
WAVE OPTICS Jaan Kalda 1 Basics. Double slit diffraction.
... time-scale (ato- and picosecond-scale-physics), in order to be amplitude on distance affects the both waves in the same able to see an interference pattern, the light needs to come way, i.e. |a1 (l1 )| = |a2 (l2 )|. The two Huygens sources are from the same light source, even in the case of lasers. ...
... time-scale (ato- and picosecond-scale-physics), in order to be amplitude on distance affects the both waves in the same able to see an interference pattern, the light needs to come way, i.e. |a1 (l1 )| = |a2 (l2 )|. The two Huygens sources are from the same light source, even in the case of lasers. ...
Geometrical and diffraction optics
... The Strehl ratio (SR) is the ratio of the observed peak intensity of the PSF compared to the theoretical maximum peak intensity of a point source seen with a perfect imaging system working at the diffraction limit. Using the wave number k=2/LJ and the RMS wavefront error ǐ one can calculate that: ...
... The Strehl ratio (SR) is the ratio of the observed peak intensity of the PSF compared to the theoretical maximum peak intensity of a point source seen with a perfect imaging system working at the diffraction limit. Using the wave number k=2/LJ and the RMS wavefront error ǐ one can calculate that: ...
Energy and angular momentum transfers from an
... or using interferences with plane waves [34] or self interferences using triangular apertures [35] or Young double slit experiments [36]. For review articles the reader can refer, for example, to [10, 11, 12, 37]. Concerning the applications, some authors take advantages of the vortex structure to g ...
... or using interferences with plane waves [34] or self interferences using triangular apertures [35] or Young double slit experiments [36]. For review articles the reader can refer, for example, to [10, 11, 12, 37]. Concerning the applications, some authors take advantages of the vortex structure to g ...
LASERPULSE™ LIGHT ARM FOR PIV MODEL 610015
... in delivering the light sheet for Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) measurements or for other high energy laser applications. Featuring a beam path that can be fully enclosed from the laser to the measurement area, it is essential for safely delivering high-energy, pulsed YAG laser beams. ...
... in delivering the light sheet for Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) measurements or for other high energy laser applications. Featuring a beam path that can be fully enclosed from the laser to the measurement area, it is essential for safely delivering high-energy, pulsed YAG laser beams. ...
ABCD law for Gaussian laser beams
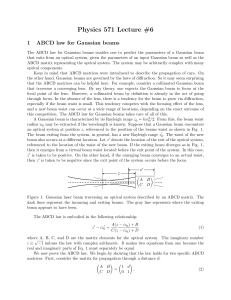
... through a distance d and transmission through a thin lens with focal length f (or a concave mirror with focal length f ). From these elements we can derive more complicated systems. The ABCD matrix for a thick lens cannot be constructed from just these two elements. However, we can construct the mat ...
... through a distance d and transmission through a thin lens with focal length f (or a concave mirror with focal length f ). From these elements we can derive more complicated systems. The ABCD matrix for a thick lens cannot be constructed from just these two elements. However, we can construct the mat ...
Lecture 35: Holography.
... information (in-phase - maximum amplitude, out-ofphase – minimum amplitude) Interfere wavefront of light from a scene with a reference wave The hologram is a complex interference pattern of ...
... information (in-phase - maximum amplitude, out-ofphase – minimum amplitude) Interfere wavefront of light from a scene with a reference wave The hologram is a complex interference pattern of ...
properties of laser beams
... called mode locking, it is possible to produce light pulses whose duration is roughly equal to the inverse of the linewidth of the laser transition 2→1. • If the line width is narrow the pulse width is very short~ 0.1-1 ns some flash lamps can emit light pulses with a duration of somewhat less than ...
... called mode locking, it is possible to produce light pulses whose duration is roughly equal to the inverse of the linewidth of the laser transition 2→1. • If the line width is narrow the pulse width is very short~ 0.1-1 ns some flash lamps can emit light pulses with a duration of somewhat less than ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... Cells from the human dermis after lysis form a protective coating. Butterfly epidermal cells also form a coating upon cell death. According to H. Ghiradella “…scales are highly structures, scale formation is a virtuoso exercise in biological pattern formation at the cellular level”. The scales chang ...
... Cells from the human dermis after lysis form a protective coating. Butterfly epidermal cells also form a coating upon cell death. According to H. Ghiradella “…scales are highly structures, scale formation is a virtuoso exercise in biological pattern formation at the cellular level”. The scales chang ...
244061
... composition, and source-related parameters in nano-optical systems, the simulation times can be too large to optimize practical nano-optical systems. To obtain accurate and fast computational solutions of nano-optical systems that involve a large number of geometry, material composition, and source- ...
... composition, and source-related parameters in nano-optical systems, the simulation times can be too large to optimize practical nano-optical systems. To obtain accurate and fast computational solutions of nano-optical systems that involve a large number of geometry, material composition, and source- ...












![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852310_1-c57a219e2d0af9e07138a16c6144f432-300x300.png)








