4th Science: 4 Units They are not presented in the order in which
... D-cell - a battery that changes chemical energy into electrical energy Electrical charge - the positive or negative property of particles Electricity - the energy caused by the flow electrical charges Electromagnet - a temporary magnet created when current flows through wire wrapped in coils Force ...
... D-cell - a battery that changes chemical energy into electrical energy Electrical charge - the positive or negative property of particles Electricity - the energy caused by the flow electrical charges Electromagnet - a temporary magnet created when current flows through wire wrapped in coils Force ...
Capacitance
... Note: This lab assumes familiarity with the relationship C=Q/V and investigates physical factors that affect capacitance. Directions: Access the PhET “Capacitor Lab” Simulation at http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/capacitor-lab. On the iMacs you must click “Download Now” in blue, and then open ...
... Note: This lab assumes familiarity with the relationship C=Q/V and investigates physical factors that affect capacitance. Directions: Access the PhET “Capacitor Lab” Simulation at http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/capacitor-lab. On the iMacs you must click “Download Now” in blue, and then open ...
© DISNEY 2012
... Every circuit must also have a conductor – a material, like most metals, that freely gives up electrons, allowing electricity to flow. Materials that hold their electrons tightly, such as rubber, cotton or glass are called insulators and electricity does not flow through these materials very well. I ...
... Every circuit must also have a conductor – a material, like most metals, that freely gives up electrons, allowing electricity to flow. Materials that hold their electrons tightly, such as rubber, cotton or glass are called insulators and electricity does not flow through these materials very well. I ...
electric potential
... Determine the potential at a distance r from the center of a uniformly charged conducting sphere of a radius ro for a) r>ro b) r=ro c) r
... Determine the potential at a distance r from the center of a uniformly charged conducting sphere of a radius ro for a) r>ro b) r=ro c) r
CAPACITORS: are any physical objects that can store charge. I
... • In a sense, big C means it's "easy" to store up a bunch of charges. A capacitor can store charge (and energy) for you - that's why they're useful. Think of a closet with lots of bowling balls up on the shelf at high gravitational potential. You can let them fall down whenever you like, to do lots ...
... • In a sense, big C means it's "easy" to store up a bunch of charges. A capacitor can store charge (and energy) for you - that's why they're useful. Think of a closet with lots of bowling balls up on the shelf at high gravitational potential. You can let them fall down whenever you like, to do lots ...
Three dimensions Consider a point charge in three
... You already know that there is a zero electric field inside a conductor; therefore, if you surround any internal point with a Gaussian surface, there will be no flux at any point on this surface, and hence the surface will enclose zero net charge. This surface can be imagined around any point inside ...
... You already know that there is a zero electric field inside a conductor; therefore, if you surround any internal point with a Gaussian surface, there will be no flux at any point on this surface, and hence the surface will enclose zero net charge. This surface can be imagined around any point inside ...
Electricity and Magnetism Summary Notes
... • If the charges are opposite - they attract • If one is charged and the other is not - they attract ...
... • If the charges are opposite - they attract • If one is charged and the other is not - they attract ...
4.A Electricity and Magnetism Pre Assessment
... a. uses a magnet to help us find which way gravity is pulling. b. uses a freely moving magnetic needle to point out direction. c. tells us something about north, south, east, or west forces. d. tells us what time it is in different parts of the world. 5. What is the name for the type of electricity ...
... a. uses a magnet to help us find which way gravity is pulling. b. uses a freely moving magnetic needle to point out direction. c. tells us something about north, south, east, or west forces. d. tells us what time it is in different parts of the world. 5. What is the name for the type of electricity ...
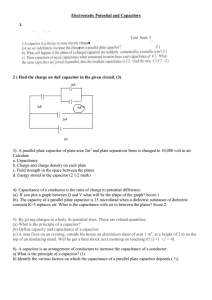
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitors 2 ) Find the charge on 4uF
... b. Whether there is a potential at a point with zero intensity of electric field? Justify. 10)(a) Given n capacitors each of capacitance C. How will you combine them to get (i) maximum capacitance; what is the maximum capacitance? 1 (ii) minimum capacitance; what is the minimum capacitance? 1 (b) Dr ...
... b. Whether there is a potential at a point with zero intensity of electric field? Justify. 10)(a) Given n capacitors each of capacitance C. How will you combine them to get (i) maximum capacitance; what is the maximum capacitance? 1 (ii) minimum capacitance; what is the minimum capacitance? 1 (b) Dr ...
Electric Potential
... creating it (the + and charges on the parallel plates) but in terms of the voltage between the plates and their separation l Units for electric field ◆ before we used ▲ F=qE; E=F/q (N/C) ◆ now: E=ΔVc/d (V/m) ▲ 1 N/C = 1 V/m ▲ can use either set of units depending on which is more convenient f ...
... creating it (the + and charges on the parallel plates) but in terms of the voltage between the plates and their separation l Units for electric field ◆ before we used ▲ F=qE; E=F/q (N/C) ◆ now: E=ΔVc/d (V/m) ▲ 1 N/C = 1 V/m ▲ can use either set of units depending on which is more convenient f ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.