Convex and Concave Mirrors Prac
... This practical activity involves ray tracing. If, for example, a light ray appears like Figure 1, you will need to concave mirror 1. Trace the curve of the mirror. Figure 2 Figure 3 2. Place two small dots on the incident ray and two on the reflected Figure 1 ray (see figure 2). 3. Remove the light ...
... This practical activity involves ray tracing. If, for example, a light ray appears like Figure 1, you will need to concave mirror 1. Trace the curve of the mirror. Figure 2 Figure 3 2. Place two small dots on the incident ray and two on the reflected Figure 1 ray (see figure 2). 3. Remove the light ...
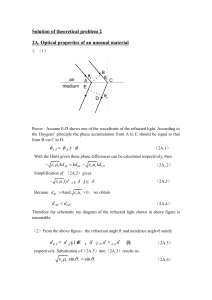
(等倾干涉) — equal thickness interference.
... A thin film with index of refraction n = 1.40 is placed in one arm of a Michelson interferometer, perpendicular to the optical path. If this causes a shift of 7.0 fringes of the pattern produced by light of = 589 nm, what is the film thickness? Solution: The change of optical path difference due ...
... A thin film with index of refraction n = 1.40 is placed in one arm of a Michelson interferometer, perpendicular to the optical path. If this causes a shift of 7.0 fringes of the pattern produced by light of = 589 nm, what is the film thickness? Solution: The change of optical path difference due ...
6288-18 talk - LOFT, Large Optics Fabrication and Testing group
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
Slide 1
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
Slide
... 1810 - Graduated in civil engineering and went to work as a junior engineer where Napoleon planned to build a naval base 1812 – (age 23) Lost interest in engineering, being more attracted to abstract mathematics Cauchy had many major accomplishments in both mathematics and science in areas such as c ...
... 1810 - Graduated in civil engineering and went to work as a junior engineer where Napoleon planned to build a naval base 1812 – (age 23) Lost interest in engineering, being more attracted to abstract mathematics Cauchy had many major accomplishments in both mathematics and science in areas such as c ...
Light II - Galileo and Einstein
... A. No, it would always get out. B. Yes, but the distance between reflections would have to be greater. C. Same but smaller. ...
... A. No, it would always get out. B. Yes, but the distance between reflections would have to be greater. C. Same but smaller. ...
Refraction, Lenses, Aberrations
... surfaces, which are either curved (e.g., a segment of a sphere) or plain. Lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments (microscopes, telescopes, cameras, etc.) ...
... surfaces, which are either curved (e.g., a segment of a sphere) or plain. Lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments (microscopes, telescopes, cameras, etc.) ...
Properties of Multilayer Optics
... Upon strong reflection off a layer a standing wave is formed which effectively changes the refractive index felt by the total field. If the Bragg peak is placed near Brewster’s angle, only the s-component feels this electric field modulation and change in refractive index which causes a phase shift ...
... Upon strong reflection off a layer a standing wave is formed which effectively changes the refractive index felt by the total field. If the Bragg peak is placed near Brewster’s angle, only the s-component feels this electric field modulation and change in refractive index which causes a phase shift ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
Waves - Morgan Science
... Real – Light rays actually travel to that location Virtual – Light appears to be at that location Upright – image is right side up compared to object Inverted – image is upside down as compared to object ...
... Real – Light rays actually travel to that location Virtual – Light appears to be at that location Upright – image is right side up compared to object Inverted – image is upside down as compared to object ...
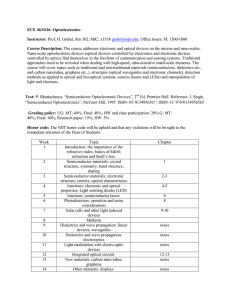
ECE 463/626: Optoelectronics Instructor: Prof. H. Grebel, Rm 302
... Course Description: The course addresses electronic and optical devices on the micron and nano-scales. Nano-scale optoelectronic devices (optical devices controlled by electronics and electronic devices controlled by optics) find themselves in the forefront of communication and sensing systems. Trad ...
... Course Description: The course addresses electronic and optical devices on the micron and nano-scales. Nano-scale optoelectronic devices (optical devices controlled by electronics and electronic devices controlled by optics) find themselves in the forefront of communication and sensing systems. Trad ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... Chapter 36 Image Formation (Lens and Mirrors) Using the ray approximation of geometric optics, we can now study how images are formed with mirrors and lens Then we can apply these principles to practical optical devices: the eye, telescopes, … First consider the common flat mirror to make some defin ...
... Chapter 36 Image Formation (Lens and Mirrors) Using the ray approximation of geometric optics, we can now study how images are formed with mirrors and lens Then we can apply these principles to practical optical devices: the eye, telescopes, … First consider the common flat mirror to make some defin ...
Link to PowerPoint Presentation
... of incidence and refraction between two different media ٭Media possess a Refractive Index (n) ٭Measures how much speed of light is slowed down by the medium ٭The more light is slowed, the higher its Refractive Index ...
... of incidence and refraction between two different media ٭Media possess a Refractive Index (n) ٭Measures how much speed of light is slowed down by the medium ٭The more light is slowed, the higher its Refractive Index ...
HP Unit 11-light & optics - student handout
... • High-energy photons are emitted as one of three types of radiation resulting from natural radioactivity. Differs from X-rays where radiation is emitted by excited nuclei rather than electrons • Gamma ray sources are used for cancer treatment and for diagnostic purposes • Highest energy EM wave, hi ...
... • High-energy photons are emitted as one of three types of radiation resulting from natural radioactivity. Differs from X-rays where radiation is emitted by excited nuclei rather than electrons • Gamma ray sources are used for cancer treatment and for diagnostic purposes • Highest energy EM wave, hi ...
Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle File
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. Two lenses of focal lengths 8 cm and 6 cm are placed at a certain distance apart. Calculate the distance between the lenses if they form an achromatic combination. 3. Explain the formation of colours in thin film. 4. Light of wavelength 6000 Å falls normally on a thin wedge shaped film of µ=1.5, ...
... 2. Two lenses of focal lengths 8 cm and 6 cm are placed at a certain distance apart. Calculate the distance between the lenses if they form an achromatic combination. 3. Explain the formation of colours in thin film. 4. Light of wavelength 6000 Å falls normally on a thin wedge shaped film of µ=1.5, ...
Chapter 5: Geometrical Optics
... Image: If a cone of rays emitted from a point source S arrives at a certain point P, then P is called the image of S. Diffraction-limited image: The size of the image for a point source is not zero. The limited size of an optical system causes the blur of the image point due to diffraction effect: ...
... Image: If a cone of rays emitted from a point source S arrives at a certain point P, then P is called the image of S. Diffraction-limited image: The size of the image for a point source is not zero. The limited size of an optical system causes the blur of the image point due to diffraction effect: ...
Prof. Lan Yang - Microlasers for Nanoscale
... Optical sensors based on Whispering-Gallery-Mode (WGM) resonators have emerged as front-runners for label-free, ultra-sensitive detection of nanoscale materials and structures due to their superior capability to significantly enhance the interactions of light with the sensing targets. A WGM resonato ...
... Optical sensors based on Whispering-Gallery-Mode (WGM) resonators have emerged as front-runners for label-free, ultra-sensitive detection of nanoscale materials and structures due to their superior capability to significantly enhance the interactions of light with the sensing targets. A WGM resonato ...
Coupled Resonator Optical Waveguides (CROWs) Fatemeh Soltani
... Dispersion relations can be improved by higher number of ring resonators. It has been shown in graph below: ...
... Dispersion relations can be improved by higher number of ring resonators. It has been shown in graph below: ...