Quantum Hilbert Hotel - APS Journals
... an analogous protocol on the orbital angular momentum (OAM) eigenstates of light, where we coherently multiply any linear superposition by a fixed integer (in our case, by three). In the Supplemental Material [3] we describe further details of the experiment and we show that the square well protocol ...
... an analogous protocol on the orbital angular momentum (OAM) eigenstates of light, where we coherently multiply any linear superposition by a fixed integer (in our case, by three). In the Supplemental Material [3] we describe further details of the experiment and we show that the square well protocol ...
Justification logic with approximate conditional probabilities
... 1 whenever the condition has probability 0. Axiom 10 is the formula that states the standard definition of the conditional probability. Finally, the Axioms 11 and 12 (together with Inference Rule 4) give us the relationship between the conditional probability infinitesimally close to the some ration ...
... 1 whenever the condition has probability 0. Axiom 10 is the formula that states the standard definition of the conditional probability. Finally, the Axioms 11 and 12 (together with Inference Rule 4) give us the relationship between the conditional probability infinitesimally close to the some ration ...
Symmetries - University of South Carolina
... The initial angular momentum of the reaction is J=1. The deuterium nucleus contains two nucleons, of positive intrinsic parity, in an S wave. Final state contains 2 identical fermions, there is one choice for this state: ...
... The initial angular momentum of the reaction is J=1. The deuterium nucleus contains two nucleons, of positive intrinsic parity, in an S wave. Final state contains 2 identical fermions, there is one choice for this state: ...
Examples of Ground Resolution Proofs 1 Ground Resolution
... We begin with a slight generalisation of a theorem that was stated in the previous lecture. In this generalisation we consider Skolemising a collection of formulas rather than a single formula. Theorem 1. Let F1 , . . . , Fn be closed rectified formulas in prenex form with respective Skolem forms G1 ...
... We begin with a slight generalisation of a theorem that was stated in the previous lecture. In this generalisation we consider Skolemising a collection of formulas rather than a single formula. Theorem 1. Let F1 , . . . , Fn be closed rectified formulas in prenex form with respective Skolem forms G1 ...
Symbolic Logic II
... Demonstration: By the definition of LP-valid, φ is LP valid iff KVI (φ) 6= 0 for each trivalent interpretation, and φ is a semantic consequence of Γ iff for every trivalent interpretation, I , if KVI (γ) 6= 0 for each γ ∈ Γ, then KVI (φ) 6= 0. Thus, to show that P → Q, Q → R 2LP P → R, we need to s ...
... Demonstration: By the definition of LP-valid, φ is LP valid iff KVI (φ) 6= 0 for each trivalent interpretation, and φ is a semantic consequence of Γ iff for every trivalent interpretation, I , if KVI (γ) 6= 0 for each γ ∈ Γ, then KVI (φ) 6= 0. Thus, to show that P → Q, Q → R 2LP P → R, we need to s ...
Higgs Field and Quantum Entanglement
... system as a whole. It thus appears that one particle of an entangled pair "knows" what measurement has been performed on the other, and with what outcome, even though there is no known means for such information to be communicated between the particles, which at the time of measurement may be separa ...
... system as a whole. It thus appears that one particle of an entangled pair "knows" what measurement has been performed on the other, and with what outcome, even though there is no known means for such information to be communicated between the particles, which at the time of measurement may be separa ...
pdf
... of the reaction force due to radiation emitted by an accelerating charged particle. Abraham argued that the photon inside the medium would have a lower velocity and lower momentum, the medium itself absorbing the difference. In classical terms, Abraham’s momentum is ∫ d3x E × H, or in quantum terms ...
... of the reaction force due to radiation emitted by an accelerating charged particle. Abraham argued that the photon inside the medium would have a lower velocity and lower momentum, the medium itself absorbing the difference. In classical terms, Abraham’s momentum is ∫ d3x E × H, or in quantum terms ...
A Recursively Axiomatizable Subsystem of Levesque`s Logic of Only
... that serves as the skeleton for our model. Next, we associate to every node of the tree a maximal consistent set of sentences of a suitable language. Then we associate to every node of the tree a di erent possible world (i.e., set of atomic sentences). Finally, an accessibility relation is de ned on ...
... that serves as the skeleton for our model. Next, we associate to every node of the tree a maximal consistent set of sentences of a suitable language. Then we associate to every node of the tree a di erent possible world (i.e., set of atomic sentences). Finally, an accessibility relation is de ned on ...
Classicality as a Property of Predicate Symbols
... Obviously, the disjunction property does not hold for the entire L(D) for any non-empty D. The existence property does not hold in L(D) with non-empty D either. The following two theorems give an insight on the extent of the disjunction and existence properties. Theorem. If formula F∨G is derivable ...
... Obviously, the disjunction property does not hold for the entire L(D) for any non-empty D. The existence property does not hold in L(D) with non-empty D either. The following two theorems give an insight on the extent of the disjunction and existence properties. Theorem. If formula F∨G is derivable ...
A writeup on the State Assignments using the example given in class
... least amount of logic. However, this is not practical when there are more than a handful of states. A more practical approach is to follow a set of guidelines that tend to result in a lot of 1’s next to each other in the required K-maps. (Recall that adjacent cells in a Kmap differ by only one varia ...
... least amount of logic. However, this is not practical when there are more than a handful of states. A more practical approach is to follow a set of guidelines that tend to result in a lot of 1’s next to each other in the required K-maps. (Recall that adjacent cells in a Kmap differ by only one varia ...
Logic - UNM Computer Science
... circuits. In this section, we will show how a NAND gate can be implemented using transistors. The underlying principle also extends to the more modern CMOS technology. A transistor is a semiconductor device invented in 1947 by William Shockley, John Bardeen, and Walter Brattain at AT&T’s Bell Labs, ...
... circuits. In this section, we will show how a NAND gate can be implemented using transistors. The underlying principle also extends to the more modern CMOS technology. A transistor is a semiconductor device invented in 1947 by William Shockley, John Bardeen, and Walter Brattain at AT&T’s Bell Labs, ...
23 Up until now two main classes of quantum algorithms can be
... quantum way to compute such a function is a unitary operator Uf acting on a two-qubit state |x, yi: Uf |x, yi = |x, y ⊕ f (x)i where ⊕ means (as usual) addition modulo 2, or XOR. Of course we have to show that U is unitary, which we do by brute force, that is, by inspecting all possible cases. There ...
... quantum way to compute such a function is a unitary operator Uf acting on a two-qubit state |x, yi: Uf |x, yi = |x, y ⊕ f (x)i where ⊕ means (as usual) addition modulo 2, or XOR. Of course we have to show that U is unitary, which we do by brute force, that is, by inspecting all possible cases. There ...
Propositional Logic
... operators from Propositional Logic; so x P(x) Q(x) is not logically equivalent to x (P(x) Q(x)) • x (P(x) Q(x)) x R(x) Say P(x): x is odd, Q(x): x is divisible by 3, R(x): (x=0) (2x >x) ...
... operators from Propositional Logic; so x P(x) Q(x) is not logically equivalent to x (P(x) Q(x)) • x (P(x) Q(x)) x R(x) Say P(x): x is odd, Q(x): x is divisible by 3, R(x): (x=0) (2x >x) ...
PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC 1 Propositional Logic - Glasnost!
... leap forward in both logic and mathematics. In 1847 Boole published his first book, The Mathematical Analysis of Logic. As a result of this publication and on the recommendation of many of the leading British mathematicians of the day, Boole was appointed first Professor of Mathematics at the newly ...
... leap forward in both logic and mathematics. In 1847 Boole published his first book, The Mathematical Analysis of Logic. As a result of this publication and on the recommendation of many of the leading British mathematicians of the day, Boole was appointed first Professor of Mathematics at the newly ...
Electrogravitational Energy Resonance
... loss frequency such as energy spreading or entropy would be associated with. Then the energy that drives the gravitational action force is work being done and thus gravity cannot be considered purely as a static field. In fact, it is my contention that there is no such thing as a static field, even ...
... loss frequency such as energy spreading or entropy would be associated with. Then the energy that drives the gravitational action force is work being done and thus gravity cannot be considered purely as a static field. In fact, it is my contention that there is no such thing as a static field, even ...
CHAPTER 5 SOME EXTENSIONAL SEMANTICS
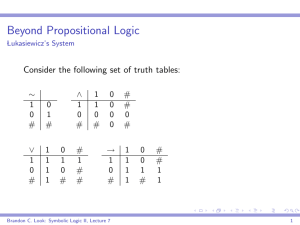
... Many valued logics in general and 3-valued logics in particular is an old object of study which had its beginning in the work of Lukasiewicz (1920). He was the first to define a 3- valued semantics for a language L¬,∩,∪,⇒ of classical logic, and called it a three valued logic for short. He left the ...
... Many valued logics in general and 3-valued logics in particular is an old object of study which had its beginning in the work of Lukasiewicz (1920). He was the first to define a 3- valued semantics for a language L¬,∩,∪,⇒ of classical logic, and called it a three valued logic for short. He left the ...
Document
... it I began to think that this story reflected some of the problems that I had been thinking about in philosophy for a long time. • How do we know why people do what they do, and even how one knows what one does oneself? It's a fundamental question... this is the heart of the play. (…) We can never k ...
... it I began to think that this story reflected some of the problems that I had been thinking about in philosophy for a long time. • How do we know why people do what they do, and even how one knows what one does oneself? It's a fundamental question... this is the heart of the play. (…) We can never k ...
A Logic of Explicit Knowledge - Lehman College
... Now we drop the operator K from the language, and introduce a family of explicit reasons instead— I’ll use t as a typical one. Following [1, 2] I’ll write t:X to indicate that t applies to X—read it as “X is known for reason t.” Formally, if t is a reason and X is a formula, t:X is a formula. Of cou ...
... Now we drop the operator K from the language, and introduce a family of explicit reasons instead— I’ll use t as a typical one. Following [1, 2] I’ll write t:X to indicate that t applies to X—read it as “X is known for reason t.” Formally, if t is a reason and X is a formula, t:X is a formula. Of cou ...
RR-01-02
... classical first-order logic as base logic, augmented with the formulas in table 1 and axioms in table 2 for representing the specific problem domain of interest and for controlling deduction, and uses McCarthy’s 1986 [11] predicate circumscription 3 with forced separation as modelpreference criterio ...
... classical first-order logic as base logic, augmented with the formulas in table 1 and axioms in table 2 for representing the specific problem domain of interest and for controlling deduction, and uses McCarthy’s 1986 [11] predicate circumscription 3 with forced separation as modelpreference criterio ...