Unit 8: Electron Configuration
... certain amounts of energy as well. That is why we can only see certain colors at certain wavelengths. Things to know: • Electrons only give off energy when they return to a lower energy level. • Highest probablity of finding an electron is in the electron cloud where it is most dense. ...
... certain amounts of energy as well. That is why we can only see certain colors at certain wavelengths. Things to know: • Electrons only give off energy when they return to a lower energy level. • Highest probablity of finding an electron is in the electron cloud where it is most dense. ...
File
... 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are not ...
... 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are not ...
Which frequency of light has the most energy
... In what way do atomic spectra support the Bohr model of the atom? A. The spectra indicate that electrons have practically no mass. B. The spectra make it possible to calculate the charge on the electron. C. The spectra indicate that the nucleus is very small compared to the atom. D. The spectra cont ...
... In what way do atomic spectra support the Bohr model of the atom? A. The spectra indicate that electrons have practically no mass. B. The spectra make it possible to calculate the charge on the electron. C. The spectra indicate that the nucleus is very small compared to the atom. D. The spectra cont ...
Quantum and Atomic Physics
... 31. In Rutherford’s experiment, most of α – particles pass through the foil without deflection. Which of the following properties of the atom can be explained by this observation? (Select 2 answers) (A) An atom’s positive charge is concentrated in the nucleus (B) The nucleus is made up neutrons and ...
... 31. In Rutherford’s experiment, most of α – particles pass through the foil without deflection. Which of the following properties of the atom can be explained by this observation? (Select 2 answers) (A) An atom’s positive charge is concentrated in the nucleus (B) The nucleus is made up neutrons and ...
Zn + HCl → ZnCl 2 + H2 NaOH + H3PO4 → Na3PO4 + H2O N2 +
... 1) Write all the reactant and product formulas on the left and right side of the equation, respectively. Make sure you have all and that you have written the formulas correctly. Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equat ...
... 1) Write all the reactant and product formulas on the left and right side of the equation, respectively. Make sure you have all and that you have written the formulas correctly. Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equat ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – The Basics of
... 2. Atoms are the smallest unit of matter. Each different type of atom represents an element (ex: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon). Scientists have created a chart called the periodic table of elements to organize elements by their atomic properties. 3. Four elements—carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), an ...
... 2. Atoms are the smallest unit of matter. Each different type of atom represents an element (ex: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon). Scientists have created a chart called the periodic table of elements to organize elements by their atomic properties. 3. Four elements—carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), an ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms are called electron configurations There are three rules on how to find the electron configuration of an ...
... arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms are called electron configurations There are three rules on how to find the electron configuration of an ...
Solon City Schools
... the ionization energies of all electrons in the atom) is known as photoelectron spectroscopy; this method uses a photon (a packet of light energy) to knock an electron out of an atom. ...
... the ionization energies of all electrons in the atom) is known as photoelectron spectroscopy; this method uses a photon (a packet of light energy) to knock an electron out of an atom. ...
Chapter 2
... the ionization energies of all electrons in the atom) is known as photoelectron spectroscopy; this method uses a photon (a packet of light energy) to knock an electron out of an atom. ...
... the ionization energies of all electrons in the atom) is known as photoelectron spectroscopy; this method uses a photon (a packet of light energy) to knock an electron out of an atom. ...
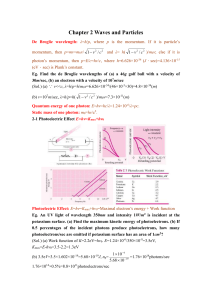
Chapter 2 Waves and Particles De Broglie wavelength: λ=h/p, where
... Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2 ...
... Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2 ...
document
... M. What is made during a reaction N. The chemicals that undergo a reaction. O. A reaction in which one element replaces another in a compound. ...
... M. What is made during a reaction N. The chemicals that undergo a reaction. O. A reaction in which one element replaces another in a compound. ...
Basic Chemistry
... Matter – anything made of mass and takes up volume Atom – basic unit of matter (so small that 100 million in a row only take up 1 centimeter of space), which has sub-atomic particles smaller than them. Nucleus – the center of an atom which has Protons (+ charge), and Neutrons (no charge) •Protons an ...
... Matter – anything made of mass and takes up volume Atom – basic unit of matter (so small that 100 million in a row only take up 1 centimeter of space), which has sub-atomic particles smaller than them. Nucleus – the center of an atom which has Protons (+ charge), and Neutrons (no charge) •Protons an ...
Article 2: Key Concepts and Vocabulary
... carrying one negative electric charge. In an electrically neutral atom, the positive charge of the nucleus is balanced by the negative charges of electrons. When there is not perfect balance, the atom is called an ion; an ion can be positively or negatively charged. At a very high temperature, such ...
... carrying one negative electric charge. In an electrically neutral atom, the positive charge of the nucleus is balanced by the negative charges of electrons. When there is not perfect balance, the atom is called an ion; an ion can be positively or negatively charged. At a very high temperature, such ...
Homework Problem Set 7 - Illinois State Chemistry
... b.) Using the analytic solution to Newton's equations for the harmonic oscillator, plot the bond displacement coordinate x as a function of time for this system. c.) Using the analytic solution to Newton's equations for the harmonic oscillator, plot the velocity as a function of time for this system ...
... b.) Using the analytic solution to Newton's equations for the harmonic oscillator, plot the bond displacement coordinate x as a function of time for this system. c.) Using the analytic solution to Newton's equations for the harmonic oscillator, plot the velocity as a function of time for this system ...
Chapter 5/6 Notes
... BIG SOLUTION: In 1913, Neils Bohr (Danish), stated that electrons could occupy fixed Chem Stud orbitals without giving off energy. ...
... BIG SOLUTION: In 1913, Neils Bohr (Danish), stated that electrons could occupy fixed Chem Stud orbitals without giving off energy. ...
Final Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... The left-hand end of a long horizontal stretched cord oscillates transversally in simple harmonic motion with frequency f = 0.10 kHz and amplitude 2 cm. The cord is under a tension of 40 N and has a linear density µ = 4 g/cm. At time t = 0, the end of the cord has an upward displacement of 2 cm and ...
... The left-hand end of a long horizontal stretched cord oscillates transversally in simple harmonic motion with frequency f = 0.10 kHz and amplitude 2 cm. The cord is under a tension of 40 N and has a linear density µ = 4 g/cm. At time t = 0, the end of the cord has an upward displacement of 2 cm and ...
Final
... Be able to determine the oxidation state of elements in a compound Be able to identify the element that is oxidized and the element that is reduced Be able to identify the oxidizing reactant and the reducing reactant. Redox Reactions - Activity series Determine the order of reactivity for a set of e ...
... Be able to determine the oxidation state of elements in a compound Be able to identify the element that is oxidized and the element that is reduced Be able to identify the oxidizing reactant and the reducing reactant. Redox Reactions - Activity series Determine the order of reactivity for a set of e ...
The stability of an atom depends on the ratio and number of protons
... Radioactive decay results in the emission of gamma rays and/or subatomic particles such as alpha or beta particles, as shown in . These emissions constituteionizing radiation. Radionuclides occur naturally but can also be produced artificially. ...
... Radioactive decay results in the emission of gamma rays and/or subatomic particles such as alpha or beta particles, as shown in . These emissions constituteionizing radiation. Radionuclides occur naturally but can also be produced artificially. ...
Name
... likely it is to find an electron in various locations around the atom. The quantum mechanical model is based on mathematics, not on experimental evidence. This model does not specify an exact path an electron takes around the nucleus, but gives the probability of finding an electron within a certain ...
... likely it is to find an electron in various locations around the atom. The quantum mechanical model is based on mathematics, not on experimental evidence. This model does not specify an exact path an electron takes around the nucleus, but gives the probability of finding an electron within a certain ...
Unit 2 Review Questions Fill in the blank In a(n) change, a new
... The mass number is the sum of electrons and protons in the atom. l. A Bohr diagram shows electrons in orbits about the nucleus. m. A row of the periodic table is called a period. n. The size of atoms increase down a column of the periodic table. o. Alkali metals include fluorine, chlorine, and iodin ...
... The mass number is the sum of electrons and protons in the atom. l. A Bohr diagram shows electrons in orbits about the nucleus. m. A row of the periodic table is called a period. n. The size of atoms increase down a column of the periodic table. o. Alkali metals include fluorine, chlorine, and iodin ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.