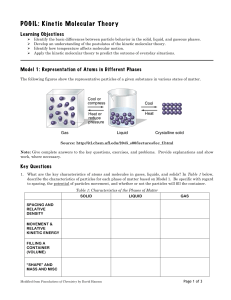
POGIL: Kinetic Molecular Theory
... Gases consist of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). These particles are so small compared with the distance between them that the volume (size) of the individual particles can be assumed to be negligible (zero). The particles are in constant random motion, colliding with the walls of the container ...
... Gases consist of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). These particles are so small compared with the distance between them that the volume (size) of the individual particles can be assumed to be negligible (zero). The particles are in constant random motion, colliding with the walls of the container ...
Temperature
... mol. Since we can’t count molecules, we can convert measured mass (in kg) to the number of moles, n, using the molecular or formula weight of the gas. By definition, one mole of a substance contains approximately 6.022 x 1023 particles of the substance. You can understand why we use mass and moles! ...
... mol. Since we can’t count molecules, we can convert measured mass (in kg) to the number of moles, n, using the molecular or formula weight of the gas. By definition, one mole of a substance contains approximately 6.022 x 1023 particles of the substance. You can understand why we use mass and moles! ...
Document
... 13.11.2014 => Calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 20.11.2014 => Standard free energy, equilibrium constant, calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 27 ...
... 13.11.2014 => Calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 20.11.2014 => Standard free energy, equilibrium constant, calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 27 ...
1st law of Thermodynamics Worksheet
... In the figure above, two cylinders are filled with the same ideal gas. A piston is fit so that no gas escapes; friction is negligible between the piston and the cylinder walls. The block is removed from each piston, the piston moves upward. 10. In each case, does the gas do work or is work done on t ...
... In the figure above, two cylinders are filled with the same ideal gas. A piston is fit so that no gas escapes; friction is negligible between the piston and the cylinder walls. The block is removed from each piston, the piston moves upward. 10. In each case, does the gas do work or is work done on t ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... Irreversible process is one in which thermal system’s changes cannot be retraced, such as gas expanding to fill a vacuum through an open stopcock. A thermodynamic system can transfer its internal energy by changing the temperature (or phase) of another system of it can use its internal energy to do ...
... Irreversible process is one in which thermal system’s changes cannot be retraced, such as gas expanding to fill a vacuum through an open stopcock. A thermodynamic system can transfer its internal energy by changing the temperature (or phase) of another system of it can use its internal energy to do ...
midterm 2 exam for section 3 from 2015
... (i) Hof is zero because nanotubes are just another elemental form of carbon. (ii) Hof is zero because changing the subscripts of an elemental formula does not change the standard heat of formation. (iii) Hof is not zero because carbon nanotubes are not the most stable form of the element under st ...
... (i) Hof is zero because nanotubes are just another elemental form of carbon. (ii) Hof is zero because changing the subscripts of an elemental formula does not change the standard heat of formation. (iii) Hof is not zero because carbon nanotubes are not the most stable form of the element under st ...
Author template for journal articles
... a thin wire of length l and cross sectional area A (Figure A1). As an ideal case, we consider that no heat transfer from the surface of the wire to the ambient occurs and the temperature at both ends of the wire is constant at T0. In this case, the temperature takes its maximum value at the middle o ...
... a thin wire of length l and cross sectional area A (Figure A1). As an ideal case, we consider that no heat transfer from the surface of the wire to the ambient occurs and the temperature at both ends of the wire is constant at T0. In this case, the temperature takes its maximum value at the middle o ...