Time-domain optical data storage by use of Raman coherent population trapping
... intensities are chosen to give maximum signal-tonoise ratios. We suppress the effects of laser jitter (- 1 MHz) by generating all the required optical fields from a single laser, using acousto- and electro-optic modulators. To recall the stored data, rephasing and probe fields are also required, as ...
... intensities are chosen to give maximum signal-tonoise ratios. We suppress the effects of laser jitter (- 1 MHz) by generating all the required optical fields from a single laser, using acousto- and electro-optic modulators. To recall the stored data, rephasing and probe fields are also required, as ...
Wave Refraction in Negative-Index Media: Always Positive
... to be used for the propagation of a finite pulse through a finite aperture [15]. The results (Fig. 4) are qualitatively similar to those for infinite apertures, showing the large angle (upg 艐 84±) between the output signal y g and the average phase velocity 具y p 典. The resulting inhomogeneous wave ...
... to be used for the propagation of a finite pulse through a finite aperture [15]. The results (Fig. 4) are qualitatively similar to those for infinite apertures, showing the large angle (upg 艐 84±) between the output signal y g and the average phase velocity 具y p 典. The resulting inhomogeneous wave ...
EM theory - McMaster University > ECE
... J=0, but the time-varying electric field intensity or displacement current density (second term on the right hand side of Eq.(1.47)) leads to magnetic field intensity, which in turn leads to electric field intensity (Eq.(1.46)). This process continues and the generated electromagnetic wave propagates ...
... J=0, but the time-varying electric field intensity or displacement current density (second term on the right hand side of Eq.(1.47)) leads to magnetic field intensity, which in turn leads to electric field intensity (Eq.(1.46)). This process continues and the generated electromagnetic wave propagates ...
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4th ed Donald R
... Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) - Electronic p-n junction devices that convert an electrical signal into visible light. Electroluminescence - Use of an applied electrical signal to stimulate photons from a material. Laser - The acronym stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
... Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) - Electronic p-n junction devices that convert an electrical signal into visible light. Electroluminescence - Use of an applied electrical signal to stimulate photons from a material. Laser - The acronym stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
Waves and Radiation Pupil Booklet
... When light hits a boundary at an angle greater than the _________________________, the light does not pass through but instead is _____________________. This is called total internal reflection since the ray stays __________ the glass. ...
... When light hits a boundary at an angle greater than the _________________________, the light does not pass through but instead is _____________________. This is called total internal reflection since the ray stays __________ the glass. ...
Surface plasmon resonance sensors based on uniform
... taining the same sensitivity. In Fig. 5, the comparison between the operation with optimized polarization (open circles) and without a polarizer (solid diamonds) is shown. This means that we can use these devices virtually as polarization-independent ones. If we are using unpolarized sources, as in ...
... taining the same sensitivity. In Fig. 5, the comparison between the operation with optimized polarization (open circles) and without a polarizer (solid diamonds) is shown. This means that we can use these devices virtually as polarization-independent ones. If we are using unpolarized sources, as in ...
Demonstrating the style for the Journal of Physics: Conference series
... 3.2. Trion optically-induced spin dynamics We apply the model to modulation-doped lens-shaped quantum dots with lateral dimensions largely exceeding the height that is sufficiently general to represent a wide class of zero-dimensional systems. Due to the quasi cylindrical symmetry, the energy level ...
... 3.2. Trion optically-induced spin dynamics We apply the model to modulation-doped lens-shaped quantum dots with lateral dimensions largely exceeding the height that is sufficiently general to represent a wide class of zero-dimensional systems. Due to the quasi cylindrical symmetry, the energy level ...
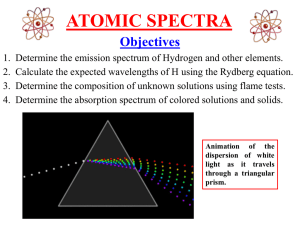
Atomic_spectra
... Wavelength (): Distance between two consecutive peaks [unit: nm] Frequency (): Number of waves per second that pass a given point in space [unit: s-1 (Hertz)] ...
... Wavelength (): Distance between two consecutive peaks [unit: nm] Frequency (): Number of waves per second that pass a given point in space [unit: s-1 (Hertz)] ...
Numerical simulation of diffraction grating alignment and phase noise
... Choosing dimensions depends on the problem Need balance between accuracy and computation speed Major limitation is computational requirements, they increase very rapidly with finer grid sizes ...
... Choosing dimensions depends on the problem Need balance between accuracy and computation speed Major limitation is computational requirements, they increase very rapidly with finer grid sizes ...
6.1. Gabor`s (In-line) Holography. In 1948, Dennis Gabor introduced
... , the last two terms in Eq. 13 generate Fourier transforms that are shifted symmetrically with ...
... , the last two terms in Eq. 13 generate Fourier transforms that are shifted symmetrically with ...
An overview of the terdiurnal tide observed by polar radars and optics
... An 2 hr component is generally smaller than the diurnal ,. hr and semidiurnal +, hr components, but has definitely been identified in various radar and optical observations. Earlier observations at Garchy (.1῍N) show small amplitude with intermittent occurrence like internal gravity waves and short ve ...
... An 2 hr component is generally smaller than the diurnal ,. hr and semidiurnal +, hr components, but has definitely been identified in various radar and optical observations. Earlier observations at Garchy (.1῍N) show small amplitude with intermittent occurrence like internal gravity waves and short ve ...
Unit – 1 1. Explain the formation Ionic, Covalent and Metallic
... Explain indetail Point Defects, Frenkel and Schottky Defects. ...
... Explain indetail Point Defects, Frenkel and Schottky Defects. ...