AICE Environmental Management GIZMOS Class Code
... Both P and S waves are known as body waves because they travel through solid rock below Earth’s surface. When these waves reach the surface, their effects combine in surface waves, which shake the ground back and forth, up and down, and side to side. Surface waves account for the largest wiggles on ...
... Both P and S waves are known as body waves because they travel through solid rock below Earth’s surface. When these waves reach the surface, their effects combine in surface waves, which shake the ground back and forth, up and down, and side to side. Surface waves account for the largest wiggles on ...
Seismic hazard for some regions of the world examined using strain
... of the world (some regions of Eurasian belt, as well as Japan and California). The representative parameters applied for this evaluation are related to the physical release process of the strain energy. These parameters are the magnitude, M2, which is equivalent to the mean annual total strain energ ...
... of the world (some regions of Eurasian belt, as well as Japan and California). The representative parameters applied for this evaluation are related to the physical release process of the strain energy. These parameters are the magnitude, M2, which is equivalent to the mean annual total strain energ ...
Full Scale Dynamic Behaviour of a RC-building under low to
... understanding the behaviour of complex structures and fixing their elastic properties by means of their modal parameters (frequency, damping and modal shape). These are the main parameters controlling building response and vulnerability since two structures with the same mass distribution and the sa ...
... understanding the behaviour of complex structures and fixing their elastic properties by means of their modal parameters (frequency, damping and modal shape). These are the main parameters controlling building response and vulnerability since two structures with the same mass distribution and the sa ...
Electromagnetic Disturbances Associated With Earthquakes: An
... different experiments at different altitudes, from ground level up to the geostationary orbit. For approximately 30 years, a French geophysical station has been operational in the Kerguelen Islands (49"26'S, 70°25'E), and in April 1980 three earthquakes occurred very close by. Their magnitude was mo ...
... different experiments at different altitudes, from ground level up to the geostationary orbit. For approximately 30 years, a French geophysical station has been operational in the Kerguelen Islands (49"26'S, 70°25'E), and in April 1980 three earthquakes occurred very close by. Their magnitude was mo ...
Earthquakes
... The modern Himalayan Mountains are an extensive mountain belt that formed when the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Mountain building continues as India is driven northeastward with respect to Eurasia due to spreading along the oceanic ridge to the west of India. ...
... The modern Himalayan Mountains are an extensive mountain belt that formed when the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Mountain building continues as India is driven northeastward with respect to Eurasia due to spreading along the oceanic ridge to the west of India. ...
1 GEOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS ON ACTIVE
... mechanisms and seismic hazard within continental interiors (Johnston & Kanter, 1990). Although accounting for less than one percent of the Earth’s total seismic energy release, SCR seismicity presents substantial risk because earthquake rupture is general shallow and seismic attenuation is low. The ...
... mechanisms and seismic hazard within continental interiors (Johnston & Kanter, 1990). Although accounting for less than one percent of the Earth’s total seismic energy release, SCR seismicity presents substantial risk because earthquake rupture is general shallow and seismic attenuation is low. The ...
BAM EARTHQUAKE, IRAN: LESSONS ON THE SEISMIC
... In overall terms the damage observed in the city of Bam varied depending upon location and building construction. The damage was very severe in the old part of the city in the Northeast and around Bam Citadel where the construction was dominated by adobe type building structures. Severe damage was a ...
... In overall terms the damage observed in the city of Bam varied depending upon location and building construction. The damage was very severe in the old part of the city in the Northeast and around Bam Citadel where the construction was dominated by adobe type building structures. Severe damage was a ...
Souces and scenarios for tsunami hazard assessment in the
... Discretization of a given “tsunamigenic domain” with sources distributed on a regular grid of cells, independently on the tsunami history. Tsunami scenarios are computed for each grid cell and for different EQ magnitudes starting from “standard” tsunami initial conditions (practice by Global Disaste ...
... Discretization of a given “tsunamigenic domain” with sources distributed on a regular grid of cells, independently on the tsunami history. Tsunami scenarios are computed for each grid cell and for different EQ magnitudes starting from “standard” tsunami initial conditions (practice by Global Disaste ...
Lessons learned from the Tohoku earthquake / tsunami and
... A national history book depicts strong shakings, large tsunami inundation and the associated damage including 1,000 drowned people. In addition, sand brought by this tsunami, called tsunami deposits, had been found in geological layers in coastal lowland, more than 5 km from the current coast in the ...
... A national history book depicts strong shakings, large tsunami inundation and the associated damage including 1,000 drowned people. In addition, sand brought by this tsunami, called tsunami deposits, had been found in geological layers in coastal lowland, more than 5 km from the current coast in the ...
Initiation of plate boundary slip in the Nankai Trough off the Muroto
... the SOM classification boundary described above (Figure 4a). Site 808 is located 1.7 km landward of the proto-thrust and on the landward side of the SOM classification boundary. At Site 1174, the porosity of the décollement measured from core samples changes little across the décollement by compar ...
... the SOM classification boundary described above (Figure 4a). Site 808 is located 1.7 km landward of the proto-thrust and on the landward side of the SOM classification boundary. At Site 1174, the porosity of the décollement measured from core samples changes little across the décollement by compar ...
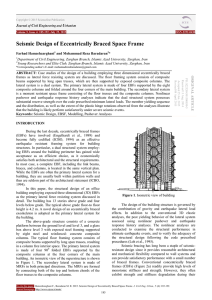
Seismic Design of Eccentrically Braced Space Frame J C
... frames at the building perimeter is shown in Figure 4. Each EBF is folded into a 900 angle at the corner of the link beams to fit into the four corners of the building. Therefore, a series of link beams are created at the building corners with one half of the link beam length shown at each face of t ...
... frames at the building perimeter is shown in Figure 4. Each EBF is folded into a 900 angle at the corner of the link beams to fit into the four corners of the building. Therefore, a series of link beams are created at the building corners with one half of the link beam length shown at each face of t ...
Abstract_Midcontinen..
... look at the role of faults in the release of stress accumulated by the relative motion of tectonic plates. The stage will then be set for contrasting these conventional interplate earthquakes with those that occur within the stable continent, where tectonic loading is instead accommodated by a compl ...
... look at the role of faults in the release of stress accumulated by the relative motion of tectonic plates. The stage will then be set for contrasting these conventional interplate earthquakes with those that occur within the stable continent, where tectonic loading is instead accommodated by a compl ...
types of sesmic waves 4.96MB 2017-03-29 12
... S waves • S waves (secondary waves) are transverse which means that the ground is displaced perpendicularly (sideways) to the direction of movement. • The ground moves alternately to one side and then the other. (or up or down… depending on the direction of the wave.) • S waves can travel only thro ...
... S waves • S waves (secondary waves) are transverse which means that the ground is displaced perpendicularly (sideways) to the direction of movement. • The ground moves alternately to one side and then the other. (or up or down… depending on the direction of the wave.) • S waves can travel only thro ...
Earthquakes
... Types of Seismic Waves cont. P- waves- primary waves. First to arrive. Compress and expand the ground like an accordion. S- waves- Secondary waves vibrate side to side and up and down. S waves cannot travel through a liquid. These are the waves that shake structures. Surface waves- when S and P wav ...
... Types of Seismic Waves cont. P- waves- primary waves. First to arrive. Compress and expand the ground like an accordion. S- waves- Secondary waves vibrate side to side and up and down. S waves cannot travel through a liquid. These are the waves that shake structures. Surface waves- when S and P wav ...
A first-order second-moment calculation for seismic hazard
... On the other hand, a recently implemented technical guideline prescribes the use of PSHA for designing critical structures under earthquake conditions (US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 2007). Nevertheless, it is worth noting that the two analyses are associated with a specific algorithm, rather tha ...
... On the other hand, a recently implemented technical guideline prescribes the use of PSHA for designing critical structures under earthquake conditions (US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 2007). Nevertheless, it is worth noting that the two analyses are associated with a specific algorithm, rather tha ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... In this paper, we use this knowledge in the analysis of aftershocks after the SumatraAndaman earthquake on 26.12.2004, M = 9 (e.g., see [Lay et al., 2005; Park et al., 2005; Zavyalov, 2005]). We paid attention to the two interesting manifestations of the induced seismicity. First is the large afters ...
... In this paper, we use this knowledge in the analysis of aftershocks after the SumatraAndaman earthquake on 26.12.2004, M = 9 (e.g., see [Lay et al., 2005; Park et al., 2005; Zavyalov, 2005]). We paid attention to the two interesting manifestations of the induced seismicity. First is the large afters ...
The Nature and Cause of Earthquakes
... motion): ground movement or motion of the earth that causes structures to react, i.e., that induces motion in the structure that can lead to failure. ...
... motion): ground movement or motion of the earth that causes structures to react, i.e., that induces motion in the structure that can lead to failure. ...
Document
... seismic design methodologies for RWFD buildings may be possible to simplify the design process and provide a more rational design approach. Typical RWFD Structure Description Structures containing rigid walls with flexible diaphragms are ubiquitous across our urban environment. Often labeled as “bi ...
... seismic design methodologies for RWFD buildings may be possible to simplify the design process and provide a more rational design approach. Typical RWFD Structure Description Structures containing rigid walls with flexible diaphragms are ubiquitous across our urban environment. Often labeled as “bi ...
measured and predicted seismic response of two similar buildings
... that the registered signals available to work with are very scarce. The first six modes of the isolated building are related to approximately rigid body motions of the building and high deformations on the isolators, because of the horizontal and vertical flexibility of the spring isolators. Therefo ...
... that the registered signals available to work with are very scarce. The first six modes of the isolated building are related to approximately rigid body motions of the building and high deformations on the isolators, because of the horizontal and vertical flexibility of the spring isolators. Therefo ...
Finding an Epicenter - Phoenix Central School District
... movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
... movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
Document
... of building collapse, should severe ground shaking occur. Final Scores typically range from 0 to 7, with higher scores corresponding to better expected seismic performance and a lower potential for collapse in a design earthquake. Note that Figs. 1 and 2 are drafts; revisions are anticipated. Buildi ...
... of building collapse, should severe ground shaking occur. Final Scores typically range from 0 to 7, with higher scores corresponding to better expected seismic performance and a lower potential for collapse in a design earthquake. Note that Figs. 1 and 2 are drafts; revisions are anticipated. Buildi ...
Auxiliary Material
... expressed on the basis of a summation of normal modes on a spherically layered Earth. The normal modes approach simultaneously solves for the conservation of linear momentum, where body and surface forces compensate each other, and for perturbations in the gravitational potential, due to mass redist ...
... expressed on the basis of a summation of normal modes on a spherically layered Earth. The normal modes approach simultaneously solves for the conservation of linear momentum, where body and surface forces compensate each other, and for perturbations in the gravitational potential, due to mass redist ...
Earthquake engineering

Earthquake engineering or Seismic engineering is a branch of engineering that searches for ways to make structures, such as buildings and bridges, resistant to earthquake damage. Earthquake engineer, better known as a seismic engineer aim to develop building techniques that will prevent any damage in a minor quake and avoid serious damage or collapse in a major shake. It is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of both structural and geotechnical engineering. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance. The main objectives of earthquake engineering are: Foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.