Logic Logical Concepts Deduction Concepts Resolution
... In order to evaluate if this formula is true or false, we need to give the predicate symbol P an interpretation Suppose we interpret P as the < relation, i.e., P (x, y) means "x is less than y" Under this interpretation, the formula above is clearly true Note, however, that this would not be the cas ...
... In order to evaluate if this formula is true or false, we need to give the predicate symbol P an interpretation Suppose we interpret P as the < relation, i.e., P (x, y) means "x is less than y" Under this interpretation, the formula above is clearly true Note, however, that this would not be the cas ...
Title PI name/institution
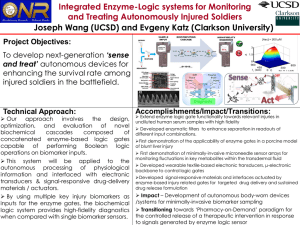
... Integrated Enzyme-Logic systems for Monitoring and Treating Autonomously Injured Soldiers Joseph Wang (UCSD) and Evgeny Katz (Clarkson University) Project Objectives: To develop next-generation ‘sense and treat’ autonomous devices for enhancing the survival rate among A) injured soldiers in the batt ...
... Integrated Enzyme-Logic systems for Monitoring and Treating Autonomously Injured Soldiers Joseph Wang (UCSD) and Evgeny Katz (Clarkson University) Project Objectives: To develop next-generation ‘sense and treat’ autonomous devices for enhancing the survival rate among A) injured soldiers in the batt ...
The Origin of Proof Theory and its Evolution
... First-Order Number Theory - PA (Peano Arithmetic) First-order logic has sufficient expressive power for the formalization of virtually all of mathematics. A first-order theory consists of a set of axioms (usually finite or recursively enumerable) and the statements deducible from them. Peano arithm ...
... First-Order Number Theory - PA (Peano Arithmetic) First-order logic has sufficient expressive power for the formalization of virtually all of mathematics. A first-order theory consists of a set of axioms (usually finite or recursively enumerable) and the statements deducible from them. Peano arithm ...
pdf
... The study of logic has evolved for nearly 2,500 years, since Aristotle’s work (350 BCE) and writings of the Stoics about the logos. For the Greeks, logic was the study of correct argument expressed in a syllogism. Leibniz (1666) explained the potential of logic to create a universal language for cod ...
... The study of logic has evolved for nearly 2,500 years, since Aristotle’s work (350 BCE) and writings of the Stoics about the logos. For the Greeks, logic was the study of correct argument expressed in a syllogism. Leibniz (1666) explained the potential of logic to create a universal language for cod ...
ppt
... statements are true, what other statements can you also deduce are true? • If I tell you that all men are mortal, and Socrates is a man, what can you deduce? ...
... statements are true, what other statements can you also deduce are true? • If I tell you that all men are mortal, and Socrates is a man, what can you deduce? ...
Propositional Logic Predicate Logic
... Definition (Well-founded Relation). A relation ≺ on S is well-founded if there is no infinite sequence x1 , x2 , . . . in S such that xi+1 ≺ xi for all i ≥ 1. Theorem. For all well-founded relations ≺ on S and all unary predicates P , ...
... Definition (Well-founded Relation). A relation ≺ on S is well-founded if there is no infinite sequence x1 , x2 , . . . in S such that xi+1 ≺ xi for all i ≥ 1. Theorem. For all well-founded relations ≺ on S and all unary predicates P , ...