
Optical Fibres
... Total internal reflection occurs when light is coming out of something dense, such as glass, water or perspex ...
... Total internal reflection occurs when light is coming out of something dense, such as glass, water or perspex ...
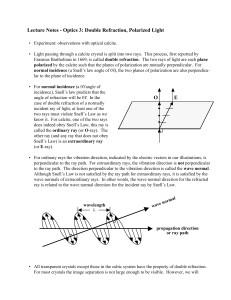
Lecture Notes - Optics 3: Double Refraction, Polarized Light E O
... • Light passing through a calcite crystal is split into two rays. This process, first reported by Erasmus Bartholinus in 1669, is called double refraction. The two rays of light are each plane polarized by the calcite such that the planes of polarization are mutually perpendicular. For normal incide ...
... • Light passing through a calcite crystal is split into two rays. This process, first reported by Erasmus Bartholinus in 1669, is called double refraction. The two rays of light are each plane polarized by the calcite such that the planes of polarization are mutually perpendicular. For normal incide ...
GRADE 10 SA2 PHYSICS revision worksheet-2
... B. An object of size 5 cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm from the optical centre of converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Calculate the distance of the image from the lens and size of the image 2. (a) Draw a ray diagram showing the path of a ray of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) fr ...
... B. An object of size 5 cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm from the optical centre of converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Calculate the distance of the image from the lens and size of the image 2. (a) Draw a ray diagram showing the path of a ray of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) fr ...
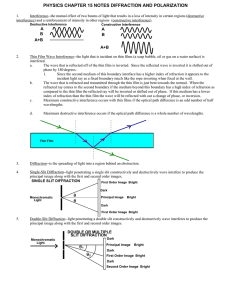
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of phase. If this medium has a lower index of refraction than the thin film the wave will be reflected with out a change of phase, or inversion. ...
... compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of phase. If this medium has a lower index of refraction than the thin film the wave will be reflected with out a change of phase, or inversion. ...
The principles of statistical optics and image formation A Statistical
... The principles of statistical optics and image formation A Statistical Description of Optical Science Course Objective: This course aims to introduce the intrinsic nature of optical fields, their propagation, statistical properties (i.e., coherence), and imaging methods based on statistical properti ...
... The principles of statistical optics and image formation A Statistical Description of Optical Science Course Objective: This course aims to introduce the intrinsic nature of optical fields, their propagation, statistical properties (i.e., coherence), and imaging methods based on statistical properti ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester Lecture 28 – Geometric Optics
... Can use two principal points (planes) and effective focal length f to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
... Can use two principal points (planes) and effective focal length f to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
Waves & Oscillations Geometric Optics Physics 42200 3/20/2016
... – Given an optical system, what are the properties of the image that is formed (if any)? – What configuration of optical elements (if any) will produce an image with certain desired characteristics? ...
... – Given an optical system, what are the properties of the image that is formed (if any)? – What configuration of optical elements (if any) will produce an image with certain desired characteristics? ...
13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]
... at the exact centre of the lens. • The Principal Focus (F) is the point at the principal axis of a lens where light rays parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction. • The Secondary Principal Focus (F’) is on the same side of the lens relative to the incident rays. F and F’ are at an eq ...
... at the exact centre of the lens. • The Principal Focus (F) is the point at the principal axis of a lens where light rays parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction. • The Secondary Principal Focus (F’) is on the same side of the lens relative to the incident rays. F and F’ are at an eq ...
Chapt23_VG0
... Different colors are associated with light of different wavelengths. However, color is a perception, and most of that perception is based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original compo ...
... Different colors are associated with light of different wavelengths. However, color is a perception, and most of that perception is based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original compo ...
Difficulties associated with working with UV and IR optics
... microns, but bandpass filters can still be designed and fabricated to operate in this region. Reflective coatings are limited to wavelengths greater than 0.15 microns if they are to be broadband, though narrow bandwidth filters can be designed for lower wavelengths [1]. One of the difficulties assoc ...
... microns, but bandpass filters can still be designed and fabricated to operate in this region. Reflective coatings are limited to wavelengths greater than 0.15 microns if they are to be broadband, though narrow bandwidth filters can be designed for lower wavelengths [1]. One of the difficulties assoc ...
Optics_pal_mac_2012
... (17) A hydrogen electron transitions from n=3 to n=1. The electron ______ a photon. (18) The photon has an energy of ________ eV. (19) The photon has an energy of _______ J. (20) The frequency of the photon is __________ Hz. (21) The wavelength o f the photon is ________ m. (22) The photon (is/is n ...
... (17) A hydrogen electron transitions from n=3 to n=1. The electron ______ a photon. (18) The photon has an energy of ________ eV. (19) The photon has an energy of _______ J. (20) The frequency of the photon is __________ Hz. (21) The wavelength o f the photon is ________ m. (22) The photon (is/is n ...
Optics supplemental notess
... • A place where many light rays from the same point on an object meet together again in a point called the focus, or focal point. – They are “pictures” of objects Two types of images: – virtual - "not real" - the image only seems to be where it is; cannot be projected onto a screen – real -can be ...
... • A place where many light rays from the same point on an object meet together again in a point called the focus, or focal point. – They are “pictures” of objects Two types of images: – virtual - "not real" - the image only seems to be where it is; cannot be projected onto a screen – real -can be ...
Light Rays
... The optical centre is the centre of a lens. Light rays passing through it do not change direction. The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. ...
... The optical centre is the centre of a lens. Light rays passing through it do not change direction. The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. ...
Problem Sheet
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
Acknowledgments
... measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved basis. In many cases these non-intrusive optical devices have significant advantages over physical probes that perturb the s ...
... measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved basis. In many cases these non-intrusive optical devices have significant advantages over physical probes that perturb the s ...
Optical Polarimetry
... In a typical polarimetry experiment, monochromatic light is passed through the sample. A sodium lamp is usually used as the light source and the wavelength of its D line is 589.3 nm. The light provided by the source is not polarized so its electromagnetic waves oscillate in all planes perpendicular ...
... In a typical polarimetry experiment, monochromatic light is passed through the sample. A sodium lamp is usually used as the light source and the wavelength of its D line is 589.3 nm. The light provided by the source is not polarized so its electromagnetic waves oscillate in all planes perpendicular ...
Sample
... properties before they consider fiber optics. Much of this information may not be new to students who have had a good introductory physics course, but you can't count on that. This review focuses upon the parts of optics relevant for fiber optics. I start with the ideas of the electromagnetic spectr ...
... properties before they consider fiber optics. Much of this information may not be new to students who have had a good introductory physics course, but you can't count on that. This review focuses upon the parts of optics relevant for fiber optics. I start with the ideas of the electromagnetic spectr ...
Problem Sheet
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that a ...
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that a ...
Instructional Software for Visualizing Optical Phenomena
... typically demonstrated in a classroom laboratory. The lab equipment may include light sources, apertures, lenses, and polarizing filters. The 2-dimensional diagrams in a textbook may illustrate invisible but important features of light (such as the electric field vector at a given point as a functio ...
... typically demonstrated in a classroom laboratory. The lab equipment may include light sources, apertures, lenses, and polarizing filters. The 2-dimensional diagrams in a textbook may illustrate invisible but important features of light (such as the electric field vector at a given point as a functio ...





![13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008538239_1-d1798f6d27c8a2d8c0931d41a70fff89-300x300.png)















