Solution to PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1A
... That is, as a matter of general principle, the beam always has the greater angle to the normal when traveling in the medium with the greater speed. (And this is always true for any kind of wave being refracted between any two different media!) So, if incident from air, the sound beam is refracted aw ...
... That is, as a matter of general principle, the beam always has the greater angle to the normal when traveling in the medium with the greater speed. (And this is always true for any kind of wave being refracted between any two different media!) So, if incident from air, the sound beam is refracted aw ...
A1990DA63800001
... be classified. The classification (later enormously extended by Arnold) was by codimension, which is the number of parameters that must typically be explored to find the singularity. Thom realized that his classification described optical caustics (via Fermat’s principle, according to which a family ...
... be classified. The classification (later enormously extended by Arnold) was by codimension, which is the number of parameters that must typically be explored to find the singularity. Thom realized that his classification described optical caustics (via Fermat’s principle, according to which a family ...
File
... 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different media A , B , C are 15o , 25o and 35o respectively. In which medium will the velocity of light b ...
... 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different media A , B , C are 15o , 25o and 35o respectively. In which medium will the velocity of light b ...
Synopsis by Lori Moore
... The degradation in the performance of an optic depends not only on the height of periodic defects, but also on the relative size of the defects. The PSD method is useful because the PSD contains information about the period of the defects on the optical surface as well as the magnitude (height) of t ...
... The degradation in the performance of an optic depends not only on the height of periodic defects, but also on the relative size of the defects. The PSD method is useful because the PSD contains information about the period of the defects on the optical surface as well as the magnitude (height) of t ...
1 - FunFACS
... the cavity, the carrier density and the dielectric polarization) evolve on very different time scales so that the numerical implementation is very inefficient. Ten years ago the USTRAT group discovered that the straightforward elimination of fast variables in laser models with diffraction can lead t ...
... the cavity, the carrier density and the dielectric polarization) evolve on very different time scales so that the numerical implementation is very inefficient. Ten years ago the USTRAT group discovered that the straightforward elimination of fast variables in laser models with diffraction can lead t ...
Photonics
... Concepts of Photonic A/D conversion basically relies on using an optical architecture to: Generate a stream of very low jitter sampling optical pulses + wavelength dispersion Modulate the height of the dispersed optical pulses by the voltage signal to be sampled through an optical modulator Sp ...
... Concepts of Photonic A/D conversion basically relies on using an optical architecture to: Generate a stream of very low jitter sampling optical pulses + wavelength dispersion Modulate the height of the dispersed optical pulses by the voltage signal to be sampled through an optical modulator Sp ...
Multiwavelength pulse generator using time
... by a 10-GHz sinusoidal drive, and a 1.1-km spool of standard single-mode fiber with dispersion of 18.7 ps兾nm. The optical spectra before and after the time lens are shown in Fig. 2. The close match between measurement and theory demonstrates the reliability and predictability of our system. We measu ...
... by a 10-GHz sinusoidal drive, and a 1.1-km spool of standard single-mode fiber with dispersion of 18.7 ps兾nm. The optical spectra before and after the time lens are shown in Fig. 2. The close match between measurement and theory demonstrates the reliability and predictability of our system. We measu ...
V. experimental setup of all-optical tunable delay
... Tunable optical delay = converted wavelength dispersion ×fiber length× tuning range of conversion Shown in fig (1) is the generic block diagram of proposed system. The input signal (t0) transmits in the wavelength converter.It uses to convert was by using the method of four-wave mixing (FWM) method. ...
... Tunable optical delay = converted wavelength dispersion ×fiber length× tuning range of conversion Shown in fig (1) is the generic block diagram of proposed system. The input signal (t0) transmits in the wavelength converter.It uses to convert was by using the method of four-wave mixing (FWM) method. ...
INTRODUCTION:
... There are mainly two types of refractive index profile: Step index profile: It is characterized by a core with a completely constant index of refraction n1 throughout its bulk and a sudden transition of index to a lower value at the core wall. Graded index profile: In this type of fiber, the mat ...
... There are mainly two types of refractive index profile: Step index profile: It is characterized by a core with a completely constant index of refraction n1 throughout its bulk and a sudden transition of index to a lower value at the core wall. Graded index profile: In this type of fiber, the mat ...
Optics 101 for non-optical engineers
... Blur Circle = The image formed by a lens on its focal surface (image plane) of a point source object. The size of the blur circle will dictated by the precision of the lens and the state of focus; The blur can be caused by aberrations in the lens, defocusing and manufacturing defects ...
... Blur Circle = The image formed by a lens on its focal surface (image plane) of a point source object. The size of the blur circle will dictated by the precision of the lens and the state of focus; The blur can be caused by aberrations in the lens, defocusing and manufacturing defects ...
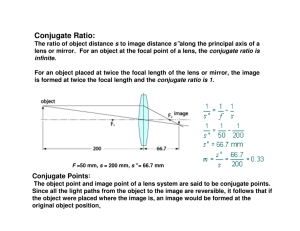
Lecture 04
... A microscope with an adjustable, small diaphragm serving as light source. While the diaphragm in the base normally controls the size of the illuminated field and is therefore called “luminous field diaphragm”, in our setup this diaphragm acts as “aperture diaphragm”, since there is no condenser used ...
... A microscope with an adjustable, small diaphragm serving as light source. While the diaphragm in the base normally controls the size of the illuminated field and is therefore called “luminous field diaphragm”, in our setup this diaphragm acts as “aperture diaphragm”, since there is no condenser used ...
Coherent manipulation of atoms with standing light waves
... starting point, the question of whether light is a particle or a wave, is embodied in the duality just mentioned as to whether a standing wave is better considered as two counter-propagating beams of photons or a stationary electromagnetic field. As we have recently discussed the history of atom opt ...
... starting point, the question of whether light is a particle or a wave, is embodied in the duality just mentioned as to whether a standing wave is better considered as two counter-propagating beams of photons or a stationary electromagnetic field. As we have recently discussed the history of atom opt ...
Liquid-crystal photonic applications
... transition to the isotropic phase. In this case, the long-range orientational order dominates over thermal fluctuations and the molecules tend to align their long axes in a common direction (denoted by the director L), as shown in Fig. 2(a). However, no long-range positional order of the molecules w ...
... transition to the isotropic phase. In this case, the long-range orientational order dominates over thermal fluctuations and the molecules tend to align their long axes in a common direction (denoted by the director L), as shown in Fig. 2(a). However, no long-range positional order of the molecules w ...
Subject: Precision Optics II Grade: 10
... 5. Lens shape and lens function identification worksheet. [Why does curve matter?] 6. Dispersion demo & glass map interpretation assignment. [Why does composition matter?] 7. Lens Maker’s Equation worksheet and Excel spreadsheet. [Why does curve & composition matter?] 8. Ideal Ray Diagram reading an ...
... 5. Lens shape and lens function identification worksheet. [Why does curve matter?] 6. Dispersion demo & glass map interpretation assignment. [Why does composition matter?] 7. Lens Maker’s Equation worksheet and Excel spreadsheet. [Why does curve & composition matter?] 8. Ideal Ray Diagram reading an ...