The Nervous System (ppt).
... failure of the cerebrum to develop Child cannot hear, see, or process sensory inputs ...
... failure of the cerebrum to develop Child cannot hear, see, or process sensory inputs ...
sensory, motor, and integrative systems
... Name the cutaneous sensations? Cutaneous sensations include tactile (touch, pressure, vibration), thermal (hot, cold) and pain. Where are these receptors located? The receptors for these sensations are located in the skin, connective tissues under the skin, mucous membranes, mouth, and anus. These r ...
... Name the cutaneous sensations? Cutaneous sensations include tactile (touch, pressure, vibration), thermal (hot, cold) and pain. Where are these receptors located? The receptors for these sensations are located in the skin, connective tissues under the skin, mucous membranes, mouth, and anus. These r ...
(一)Functional Anatomy of the Retina
... This occurs when we move from the dark into bright light. The bright light momentarily dazzles us and all we see is white light because the sensitivity of the receptors is set to dim light. Rods and cones are both stimulated and large amounts of the photopigment are broken down instantaneously, prod ...
... This occurs when we move from the dark into bright light. The bright light momentarily dazzles us and all we see is white light because the sensitivity of the receptors is set to dim light. Rods and cones are both stimulated and large amounts of the photopigment are broken down instantaneously, prod ...
Document
... Perception is the awareness and conscious interpretation of sensations. It is how the brain makes sense of or assigns meaning to the sensation. We not aware of X-rays, ultra high frequency sound waves, UV light - We have no sensory receptors for those stimuli Integration of sensory and motor functio ...
... Perception is the awareness and conscious interpretation of sensations. It is how the brain makes sense of or assigns meaning to the sensation. We not aware of X-rays, ultra high frequency sound waves, UV light - We have no sensory receptors for those stimuli Integration of sensory and motor functio ...
MOTOR NEURON DISEASE
... Autonomic dysfunction Absence of fever at onset Laboratory features supportive of diagnosis Elevated cerebrospinal fluid protein with normal cells count Elcctrodiagnostic features of nerve conduction slowing or block ...
... Autonomic dysfunction Absence of fever at onset Laboratory features supportive of diagnosis Elevated cerebrospinal fluid protein with normal cells count Elcctrodiagnostic features of nerve conduction slowing or block ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
Spinal nerves 1
... Drawing of Purkyně cells (A) and granule cells (B) from pigeon cerebellum by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1899) ...
... Drawing of Purkyně cells (A) and granule cells (B) from pigeon cerebellum by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1899) ...
The Nervous System Worksheet
... They are fast, automatic, protective, biological control ……………… systems that link a stimulus to a response. b) Reflexes help animals survive. Name one reflex action that helps in survival. ...
... They are fast, automatic, protective, biological control ……………… systems that link a stimulus to a response. b) Reflexes help animals survive. Name one reflex action that helps in survival. ...
BRAIN
... • Functional: – Sensory (afferent) — transmit impulses toward the CNS – Motor (efferent) — carry impulses away from the CNS – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways; Responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an efferent response to include hi ...
... • Functional: – Sensory (afferent) — transmit impulses toward the CNS – Motor (efferent) — carry impulses away from the CNS – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways; Responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an efferent response to include hi ...
How do we manage to remember smells despite the fact
... they share a common feature. The brain (specifically, the olfactory bulb and olfactory cortex) then looks at the combination of sensory neurons activated at any given time and interprets that pattern in the context of previous patterns that have been experienced and other kinds of available informat ...
... they share a common feature. The brain (specifically, the olfactory bulb and olfactory cortex) then looks at the combination of sensory neurons activated at any given time and interprets that pattern in the context of previous patterns that have been experienced and other kinds of available informat ...
Danczi Csaba László - 2nd WORLD CONGRESS OF ARTS
... stimulus moving continuously across the cutaneous surface (2). The presence of extensive connections between superficial and deep regions of the colliculus in the cat supports the idea that receptive field organization in the deep layers is modulated by visual input from the overlying layers. Thus, ...
... stimulus moving continuously across the cutaneous surface (2). The presence of extensive connections between superficial and deep regions of the colliculus in the cat supports the idea that receptive field organization in the deep layers is modulated by visual input from the overlying layers. Thus, ...
Neuro_quiz3
... 87. What is the difference between touch sensation & pressure sensation? 88. Rapidly repetitive sensory signals result in ________ sense. 89. Free nerve endings can detect primitive AKA ________ touch. Their speed of conduction is ________ metres/second. They are small/large and of what type(s)? ___ ...
... 87. What is the difference between touch sensation & pressure sensation? 88. Rapidly repetitive sensory signals result in ________ sense. 89. Free nerve endings can detect primitive AKA ________ touch. Their speed of conduction is ________ metres/second. They are small/large and of what type(s)? ___ ...
The Brain
... At the bottom of this fissure, the hemispheres are connected by a thick “C” shaped bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum o Lobes: Frontal lobe – behind frontal bone, concerned with cognition, speech, and motor control Parietal lobe – under parietal bones, concerned with receiving a ...
... At the bottom of this fissure, the hemispheres are connected by a thick “C” shaped bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum o Lobes: Frontal lobe – behind frontal bone, concerned with cognition, speech, and motor control Parietal lobe – under parietal bones, concerned with receiving a ...
Sensory Physiology
... Perception level – Tertiary neuron running from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex or a special senses cortex ...
... Perception level – Tertiary neuron running from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex or a special senses cortex ...
Sensory Physiology
... Perception level – Tertiary neuron running from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex or a special senses cortex ...
... Perception level – Tertiary neuron running from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex or a special senses cortex ...
The Nervous System
... touch a warm surface, the neurons send a message straight to the brain. This action of getting information from the surrounding environment is called sensory input because things are being sent to the brain by way of the senses. ...
... touch a warm surface, the neurons send a message straight to the brain. This action of getting information from the surrounding environment is called sensory input because things are being sent to the brain by way of the senses. ...
brain - Austin Community College
... There are 3 classes of neurons 1. Afferent – transmit sensory impulses from PNS to the CNS. - Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints - Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs 2. Efferent - transmit motor impulses from CNS to PNS - S ...
... There are 3 classes of neurons 1. Afferent – transmit sensory impulses from PNS to the CNS. - Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints - Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs 2. Efferent - transmit motor impulses from CNS to PNS - S ...
The Visual Perception System
... The visual perception system consists of the complete network of physical structures involved in vision. These are all parts of the eyes, the specific neural pathways that connect eyes to the brain and the visual processing areas in the cortex in the brain. The perceptual experiences also involves m ...
... The visual perception system consists of the complete network of physical structures involved in vision. These are all parts of the eyes, the specific neural pathways that connect eyes to the brain and the visual processing areas in the cortex in the brain. The perceptual experiences also involves m ...
Sensation and Perception
... Ex. Things seen in low levels of light, such as twilight or in a dimly lit room, are fuzzy and grayish ...
... Ex. Things seen in low levels of light, such as twilight or in a dimly lit room, are fuzzy and grayish ...
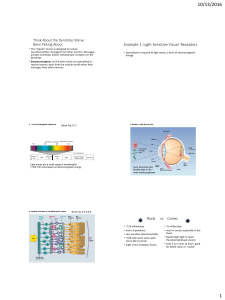
Think About the Dendrites We`ve Been Talking About
... separate regions devoted to shape, color, location, & movement that extend beyond occipital lobe. ...
... separate regions devoted to shape, color, location, & movement that extend beyond occipital lobe. ...
The Special Senses
... Modern concept of a taste map • Taste researchers have known for many years that these tongue maps are wrong. The maps arose early in the 20th century as a result of a misinterpretation of research reported in the late 1800s, and they have been almost impossible to purge from the literature. In rea ...
... Modern concept of a taste map • Taste researchers have known for many years that these tongue maps are wrong. The maps arose early in the 20th century as a result of a misinterpretation of research reported in the late 1800s, and they have been almost impossible to purge from the literature. In rea ...
5 Senses Powerpoint - Solon City Schools
... Bones of the middle ear = the hammer, anvil, stirrup which vibrate with the eardrum. ...
... Bones of the middle ear = the hammer, anvil, stirrup which vibrate with the eardrum. ...