cerebral cortex
... different layers of neurons, in human only about 5% of surface of cerebral cortex • from phylogenetical viewopoint, we distinguish two developmental stages of allocortex: a) paleocortex: original cerebral cortex, which present so called olfactory brain (rhinencephalon), in human paleocortex occupies ...
... different layers of neurons, in human only about 5% of surface of cerebral cortex • from phylogenetical viewopoint, we distinguish two developmental stages of allocortex: a) paleocortex: original cerebral cortex, which present so called olfactory brain (rhinencephalon), in human paleocortex occupies ...
Occipital Lobe
... The occipital lobe always works with the temporal lobe on keeping balance and sensory information It also works the the retina in the eye to see things. It takes what we see from our eyes to the retina through the optic nerve to the occipital lobe. Then send the information to the sensory nerves to ...
... The occipital lobe always works with the temporal lobe on keeping balance and sensory information It also works the the retina in the eye to see things. It takes what we see from our eyes to the retina through the optic nerve to the occipital lobe. Then send the information to the sensory nerves to ...
Towards natural stimulation in fMRI—Issues of data analysis
... scenes and that the intensities of activations in certain brain areas correlate linearly with the percepts. To validate and compare analysis methods suited for fMRI studies of natural hearing, natural vision, and natural touch, we designed a stimulus sequence in which auditory, visual and tactile st ...
... scenes and that the intensities of activations in certain brain areas correlate linearly with the percepts. To validate and compare analysis methods suited for fMRI studies of natural hearing, natural vision, and natural touch, we designed a stimulus sequence in which auditory, visual and tactile st ...
Slide 1
... Protected by bone, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid Spinal cord made of a core of gray matter surrounded by white matter 31 pairs of spinal nerves branch off spinal cord through intervertebral foramen Functions in many ways: ...
... Protected by bone, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid Spinal cord made of a core of gray matter surrounded by white matter 31 pairs of spinal nerves branch off spinal cord through intervertebral foramen Functions in many ways: ...
brain
... times the amount of gray matter related to general intelligence than women, and women have nearly 10 times the amount of white matter related to intelligence than men. Gray matter represents information processing centers in the brain, and white matter represents the networking of – or connections b ...
... times the amount of gray matter related to general intelligence than women, and women have nearly 10 times the amount of white matter related to intelligence than men. Gray matter represents information processing centers in the brain, and white matter represents the networking of – or connections b ...
Anatomical diagram
... followed by a loss of the motor and sensory function. The recovery process can be a few minutes to 12 weeks long. Prevention • maintaining an equal tension between the differents ropes helps to build a safer structure • let your partner adjust their position in the ropes • be especially careful duri ...
... followed by a loss of the motor and sensory function. The recovery process can be a few minutes to 12 weeks long. Prevention • maintaining an equal tension between the differents ropes helps to build a safer structure • let your partner adjust their position in the ropes • be especially careful duri ...
presentation source
... SOMATOTOPIC ORGANIZATION MORE AREA TAKEN BY SENSITIVE REGIONS (GREATER RECEPTOR DENSITYSMALLER RECEPTIVE FIELDS) CELLS RESPONDING TO ONE TYPE OF SENSATION IN VERTICLE COLUMNS(FOR EXAMPLE..PACINIAN CORPUSCLES IN A FINGERTIP) ...
... SOMATOTOPIC ORGANIZATION MORE AREA TAKEN BY SENSITIVE REGIONS (GREATER RECEPTOR DENSITYSMALLER RECEPTIVE FIELDS) CELLS RESPONDING TO ONE TYPE OF SENSATION IN VERTICLE COLUMNS(FOR EXAMPLE..PACINIAN CORPUSCLES IN A FINGERTIP) ...
Neuro Quiz 4 – Notes from April 9 to April 16 First order neurons
... 30. Acute pain is a (localized/unlocalized) pain. It occurs within ____ seconds when stimulus is applied, and is transmitted through the (large/small), (myelinated/unmyelinated) Type _ fibers. 31. Which type of pain would be described as sharp, prickly, electrical, felt mainly in the superficical la ...
... 30. Acute pain is a (localized/unlocalized) pain. It occurs within ____ seconds when stimulus is applied, and is transmitted through the (large/small), (myelinated/unmyelinated) Type _ fibers. 31. Which type of pain would be described as sharp, prickly, electrical, felt mainly in the superficical la ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System
... From there, the optic radiation fibers run to the visual cortex ...
... From there, the optic radiation fibers run to the visual cortex ...
Phineas Gage (Lobes)
... shape, colour and motion perception. The Primary Visual Cortex at the base of the Occipital lobe receives information from the visual sensory neurons on the retina and assists the brain in making an image. ...
... shape, colour and motion perception. The Primary Visual Cortex at the base of the Occipital lobe receives information from the visual sensory neurons on the retina and assists the brain in making an image. ...
Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
Infant Physical Development2016
... ◦ By 10 to 12 months, lose capacity to discriminate sounds not found in native language ...
... ◦ By 10 to 12 months, lose capacity to discriminate sounds not found in native language ...
Program - Harvard Medical School
... Develop a new gene therapy using base editor Advisor: David R. Liu, PhD - Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University My project focuses on developing a new therapy to rescue the impaired hearing functions by utilizing ...
... Develop a new gene therapy using base editor Advisor: David R. Liu, PhD - Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University My project focuses on developing a new therapy to rescue the impaired hearing functions by utilizing ...
Station 1: Sensory Adaptation
... noticeable. However, until I brought it up again, you may not have even noticed it any more. Have you ever put your pencil behind your ear, and later spent time looking for it because you completely forgot where it was? This is an example of sensory adaptation. ...
... noticeable. However, until I brought it up again, you may not have even noticed it any more. Have you ever put your pencil behind your ear, and later spent time looking for it because you completely forgot where it was? This is an example of sensory adaptation. ...
Neuron highlight
... to specific, complex, and increasingly abstracted combinations of such low-level features. In this manner, these neurons become detectors of essential feature combinations which characterize particular visual objects irrespective of the precise position, size, or contrast of the visual stimulus. The ...
... to specific, complex, and increasingly abstracted combinations of such low-level features. In this manner, these neurons become detectors of essential feature combinations which characterize particular visual objects irrespective of the precise position, size, or contrast of the visual stimulus. The ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 15 Martini Lecture Outline
... If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract that delivers information from the vestibu ...
... If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract that delivers information from the vestibu ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract that delivers information from the vestibu ...
... If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract that delivers information from the vestibu ...
Title: Multimodal imagery in music: Active ingredients and
... therapeutic. What indeed are the ‘active ingredients’ that facilitate this therapeutic process? In this article, we address one candidate of such an active ingredient: multimodality, and in particular, the interaction of interoception with other sensory modes (vision, hearing, touch) and movement. T ...
... therapeutic. What indeed are the ‘active ingredients’ that facilitate this therapeutic process? In this article, we address one candidate of such an active ingredient: multimodality, and in particular, the interaction of interoception with other sensory modes (vision, hearing, touch) and movement. T ...
sample_exam_questions_2_0
... placed on top of the head are transmitted through the skull to both ears. Bone conduction of sound through the skull should be equal in both ears. With sensorineural hearing loss, the patient will hear the midline fork more loudly in the unaffected ear. Sensorineural hearing loss is the deafness tha ...
... placed on top of the head are transmitted through the skull to both ears. Bone conduction of sound through the skull should be equal in both ears. With sensorineural hearing loss, the patient will hear the midline fork more loudly in the unaffected ear. Sensorineural hearing loss is the deafness tha ...
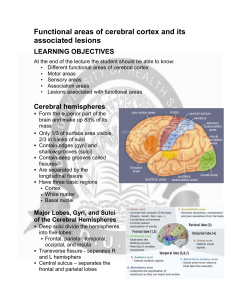
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... The three types of functional areas are: Motor areas – control voluntary movement Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensation Association areas – integrate diverse information Cerebral Cortex: Motor Areas Primary (somatic) motor cortex. Precentral gyrus, area 4 Premotor cortex,area ...
... The three types of functional areas are: Motor areas – control voluntary movement Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensation Association areas – integrate diverse information Cerebral Cortex: Motor Areas Primary (somatic) motor cortex. Precentral gyrus, area 4 Premotor cortex,area ...
Nervous System - El Camino College
... General Motor area lies in front of central sulcus and control voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The area just behind central sulcus is the general Sensory Area to receive sensory input. Primary vision area lies in visual cortex in occipital lobe. Primary Gustatory Area lies on lateral side o ...
... General Motor area lies in front of central sulcus and control voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The area just behind central sulcus is the general Sensory Area to receive sensory input. Primary vision area lies in visual cortex in occipital lobe. Primary Gustatory Area lies on lateral side o ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function independently. • D. The corpus callosum is found in the cerebral cortex, and connects the two hemispheres of the b ...
... • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function independently. • D. The corpus callosum is found in the cerebral cortex, and connects the two hemispheres of the b ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 2.1 Locomotor behavior in hydra
... and cerebral nuclei (basal ganglia), the interbrain vesicle divides into thalamus and hypothalamus, the midbrain vesicle divides into tectum and tegmentum, the hindbrain vesicle becomes known as the rhombicbrain and divides into rhombic lip, alar plate, and basal plate, and the spinal cord divides i ...
... and cerebral nuclei (basal ganglia), the interbrain vesicle divides into thalamus and hypothalamus, the midbrain vesicle divides into tectum and tegmentum, the hindbrain vesicle becomes known as the rhombicbrain and divides into rhombic lip, alar plate, and basal plate, and the spinal cord divides i ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Allows CNS to receive information and initiate action Sensory inputs and motor outputs categorized as Somatic or visceral General or special Basic Structure of PNS Sensory receptors—pick up stimuli from inside or outside the body Nerves and ganglia Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons Ganglia—clusters ...
... Allows CNS to receive information and initiate action Sensory inputs and motor outputs categorized as Somatic or visceral General or special Basic Structure of PNS Sensory receptors—pick up stimuli from inside or outside the body Nerves and ganglia Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons Ganglia—clusters ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases becau ...
... f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases becau ...