Downloaded
... the colored DAE film generated higher carrier/photon efficiency than did the long-wavelength light corresponding to the low-energy absorption band. © 2004 American Institute of Physics. [DOI: 10.1063/1.1806270] Photochromism is defined as a reversible transformation by photoirradiation between two i ...
... the colored DAE film generated higher carrier/photon efficiency than did the long-wavelength light corresponding to the low-energy absorption band. © 2004 American Institute of Physics. [DOI: 10.1063/1.1806270] Photochromism is defined as a reversible transformation by photoirradiation between two i ...
How does a confocal microscope work
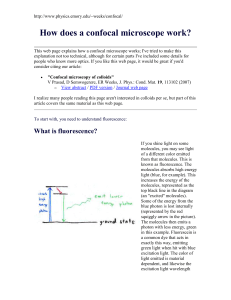
... Imagine we have some lenses inside the microscope, that focus light from the focal point of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the le ...
... Imagine we have some lenses inside the microscope, that focus light from the focal point of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the le ...
Relativity
... transformation. He took advantage of this transformation. From the "ether" line changed to any other frame of reference, as long as the speed is less than c, electron theory equations of motion were held constant, the speed of light in all inertial frames are the same. Thus explaining the zero resul ...
... transformation. He took advantage of this transformation. From the "ether" line changed to any other frame of reference, as long as the speed is less than c, electron theory equations of motion were held constant, the speed of light in all inertial frames are the same. Thus explaining the zero resul ...
Verification on Malus`s Law
... using very low cost and easily available material: polarized sunglasses, PVC tubes, light-dependent resistors, LED, etc. With this set, the experiment of the Malus’s Law verification of light polarization can be done without the need of expensive optical detector for quantitative measurement. Studen ...
... using very low cost and easily available material: polarized sunglasses, PVC tubes, light-dependent resistors, LED, etc. With this set, the experiment of the Malus’s Law verification of light polarization can be done without the need of expensive optical detector for quantitative measurement. Studen ...
Light Measurement Handbook
... at every wavelength. Another approach is to use a narrow band filter to measure only within a small wavelength band. This is acceptable if the lamp has been fully characterized and the color temperature is carefully monitored. The difficulty with narrow band measurements, however, is that they only ...
... at every wavelength. Another approach is to use a narrow band filter to measure only within a small wavelength band. This is acceptable if the lamp has been fully characterized and the color temperature is carefully monitored. The difficulty with narrow band measurements, however, is that they only ...
Speed of light and Maxwell`s constant (Relative Relativity)
... size. In fact, it is a speed of moving of photons as quanta of electromagnetic radiation. The size of this fundamental physical constants is determined - on the one hand - on the basis of values obtained by measuring , and on the other hand - on the basis of electro magnetic theory by J. C. Maxwell ...
... size. In fact, it is a speed of moving of photons as quanta of electromagnetic radiation. The size of this fundamental physical constants is determined - on the one hand - on the basis of values obtained by measuring , and on the other hand - on the basis of electro magnetic theory by J. C. Maxwell ...
Projekt z Obrazového inženýrství
... assuming no outside influences, travels in the straight line indicated by the blue arrow. The light energy does not "wiggle" back and forth as it moves along its path. As an electromagnetic wave, light has some characteristics in common with all forms of electromagnetic energy. These include wavelen ...
... assuming no outside influences, travels in the straight line indicated by the blue arrow. The light energy does not "wiggle" back and forth as it moves along its path. As an electromagnetic wave, light has some characteristics in common with all forms of electromagnetic energy. These include wavelen ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.