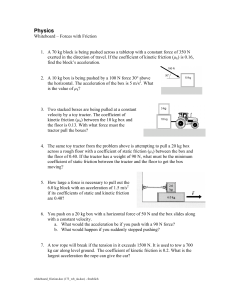
Class- XII- A Physics- HW
... charge and electric dipole moment of the system. 26. ABCD is a square of side 5m, charges of +50C, -50C and +50C are placed at A, C and D respectively. Find the resultant electric field at B. 27. .An electron is projected with velocity vx = 2 x 106 m/s in the region between 2 charged plates. If E be ...
... charge and electric dipole moment of the system. 26. ABCD is a square of side 5m, charges of +50C, -50C and +50C are placed at A, C and D respectively. Find the resultant electric field at B. 27. .An electron is projected with velocity vx = 2 x 106 m/s in the region between 2 charged plates. If E be ...
as Powerpoint
... to compensate for that, a charge q must be present on the outer surface of the conductor. ...
... to compensate for that, a charge q must be present on the outer surface of the conductor. ...
Electric Potential Energy
... The Electric Potential of a Charged Sphere In prac(ce, you are more likely to work with a charged sphere, of radius R and total charge Q, than with a point charge. Outside a uniformly charged sphere, the ele ...
... The Electric Potential of a Charged Sphere In prac(ce, you are more likely to work with a charged sphere, of radius R and total charge Q, than with a point charge. Outside a uniformly charged sphere, the ele ...
PH504lec0910-5
... and hence can only have a radial component. Take as a Gaussian surface (G) a sphere of radius r (>a) placed concentric to the conductor. By symmetry the field E must be constant at all points on G and also normal to G. Flux through G = field x surface area = E.4r2 Total charge enclosed by surface i ...
... and hence can only have a radial component. Take as a Gaussian surface (G) a sphere of radius r (>a) placed concentric to the conductor. By symmetry the field E must be constant at all points on G and also normal to G. Flux through G = field x surface area = E.4r2 Total charge enclosed by surface i ...
Lect04
... charged surfaces, we must always first chose an appropriate Gaussian surface. In this case, for r
... charged surfaces, we must always first chose an appropriate Gaussian surface. In this case, for r
Homework-Coulomb
... Instructor notes: This problem was given in the Gauss’ Law section to see if they knew when they could use Gauss’ Law (which you can’t in this situation). About 40% of students used Gauss’ Law for part (c). Students still struggled with setting up “dA” and “curly R”. In part (a) several students st ...
... Instructor notes: This problem was given in the Gauss’ Law section to see if they knew when they could use Gauss’ Law (which you can’t in this situation). About 40% of students used Gauss’ Law for part (c). Students still struggled with setting up “dA” and “curly R”. In part (a) several students st ...
Document
... charged surfaces, we must always first chose an appropriate Gaussian surface. In this case, for r
... charged surfaces, we must always first chose an appropriate Gaussian surface. In this case, for r
Slide 1
... Advantages over DC • Low voltage, portable (~1 – 10 volts) • Good flow rates (~mm/s) ...
... Advantages over DC • Low voltage, portable (~1 – 10 volts) • Good flow rates (~mm/s) ...
MICHAEL FARADAY, EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCHES IN
... way, is then suddenly stopped, and finally moves the other way. 41. If such a hollow helix as that described (34) be laid east and west (or in any other constant position), and a magnet be retained east and west, its marked pole always being one way; then whichever end of the helix the magnet goes i ...
... way, is then suddenly stopped, and finally moves the other way. 41. If such a hollow helix as that described (34) be laid east and west (or in any other constant position), and a magnet be retained east and west, its marked pole always being one way; then whichever end of the helix the magnet goes i ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.