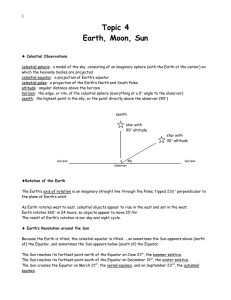
Topic 4: Earth-Moon-Sun
... Seasons on the Earth are caused by: 1) the revolution of the Earth around the Sun 2) the tilt of the Earth on its axis 3) the parallelism of the Earth’s axis (every position of the Earth’s axis is parallel to every other position of the Earth’s axis) On about June 21st, the Northern Hemisphere is ti ...
... Seasons on the Earth are caused by: 1) the revolution of the Earth around the Sun 2) the tilt of the Earth on its axis 3) the parallelism of the Earth’s axis (every position of the Earth’s axis is parallel to every other position of the Earth’s axis) On about June 21st, the Northern Hemisphere is ti ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... Mars is very poorly placed over the other side of the Solar System, low in the south-west at sunset, and follows the Sun down like this for the next two months or so; conjunction is on the 14th June. Jupiter is by far the most convenient planet to observe this month and can be observed all night thr ...
... Mars is very poorly placed over the other side of the Solar System, low in the south-west at sunset, and follows the Sun down like this for the next two months or so; conjunction is on the 14th June. Jupiter is by far the most convenient planet to observe this month and can be observed all night thr ...
Section 3: Three Periodicities - Wobble, Tilt, and
... motion (its "axial obliquity") ranges from a minimum of 22.1 degrees to a maximum of 24.5 degrees ("Milutin Milankovitch") (Figure 3.4). ...
... motion (its "axial obliquity") ranges from a minimum of 22.1 degrees to a maximum of 24.5 degrees ("Milutin Milankovitch") (Figure 3.4). ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... relative to one another. Why then, do we not see the patterns made up by them, the constellations, changing night by night? • The stars in each constellation are part of a "moving group," all moving the same direction, so their position relative to each other does not change. • The stars in the sky ...
... relative to one another. Why then, do we not see the patterns made up by them, the constellations, changing night by night? • The stars in each constellation are part of a "moving group," all moving the same direction, so their position relative to each other does not change. • The stars in the sky ...
CyclesOfTheSky
... Explain why Polaris is the North Star? Explain why the stars appear to revolve around the North Star? What is meant by the Earth’s precession? Is Earth’s precession a long or a short time? ...
... Explain why Polaris is the North Star? Explain why the stars appear to revolve around the North Star? What is meant by the Earth’s precession? Is Earth’s precession a long or a short time? ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... within half a degree of the ecliptic at some 85 light-years distance. In this position it is occulted occasionally by the Moon. It is a blue-white star of spectral type B7, radiating about 130 times as much light as the Sun and seen from Earth at magnitude 1.35. Regulus has an orange K1 companion wh ...
... within half a degree of the ecliptic at some 85 light-years distance. In this position it is occulted occasionally by the Moon. It is a blue-white star of spectral type B7, radiating about 130 times as much light as the Sun and seen from Earth at magnitude 1.35. Regulus has an orange K1 companion wh ...
Earth Science
... moon"), happen when the moon is at a 90 degree angle with respect to the Earth and Sun. So we are seeing exactly half of the moon illuminated and half in shadow. Waxing Gibbous- After the first quarter, the sunlit portion is still increasing, but now it is more than ...
... moon"), happen when the moon is at a 90 degree angle with respect to the Earth and Sun. So we are seeing exactly half of the moon illuminated and half in shadow. Waxing Gibbous- After the first quarter, the sunlit portion is still increasing, but now it is more than ...
Exploring the Moon and Stars
... • The Moon is illuminated by sunlight. • The portions of the Moon facing the Earth but not visible during many of the phases are hidden in the Moon’s own shadow. ...
... • The Moon is illuminated by sunlight. • The portions of the Moon facing the Earth but not visible during many of the phases are hidden in the Moon’s own shadow. ...
Space Quiz for CPS
... characteristic of the sun? A. The sun does not move. B. The sun is closer to the Earth than the other stars ...
... characteristic of the sun? A. The sun does not move. B. The sun is closer to the Earth than the other stars ...
Key Stage 2: Teacher`s Pack
... mountains (South America), such as the VLT and ALMA. What is the advantage of this location? High altitude means thin atmosphere, which decreases atmospheric distortion. 16. How does this demonstrate one advantage of building big telescopes? Increases collecting area, so can see fainter (and further ...
... mountains (South America), such as the VLT and ALMA. What is the advantage of this location? High altitude means thin atmosphere, which decreases atmospheric distortion. 16. How does this demonstrate one advantage of building big telescopes? Increases collecting area, so can see fainter (and further ...
Physics of Astronomy – Week 3 quiz
... it rotates slowly to reveal more or less of its illuminated hemisphere while remaining relatively fixed against the celestial sphere of stars. The declination of the Sun on the first day of spring is variable, depending on the year. 23.5º north. ...
... it rotates slowly to reveal more or less of its illuminated hemisphere while remaining relatively fixed against the celestial sphere of stars. The declination of the Sun on the first day of spring is variable, depending on the year. 23.5º north. ...
Precession of the Earth`s Axis
... the preceding centuries. In particular they measured the distance of the stars like Spica to the Moon and Sun at the time of lunar eclipses, and because he could compute the distance of the Moon and Sun from the equinox at these moments, he noticed that Spica and other stars appeared to have moved o ...
... the preceding centuries. In particular they measured the distance of the stars like Spica to the Moon and Sun at the time of lunar eclipses, and because he could compute the distance of the Moon and Sun from the equinox at these moments, he noticed that Spica and other stars appeared to have moved o ...
302 Final Review
... 64. A scientist looking for an optimal location for a new observatory should choose a location________. a. in a large city b. in an area with an elevation below sea level c. on a remote hilltop d. in a low-lying river valley ...
... 64. A scientist looking for an optimal location for a new observatory should choose a location________. a. in a large city b. in an area with an elevation below sea level c. on a remote hilltop d. in a low-lying river valley ...
2. Answer Key Practice Test, Topic 3
... The diagram represents Earth's revolution around the Sun. Points A, B, C, and D represent Earth's positions in its orbit on the first day of each of the four seasons. The major axis and the foci (the center of the Sun and the other focus) of Earth's orbit are shown. ...
... The diagram represents Earth's revolution around the Sun. Points A, B, C, and D represent Earth's positions in its orbit on the first day of each of the four seasons. The major axis and the foci (the center of the Sun and the other focus) of Earth's orbit are shown. ...
File - Mrs. Cole`s 5th Grade Class
... You might think that the seasons are caused by Earth’s changing distance from the Sun due to Earth’s elliptical orbit. In other words, some people believe it is warmer in the summer because we are closer to the Sun, and colder in the winter because we are farther away. But this is not true! The dif ...
... You might think that the seasons are caused by Earth’s changing distance from the Sun due to Earth’s elliptical orbit. In other words, some people believe it is warmer in the summer because we are closer to the Sun, and colder in the winter because we are farther away. But this is not true! The dif ...
The Reason for Seasons - Somers Public Schools
... You might think that the seasons are caused by Earth’s changing distance from the Sun due to Earth’s elliptical orbit. In other words, some people believe it is warmer in the summer because we are closer to the Sun, and colder in the winter because we are farther away. But this is not true! The dif ...
... You might think that the seasons are caused by Earth’s changing distance from the Sun due to Earth’s elliptical orbit. In other words, some people believe it is warmer in the summer because we are closer to the Sun, and colder in the winter because we are farther away. But this is not true! The dif ...
Earth-Moon-Sun Answer Key
... MEAP-like practice questions formally released items from Oakland Schools. S.IP.04.11 Your teacher asked you to look at the moon for a few minutes a day for 5 days. Which sentence is an observation you may make from this lesson? A. The moon circles the Earth. B. The moon spins as it travels. C. The ...
... MEAP-like practice questions formally released items from Oakland Schools. S.IP.04.11 Your teacher asked you to look at the moon for a few minutes a day for 5 days. Which sentence is an observation you may make from this lesson? A. The moon circles the Earth. B. The moon spins as it travels. C. The ...
The Earth
... • The north pole is currently pointing to a spot near the star Polaris. Because the vernal equinox is the starting point for most star charts, the charts must be made for a certain period. The star charts must be updated periodically to account for this movement of the reference point. • Because of ...
... • The north pole is currently pointing to a spot near the star Polaris. Because the vernal equinox is the starting point for most star charts, the charts must be made for a certain period. The star charts must be updated periodically to account for this movement of the reference point. • Because of ...
TOPIC 14 – MOTIONS OF EARTH, MOON, SUN
... 55. Except during lunar eclipses, how much of the moon is always receiving light from the sun? __________________________________________ 56. Why does an observer on Earth see varying amounts of this lighted half as the moon moves in its orbit? _________________________________ 57. What are the moon ...
... 55. Except during lunar eclipses, how much of the moon is always receiving light from the sun? __________________________________________ 56. Why does an observer on Earth see varying amounts of this lighted half as the moon moves in its orbit? _________________________________ 57. What are the moon ...
lecture 1 - University of Florida Astronomy
... • You can imagine that the stars and sun are attached to the surface of a great sphere • The earth appears to be at the center of the sphere • The sphere rotates from east to west on an axis that points to the north celestial pole • To explain the daily motions of the sky you can imagine the sphere ...
... • You can imagine that the stars and sun are attached to the surface of a great sphere • The earth appears to be at the center of the sphere • The sphere rotates from east to west on an axis that points to the north celestial pole • To explain the daily motions of the sky you can imagine the sphere ...
Space Revision Answers File
... and irregular. A galaxy is a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction. 3. What is the difference between a meteor, meteorite, and meteoroid? It depends on their position at the time. Meteoroid - A small particle from an asteroid o ...
... and irregular. A galaxy is a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction. 3. What is the difference between a meteor, meteorite, and meteoroid? It depends on their position at the time. Meteoroid - A small particle from an asteroid o ...
November 2014 - Hermanus Astronomy
... existence of planets around both WASP-94A and its twin, WASP-94B. "We observed the other star by accident and then found a planet around that one also!” said Marion Neveu-VanMalle from the Geneva Observatory. Hot Jupiter planets are much closer to their stars than our own Jupiter, with a ‘year’ last ...
... existence of planets around both WASP-94A and its twin, WASP-94B. "We observed the other star by accident and then found a planet around that one also!” said Marion Neveu-VanMalle from the Geneva Observatory. Hot Jupiter planets are much closer to their stars than our own Jupiter, with a ‘year’ last ...
Third Grade Astronomy
... Objects in the Sky have patterns of movement. The Sun, for example, appears to move across the sky in the same way everyday, but its path changes slowly over the seasons. The moon moves across the sky on a daily basis much like the Sun. The Sun, Moon and stars all have properties, locations and move ...
... Objects in the Sky have patterns of movement. The Sun, for example, appears to move across the sky in the same way everyday, but its path changes slowly over the seasons. The moon moves across the sky on a daily basis much like the Sun. The Sun, Moon and stars all have properties, locations and move ...
Astronomy Exam Answer Key
... 3 In New York State, the constellation Pisces can be seen in the night sky between the middle of summer and the middle of winter. The constellation Scorpio can be seen in the night sky between early spring and early fall. The reason these two constellations can be viewed only at these times is a dir ...
... 3 In New York State, the constellation Pisces can be seen in the night sky between the middle of summer and the middle of winter. The constellation Scorpio can be seen in the night sky between early spring and early fall. The reason these two constellations can be viewed only at these times is a dir ...
astronomy 31 - UNC Physics
... B. When solar eclipses occur, the moon is directly between the sun and Earth and consequently its phase must be new. However, solar eclipses do not occur every time the moon is new because the Earth-Moon plane is tipped, by about 5 degrees, with respect to the Sun-Earth plane, meaning that the moon, ...
... B. When solar eclipses occur, the moon is directly between the sun and Earth and consequently its phase must be new. However, solar eclipses do not occur every time the moon is new because the Earth-Moon plane is tipped, by about 5 degrees, with respect to the Sun-Earth plane, meaning that the moon, ...
Astronomy on Mars
.jpg?width=300)
In many cases astronomical phenomena viewed from the planet Mars are the same or similar to those seen from Earth but sometimes (as with the view of Earth as an evening/morning star) they can be quite different. For example, because the atmosphere of Mars does not contain an ozone layer, it is also possible to make UV observations from the surface of Mars.























