A twisted periscope arrangement for transporting elliptically
... many components cannot be placed close to high magnetic fields and the difficulty of arranging optics within cold environments of cryostats. In principle one can solve the problem of transporting an elliptically polarized light by using highreflectivity dielectric-multilayer based distributed Bragg ...
... many components cannot be placed close to high magnetic fields and the difficulty of arranging optics within cold environments of cryostats. In principle one can solve the problem of transporting an elliptically polarized light by using highreflectivity dielectric-multilayer based distributed Bragg ...
4 Lab 1: Scattering and Reflection of Polarized Light
... In contrast, in a smooth piece of a transparent solid (the characteristic dimension of which, L, is much larger than the wavelength of light λ, i.e., L >> λ) where the atoms are very close to each other (i.e., λ >> interatomic spacing) and are arranged in an orderly pattern, the superposition of sca ...
... In contrast, in a smooth piece of a transparent solid (the characteristic dimension of which, L, is much larger than the wavelength of light λ, i.e., L >> λ) where the atoms are very close to each other (i.e., λ >> interatomic spacing) and are arranged in an orderly pattern, the superposition of sca ...
6th grade reflection lab final
... called the angle of incidence. The angle of light that bounces off the mirror is called the angle of reflection. The Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. ...
... called the angle of incidence. The angle of light that bounces off the mirror is called the angle of reflection. The Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. ...
6.0 Mb - Todd Satogata
... § Your brain thinks the light is going straight when it’s really reflecting, so you “see” an image of an object as though the light traveled in a straight line the entire time. § Two mirrors at a 90 degree angle always reflect light back out parallel to the original incoming rays • You can do s ...
... § Your brain thinks the light is going straight when it’s really reflecting, so you “see” an image of an object as though the light traveled in a straight line the entire time. § Two mirrors at a 90 degree angle always reflect light back out parallel to the original incoming rays • You can do s ...
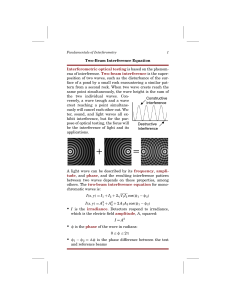
Two-Beam Interference Equation Interferometric optical testing is
... Plate beamsplitters are similar to cube beamsplitters in that they divide the amplitude of the incident light and can be made to split the light by polarization or by any desired ratio. One surface is usually AR coated, while the other has the coating to split the beam. Plate beamsplitters can be us ...
... Plate beamsplitters are similar to cube beamsplitters in that they divide the amplitude of the incident light and can be made to split the light by polarization or by any desired ratio. One surface is usually AR coated, while the other has the coating to split the beam. Plate beamsplitters can be us ...
Black Coatings to Reduce Stray Light
... view, not only does it block a portion of light which is fairly insignificant, but also scatters light towards a direction not intended by the imaging system. If many particles are there doing the same thing it will add up to be a significant problem. A similar thing will happen when an accumulation ...
... view, not only does it block a portion of light which is fairly insignificant, but also scatters light towards a direction not intended by the imaging system. If many particles are there doing the same thing it will add up to be a significant problem. A similar thing will happen when an accumulation ...
1. Wave Nature of Light
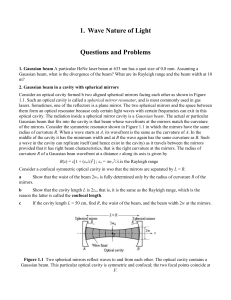
... 1. Gaussian beam A particular HeNe laser beam at 633 nm has a spot size of 0.8 mm. Assuming a Gaussian beam, what is the divergence of the beam? What are its Rayleigh range and the beam width at 10 m? 2. Gaussian beam in a cavity with spherical mirrors Consider an optical cavity formed b two aligned ...
... 1. Gaussian beam A particular HeNe laser beam at 633 nm has a spot size of 0.8 mm. Assuming a Gaussian beam, what is the divergence of the beam? What are its Rayleigh range and the beam width at 10 m? 2. Gaussian beam in a cavity with spherical mirrors Consider an optical cavity formed b two aligned ...
National 5 Waves and Radiation Summary Notes
... b) Which of the two radiations, P or Q, has the greater energy? Explain your answer. P has the greater energy because it is nearer the gamma end of the spectrum and this is the end with the highest frequency. When a radiation has a high frequency it will correspond to a high energy value. c) Name a ...
... b) Which of the two radiations, P or Q, has the greater energy? Explain your answer. P has the greater energy because it is nearer the gamma end of the spectrum and this is the end with the highest frequency. When a radiation has a high frequency it will correspond to a high energy value. c) Name a ...
20170327_AH_Interference
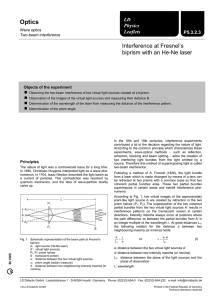
... Interference and coherence Interference comes from coherent sources having an optical path difference. Two waves are said to be coherent if they have a constant phase relationship. For two waves travelling in air to have a constant phase relationship, they must have the same frequency and wavelengt ...
... Interference and coherence Interference comes from coherent sources having an optical path difference. Two waves are said to be coherent if they have a constant phase relationship. For two waves travelling in air to have a constant phase relationship, they must have the same frequency and wavelengt ...
A Very Brief History of Light
... dynamics, optics and alchemy. Bacon also speculates within the folds of his tome about the possibility of heavier than air flying machines, as well as the construction of new optical devices, the telescope and microscope as we would call them, to improve upon human vision. Indeed, Bacon writes that ...
... dynamics, optics and alchemy. Bacon also speculates within the folds of his tome about the possibility of heavier than air flying machines, as well as the construction of new optical devices, the telescope and microscope as we would call them, to improve upon human vision. Indeed, Bacon writes that ...
Full Paper
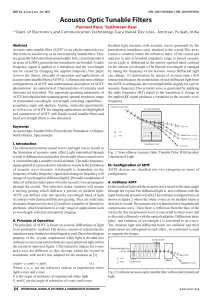
... The interaction between sound waves and light waves results in the formation of acousto- optic effect.Light transmitted through crystal is diffracted at a particular wavelength when a sound wave is excited through a suitable crystal medium. The radio frequency signal applied to a piezoelectric trans ...
... The interaction between sound waves and light waves results in the formation of acousto- optic effect.Light transmitted through crystal is diffracted at a particular wavelength when a sound wave is excited through a suitable crystal medium. The radio frequency signal applied to a piezoelectric trans ...
full Lab Facts summary
... • The optic is generally either a solid prism or hollow with coated mirror surfaces. • The common corner cube design is pyramid shaped with light entering the base. • The three faces that make the corner are orthogonal (90 degrees to each other). • There are always 3 internal reflections before the ...
... • The optic is generally either a solid prism or hollow with coated mirror surfaces. • The common corner cube design is pyramid shaped with light entering the base. • The three faces that make the corner are orthogonal (90 degrees to each other). • There are always 3 internal reflections before the ...
CV Raman Life and Work
... 1923- Theory of viscosity 1293- Scattering of Sun light by water (not because of weak fluorescence) At a very early stage in our investigations, we came across a new and entirely unexpected phenomenon. As early as 1923, it was noticed that when sunlight filtered through a violet glass passes through ...
... 1923- Theory of viscosity 1293- Scattering of Sun light by water (not because of weak fluorescence) At a very early stage in our investigations, we came across a new and entirely unexpected phenomenon. As early as 1923, it was noticed that when sunlight filtered through a violet glass passes through ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 39 – Review
... (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmitted light the same if the paths of all light rays ...
... (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmitted light the same if the paths of all light rays ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.