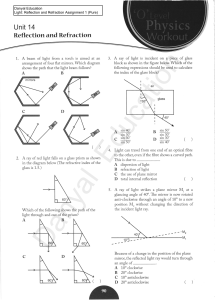
Light Reflects (Part 1) Lesson 7
... health and safety. The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 9 and 10: Science, 2009 ...
... health and safety. The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 9 and 10: Science, 2009 ...
Observation of the rotational Doppler shift of a white
... and the illuminating field has an OAM of lℏ per photon. We reported recently that this rotational Doppler effect is manifest in monochromatic laser light backscattered from a spinning object, even in cases where the linear velocity between the source and observer is zero [9]. The effect has also bee ...
... and the illuminating field has an OAM of lℏ per photon. We reported recently that this rotational Doppler effect is manifest in monochromatic laser light backscattered from a spinning object, even in cases where the linear velocity between the source and observer is zero [9]. The effect has also bee ...
Chapter 8
... a = kz-t, the resultant wave is right-circularly polarized (rotate clockwise). 2) When E0x=E0y=E0, = p /2 , E( z, t ) E0 [iˆ cos(kz t ) ˆj sin( kz t )] a = -kz +t, the resultant wave is left-circularly polarized (rotate counterclockwise). Circular light: i)The amplitude E0 does not cha ...
... a = kz-t, the resultant wave is right-circularly polarized (rotate clockwise). 2) When E0x=E0y=E0, = p /2 , E( z, t ) E0 [iˆ cos(kz t ) ˆj sin( kz t )] a = -kz +t, the resultant wave is left-circularly polarized (rotate counterclockwise). Circular light: i)The amplitude E0 does not cha ...
L2 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
... two different materials. Briefly, several things can happen there: some of the light may be reflected back into the material where it came from while some of it may continue to travel through the second medium. You can see an example of this partial reflection when you look obliquely at a window. Yo ...
... two different materials. Briefly, several things can happen there: some of the light may be reflected back into the material where it came from while some of it may continue to travel through the second medium. You can see an example of this partial reflection when you look obliquely at a window. Yo ...
Derivation of longitudinal Doppler shift equation
... single photons using de Broglie-Bohm picture: that is, the Michelson-Morley experiment showed an interference condition and did not show the simultaneous arrival of two photons (this is because there is only single photon). The Michelson-Morley experiment shows the wave property of photons: the wave ...
... single photons using de Broglie-Bohm picture: that is, the Michelson-Morley experiment showed an interference condition and did not show the simultaneous arrival of two photons (this is because there is only single photon). The Michelson-Morley experiment shows the wave property of photons: the wave ...
Contactless visible light probing for nanoscale ICs through 10 μm
... bulk silicon. Resolution is then limited to identify nodes of 120 nm technologies, 90 nm or even 60 nm only with uncertainty. As a result, solid immersion lenses (SIL) have been introduced increasing the NIR resolution by the index of refraction, 3.5 for a silicon SIL. This extends the application o ...
... bulk silicon. Resolution is then limited to identify nodes of 120 nm technologies, 90 nm or even 60 nm only with uncertainty. As a result, solid immersion lenses (SIL) have been introduced increasing the NIR resolution by the index of refraction, 3.5 for a silicon SIL. This extends the application o ...
Polarization - OpenStax CNX
... Photographs of the sky can be darkened by polarizing lters, a trick used by many photographers to make clouds brighter by contrast. Scattering from other particles, such as smoke or dust, can also polarize light. Detecting polarization in scattered EM waves can be a useful analytical tool in determ ...
... Photographs of the sky can be darkened by polarizing lters, a trick used by many photographers to make clouds brighter by contrast. Scattering from other particles, such as smoke or dust, can also polarize light. Detecting polarization in scattered EM waves can be a useful analytical tool in determ ...
Baffle Design and Analysis of Stray-light in Multispectral Camera of
... system. The vane 2 is defined to the intersection of line AB with the line determining the FOV limit. The line DC shows the path of scattered light from the aperture of the first vane to the wall. The vane 3 is determined to the intersection of line AC with the FOV. Same procedure are accomplished f ...
... system. The vane 2 is defined to the intersection of line AB with the line determining the FOV limit. The line DC shows the path of scattered light from the aperture of the first vane to the wall. The vane 3 is determined to the intersection of line AC with the FOV. Same procedure are accomplished f ...
Applications(2)
... deep ultraviolet, but geometric factors bring it close to the visible. • In doped semiconductors, the plasma frequency is usually in the infrared. • The plasmon energy for most metals corresponds to that of an ultraviolet photon. However, as mentioned above for some metals like silver, gold, the alk ...
... deep ultraviolet, but geometric factors bring it close to the visible. • In doped semiconductors, the plasma frequency is usually in the infrared. • The plasmon energy for most metals corresponds to that of an ultraviolet photon. However, as mentioned above for some metals like silver, gold, the alk ...
Assignment 1A
... in the diagram. A person looks into the container so that his line of sight includes point P above the coin, and he cannot see the coin. When water is slowly poured into the container, the person suddenly sees the coin when the water reaches a certain level. What is the reason for ...
... in the diagram. A person looks into the container so that his line of sight includes point P above the coin, and he cannot see the coin. When water is slowly poured into the container, the person suddenly sees the coin when the water reaches a certain level. What is the reason for ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.