a variation in the origin and course of the posterior circumflex
... Compression of the PCHA and the axillary nerve has been reported to cause quadrangular space syndrome [8]. It is a rare condition, which causes poorly localized pain radiating to the arm, paraesthesia and tenderness over the quadrangular space [7]. Injuries of the PCHA frequently cause ischemia of t ...
... Compression of the PCHA and the axillary nerve has been reported to cause quadrangular space syndrome [8]. It is a rare condition, which causes poorly localized pain radiating to the arm, paraesthesia and tenderness over the quadrangular space [7]. Injuries of the PCHA frequently cause ischemia of t ...
Gluteal Region, Posterior Thigh, and Popliteal Fossa
... vessels and their branches, a few lymph nodes, and fat. It is diamond shaped. A. boundaries of the popliteal fossa 1. superiorly & medial - the semimembranous and semitendinous muscles 2. superiorly & lateral - the biceps femoris muscles 3. inferiorly (medial & lateral) - the two heads of the gastro ...
... vessels and their branches, a few lymph nodes, and fat. It is diamond shaped. A. boundaries of the popliteal fossa 1. superiorly & medial - the semimembranous and semitendinous muscles 2. superiorly & lateral - the biceps femoris muscles 3. inferiorly (medial & lateral) - the two heads of the gastro ...
Volume 142, 1999 57 A REPORT ON ANOMALIES OF DIGASTRIC
... In this case, we also found other muscle anomalies, such as levator claviculae muscle (Holibková et. al.2). In our second case, that of a 64-year old man, we found in necropsy combined asymmetrical anomaly of the anterior belly of digastric muscle (Fig. 2 a, b; Sch. 2). a) The medial part of the ant ...
... In this case, we also found other muscle anomalies, such as levator claviculae muscle (Holibková et. al.2). In our second case, that of a 64-year old man, we found in necropsy combined asymmetrical anomaly of the anterior belly of digastric muscle (Fig. 2 a, b; Sch. 2). a) The medial part of the ant ...
Pdf - McMed International
... position of the tendon and its resemblance to a nerve should be borne in mind by any surgeon operating on the back of leg. Despite its small size, injuries of the plantaris muscle and tendon, which have been termed “tennis leg,” have been a source of controversy in the literature [8,9,10,11,12]. Ten ...
... position of the tendon and its resemblance to a nerve should be borne in mind by any surgeon operating on the back of leg. Despite its small size, injuries of the plantaris muscle and tendon, which have been termed “tennis leg,” have been a source of controversy in the literature [8,9,10,11,12]. Ten ...
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
... Skeletal muscle is also considered “voluntary muscle” and makes up the muscles that are attached to our skeleton by tendons. These muscles can be contracted voluntarily and function in movement and maintenance of posture. About 35-45% of the human body is made up of skeletal muscle tissue. When skel ...
... Skeletal muscle is also considered “voluntary muscle” and makes up the muscles that are attached to our skeleton by tendons. These muscles can be contracted voluntarily and function in movement and maintenance of posture. About 35-45% of the human body is made up of skeletal muscle tissue. When skel ...
Superficial Facial Musculature March 2012
... oblique parallel course and interdigitates with the frontalis. It is innervated by the temporal and/or zygomatic branch of the facial nerve. It displaces the brow inferomedially and creates vertical skin creases. Botulinum toxin is commonly injected in this muscle along with the procerus, which caus ...
... oblique parallel course and interdigitates with the frontalis. It is innervated by the temporal and/or zygomatic branch of the facial nerve. It displaces the brow inferomedially and creates vertical skin creases. Botulinum toxin is commonly injected in this muscle along with the procerus, which caus ...
Abdominal Walls and Inguinal Region
... External oblique aponeurosis over the entire length of the canal ...
... External oblique aponeurosis over the entire length of the canal ...
Unit 17: Temporal and Infratemporal Fossa
... maxillary artery may pass superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, therefore the arrangement of its branches may differ from person to person (Plates 36, 65; 7.47, 7.58). The branches of the maxillary artery tend to follow the branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, ...
... maxillary artery may pass superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, therefore the arrangement of its branches may differ from person to person (Plates 36, 65; 7.47, 7.58). The branches of the maxillary artery tend to follow the branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, ...
Clinical anatomy of the lower limb
... 4. Tibial nerve, as a continuation of the sciatic nerve it passes from the superior angle to inferior angle of the popliteal space, and is lying most superficially, close to the popliteal fascia. 5. Popliteal vein lies medially and deeper to the tibial nerve. 6. Popliteal artery lies medially and de ...
... 4. Tibial nerve, as a continuation of the sciatic nerve it passes from the superior angle to inferior angle of the popliteal space, and is lying most superficially, close to the popliteal fascia. 5. Popliteal vein lies medially and deeper to the tibial nerve. 6. Popliteal artery lies medially and de ...
PDF - International Journal of Recent Scientific Research
... muscles share a common premuscle mass from the last two occipital and upper cervical myotomes. This muscle mass splits and separates at 9 mm stage of development (Sirasanagandla, S. R et al., 2012). This myotome segregates into the ventral Sternocleidomastoid and dorsal trapezius. The trapezius and ...
... muscles share a common premuscle mass from the last two occipital and upper cervical myotomes. This muscle mass splits and separates at 9 mm stage of development (Sirasanagandla, S. R et al., 2012). This myotome segregates into the ventral Sternocleidomastoid and dorsal trapezius. The trapezius and ...
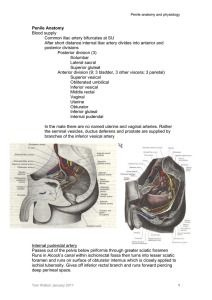
Penile Anatomy Blood supply Common iliac artery bifurcates
... Sympathetic adrenergic nerve terminals release NA which acts via mainly alpha 1 (A and D receptors) to inhibit adenylate cyclase and activate second messengers which raise intracellular inositol triphosphate. Raised IP3 leads to Ca release from sarcoplasmic reticulum and opening of calcium channels. ...
... Sympathetic adrenergic nerve terminals release NA which acts via mainly alpha 1 (A and D receptors) to inhibit adenylate cyclase and activate second messengers which raise intracellular inositol triphosphate. Raised IP3 leads to Ca release from sarcoplasmic reticulum and opening of calcium channels. ...
P4.2.3.TeacherResourceSheet
... be built, use anatomy textbooks and/or internet resources to provide guidance on the attachments of the muscle. Stress to students that the goal of independent building is to use what they have learned about muscle structure and function to explore action in another muscle region. Memorization of al ...
... be built, use anatomy textbooks and/or internet resources to provide guidance on the attachments of the muscle. Stress to students that the goal of independent building is to use what they have learned about muscle structure and function to explore action in another muscle region. Memorization of al ...
Accessory Head of Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle and its
... When the AHFPL is present, it is more likely to occur bilaterally then unilaterally, similar to the findings of Jones & Abrahams, 1997 and Hemaddy et al.. Moreover, the prevalence of 62.1% (149/240) is close to that of Hemaddy et al. and Oh et al., 2000, but differs from that of Mangini; Dellon & Ma ...
... When the AHFPL is present, it is more likely to occur bilaterally then unilaterally, similar to the findings of Jones & Abrahams, 1997 and Hemaddy et al.. Moreover, the prevalence of 62.1% (149/240) is close to that of Hemaddy et al. and Oh et al., 2000, but differs from that of Mangini; Dellon & Ma ...
Soleus Resection
... ■ Careful analysis of the popliteal trifurcation is necessary before surgery and may indicate tumor involvement and thus the need for an amputation. ...
... ■ Careful analysis of the popliteal trifurcation is necessary before surgery and may indicate tumor involvement and thus the need for an amputation. ...
Presence of an Accessory Flexor Muscle in the Posterior
... Variations of the calf muscles are rare. One such variant muscle known as the flexor accessories longus seldom encounters in the posterior crural region. This accessory muscle is believed to be a causative factor for swelling or pain in the medial aspect of leg. Therefore prior knowledge of existenc ...
... Variations of the calf muscles are rare. One such variant muscle known as the flexor accessories longus seldom encounters in the posterior crural region. This accessory muscle is believed to be a causative factor for swelling or pain in the medial aspect of leg. Therefore prior knowledge of existenc ...
Full Text
... the pelvic splanchnic and pudendal nerves. Notably, medial to the coccygeus muscle, a third parasagittal muscle, i.e., sacrococcygeus ventralis appears by the 12th week. It increases in size by the 18th week, and connects and mixes with the dorsal end of the levator ani by the 18th to 20th week. Thu ...
... the pelvic splanchnic and pudendal nerves. Notably, medial to the coccygeus muscle, a third parasagittal muscle, i.e., sacrococcygeus ventralis appears by the 12th week. It increases in size by the 18th week, and connects and mixes with the dorsal end of the levator ani by the 18th to 20th week. Thu ...
Hypertropia Associated With Superolateral Translation of the
... the right orbital roof without lateral translation of the SRM pulley. B, Patient with a 25-D left hypertropia demonstrates superolateral displacement of the left orbital roof and a 6.7-mm lateral translation of the SRM pulley. C, Patient with a right unilateral coronal synostosis combined with front ...
... the right orbital roof without lateral translation of the SRM pulley. B, Patient with a 25-D left hypertropia demonstrates superolateral displacement of the left orbital roof and a 6.7-mm lateral translation of the SRM pulley. C, Patient with a right unilateral coronal synostosis combined with front ...
Document
... Runs laterally beneath the trapezius and omohyoideus Passes through the suprascapular notch inferior to the superior transverse scapular ligament Then passes beneath the supraspinatus muscle and curves around the lateral border of the spine of the scapula to the infraspinatus muscle coracoclav ...
... Runs laterally beneath the trapezius and omohyoideus Passes through the suprascapular notch inferior to the superior transverse scapular ligament Then passes beneath the supraspinatus muscle and curves around the lateral border of the spine of the scapula to the infraspinatus muscle coracoclav ...
Laboratory Manual for Human Anatomy and Physiology I
... muscle contracts, one bone remains relatively stationary. The site of attachment of the muscle to the stationary bone is called the origin. When the muscle contracts the other bone is forced to move. The site of attachment to the moving bone is called the insertion. You will not be asked to memorize ...
... muscle contracts, one bone remains relatively stationary. The site of attachment of the muscle to the stationary bone is called the origin. When the muscle contracts the other bone is forced to move. The site of attachment to the moving bone is called the insertion. You will not be asked to memorize ...
Dissection of Intercostal Spaces
... abdominal wall. It may be divides into three portions, which are more or less separate from one another: (1) the subcostalis, (2) the intercostalis intimus, and (3) the sternocostalis. ...
... abdominal wall. It may be divides into three portions, which are more or less separate from one another: (1) the subcostalis, (2) the intercostalis intimus, and (3) the sternocostalis. ...
Flexor
... Remember that these superficial veins are somewhat conspicuous in the living individual and are frequently the sites for drawing blood and injecting medications. BUT, in the cadaver, the superficial veins are empty and generally cannot be seen through the skin. It is my opinion that you are most lik ...
... Remember that these superficial veins are somewhat conspicuous in the living individual and are frequently the sites for drawing blood and injecting medications. BUT, in the cadaver, the superficial veins are empty and generally cannot be seen through the skin. It is my opinion that you are most lik ...
bilateral pectoralis minor muscle variant
... Assistant Professor, College of Chiropractic, University of Bridgeport, Bridgeport, CT 06604. ABSTRACT During a routine anatomical dissection we discovered an aberrant muscle slip associated with the pectoralis minor muscle that occurred bilaterally. The muscle slips originated from ribs five or six ...
... Assistant Professor, College of Chiropractic, University of Bridgeport, Bridgeport, CT 06604. ABSTRACT During a routine anatomical dissection we discovered an aberrant muscle slip associated with the pectoralis minor muscle that occurred bilaterally. The muscle slips originated from ribs five or six ...
Multiple accessory structures in the upper limb of
... coracobrachialis muscle crossed the neurovascular bundle of the anterior compartment of the arm and continued with the medial head of triceps to be inserted to the olecranon process of ulna. There are only two reports in the literature similar to our finding,(3,35) but they have not given any specif ...
... coracobrachialis muscle crossed the neurovascular bundle of the anterior compartment of the arm and continued with the medial head of triceps to be inserted to the olecranon process of ulna. There are only two reports in the literature similar to our finding,(3,35) but they have not given any specif ...
PECTORALIS MAJOR FLAP
... of skin paddle depends on reconstructive requirements. In most cases, the skin paddle is located at the infero-medial border of the PM between the nipple and the edge of the sternum. In women, the skin paddle can be designed below the breast in the inframammary fold. The larger the skin paddle harve ...
... of skin paddle depends on reconstructive requirements. In most cases, the skin paddle is located at the infero-medial border of the PM between the nipple and the edge of the sternum. In women, the skin paddle can be designed below the breast in the inframammary fold. The larger the skin paddle harve ...
the neurovascular compression due to the third head of biceps
... icant differences between the populations [4,10,12-14]. No significant differences in the prevalence of variations has been reported between male and female or between left and right sides, but the variation was high unilaterally [6]. Classification of the accessory heads is according to their locat ...
... icant differences between the populations [4,10,12-14]. No significant differences in the prevalence of variations has been reported between male and female or between left and right sides, but the variation was high unilaterally [6]. Classification of the accessory heads is according to their locat ...
Smooth muscle tissue

Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two subgroups; the single-unit (unitary) and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit cells, the whole bundle or sheet contracts as a syncytium (i.e. a multinucleate mass of cytoplasm that is not separated into cells). Multiunit smooth muscle tissues innervate individual cells; as such, they allow for fine control and gradual responses, much like motor unit recruitment in skeletal muscle.Smooth muscle is found within the walls of blood vessels (such smooth muscle specifically being termed vascular smooth muscle) such as in the tunica media layer of large (aorta) and small arteries, arterioles and veins. Smooth muscle is also found in lymphatic vessels, the urinary bladder, uterus (termed uterine smooth muscle), male and female reproductive tracts, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, arrector pili of skin, the ciliary muscle, and iris of the eye. The structure and function is basically the same in smooth muscle cells in different organs, but the inducing stimuli differ substantially, in order to perform individual effects in the body at individual times. In addition, the glomeruli of the kidneys contain smooth muscle-like cells called mesangial cells.