, their impractical size, cost, and power requirements render such sources impractical for space-limited on-site applications in biomedical and clinical laboratories. Consequently, we have recently demonstrated how small-scale femtose ...
Aalborg Universitet Absorption Efficiency of Receiving Antennas Andersen, Jørgen Bach; Frandsen, Aksel
... SUALLY, the scattering properties of receiving antennas are not considered, since most important antenna properties, such as pattern, gain, and impedance, are the same as those for transmitting antennas. However, there are a few situations where the scattering is of importance, and recently there ha ...
... SUALLY, the scattering properties of receiving antennas are not considered, since most important antenna properties, such as pattern, gain, and impedance, are the same as those for transmitting antennas. However, there are a few situations where the scattering is of importance, and recently there ha ...
Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics Laboratory
... spheroidal scatterers whose interactions with light are governed by Mie theory. Mie theory provides an analytical closed-form description of optical scattering from single spheroidal particles as a function of particle size, refractive index, wavelength, observation angle, and optical polarization. ...
... spheroidal scatterers whose interactions with light are governed by Mie theory. Mie theory provides an analytical closed-form description of optical scattering from single spheroidal particles as a function of particle size, refractive index, wavelength, observation angle, and optical polarization. ...
Paper
... of the atom cloud is 27. At P 苷 4 mW, the geometric mean trapping frequency n̄ is 670 Hz. The measured frequencies [see Eq. (1)] were about half the expected values, presumably due to imperfect beam quality and the coarse measurements of P and w0 (an underestimation of w0 by 40% would account for th ...
... of the atom cloud is 27. At P 苷 4 mW, the geometric mean trapping frequency n̄ is 670 Hz. The measured frequencies [see Eq. (1)] were about half the expected values, presumably due to imperfect beam quality and the coarse measurements of P and w0 (an underestimation of w0 by 40% would account for th ...
Rapid BRDF Measurement Using an Ellipsoidal
... is combined with a projector. By placing the projector at the focal point of the ellipsoidal mirror, the projector serves as a substitute for the light source. That is, the projection of a pattern in which only one pixel is white corresponds to the illumination by a point light source. Moreover, cha ...
... is combined with a projector. By placing the projector at the focal point of the ellipsoidal mirror, the projector serves as a substitute for the light source. That is, the projection of a pattern in which only one pixel is white corresponds to the illumination by a point light source. Moreover, cha ...
Illusion Optics: The Optical Transformation of an Object into Another
... various novel applications, the most fascinating is a cloaking device designed to bend light around a concealed region, rendering any object inside the region ‘‘invisible’’ [1–10]. Cloaking can be regarded as creating an illusion of free space. In this Letter, we discuss a more generalized concept o ...
... various novel applications, the most fascinating is a cloaking device designed to bend light around a concealed region, rendering any object inside the region ‘‘invisible’’ [1–10]. Cloaking can be regarded as creating an illusion of free space. In this Letter, we discuss a more generalized concept o ...
Radiative Transfer Theory - UCL Department of Geography
... how to approach this problem). Assuming the canopy to be in air allows for power absorption by the surrounding medium to be ignored (Ulaby and Elachi, 1990; p. 136). Assuming horizontal homogeneity allows us to deal with radiation transport in only one dimension (a ‘1-D solution’), although the theo ...
... how to approach this problem). Assuming the canopy to be in air allows for power absorption by the surrounding medium to be ignored (Ulaby and Elachi, 1990; p. 136). Assuming horizontal homogeneity allows us to deal with radiation transport in only one dimension (a ‘1-D solution’), although the theo ...
Quantitative spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging
... related to molecular composition. The goal of quantitative PA imaging (QPAI) is to exploit this advantage by converting multiwavelength sets of PA images into images showing quantitatively accurate estimates of the spatially varying concentrations of chromophores (light-absorbing substances) embedde ...
... related to molecular composition. The goal of quantitative PA imaging (QPAI) is to exploit this advantage by converting multiwavelength sets of PA images into images showing quantitatively accurate estimates of the spatially varying concentrations of chromophores (light-absorbing substances) embedde ...
Light fan driven by relativistic laser pulse
... can be transported to a small volume in very short time. The twisted light with strongest torque by far can be found in twisted laser driven HHG experiments. In the experiments of Zurch et al. [21], a 800 nm laser is reflected from the spatial light modulator to obtain a twisted light with peaking i ...
... can be transported to a small volume in very short time. The twisted light with strongest torque by far can be found in twisted laser driven HHG experiments. In the experiments of Zurch et al. [21], a 800 nm laser is reflected from the spatial light modulator to obtain a twisted light with peaking i ...
Photoinduced Deformation of Crosslinked LiquidCrystalline Polymer
... fabrication. Of many methods, the preferred modification technique is mechanical rubbing. Typically, an aligned polyimide (PI) layer with parallel grooves is firstly generated by mechanical rubbing along one direction, and the grooves are then used to orient the LC molecules.[12] However, there rema ...
... fabrication. Of many methods, the preferred modification technique is mechanical rubbing. Typically, an aligned polyimide (PI) layer with parallel grooves is firstly generated by mechanical rubbing along one direction, and the grooves are then used to orient the LC molecules.[12] However, there rema ...
Beam manipulation: prisms vs. mirrors
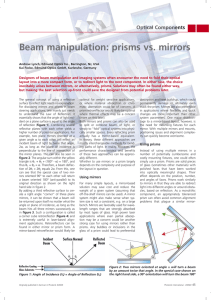
... are commonly used in beam manipulation applications include: the right angle prism, the dove prism, the rhomboid prism, and wedge prisms (see figure 6). The right angle prism is quite a versatile component. Depending on orientation, a right angle prism can either be used to turn a beam 90° by reflec ...
... are commonly used in beam manipulation applications include: the right angle prism, the dove prism, the rhomboid prism, and wedge prisms (see figure 6). The right angle prism is quite a versatile component. Depending on orientation, a right angle prism can either be used to turn a beam 90° by reflec ...
Digital High-Speed Optical Systems Interconnections for
... lasers were then fabricated in a &shion similar to the procedure described in Reference 10. The width of the rransponed region was about 0.2 pm with a nominal ac~ tive-region width of 1.5 J.1ffi, and the laser wafer was thinned to a thickness of 75 ,urn. The ohmic contactS to the n-type: and p--type ...
... lasers were then fabricated in a &shion similar to the procedure described in Reference 10. The width of the rransponed region was about 0.2 pm with a nominal ac~ tive-region width of 1.5 J.1ffi, and the laser wafer was thinned to a thickness of 75 ,urn. The ohmic contactS to the n-type: and p--type ...
Session 10 Wave Optics
... You will need to carry out the experiment at some stage. You can of course do this whenever you wish: it may be helpful to wait till we have been through sufficient background to clarify the measurements you need to make; or you may prefer to investigate now how the spot separation depends on the os ...
... You will need to carry out the experiment at some stage. You can of course do this whenever you wish: it may be helpful to wait till we have been through sufficient background to clarify the measurements you need to make; or you may prefer to investigate now how the spot separation depends on the os ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.