3 phases Charger Inverter Introduction
... R – N : 6KW 1-Phase S – N : 6KW 1-Phase T – N : 6KW 1-Phase ...
... R – N : 6KW 1-Phase S – N : 6KW 1-Phase T – N : 6KW 1-Phase ...
Chapter 7
... Used when there are two or more resistances of equal value. The total resistance is equal to the value of one resistor divided by the total number of resistors in the parallel circuit ...
... Used when there are two or more resistances of equal value. The total resistance is equal to the value of one resistor divided by the total number of resistors in the parallel circuit ...
Document
... • Programmable using flowcharts • Can be programmed many times • Remembers program even when the power is off ...
... • Programmable using flowcharts • Can be programmed many times • Remembers program even when the power is off ...
Lab: " Ohm`s Law "
... B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the power supply. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to read DCV 20. Connect it in parallel (across) the resistor. Turn on the ammeter and adjust it to read 10 A. Place it in series with ...
... B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the power supply. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to read DCV 20. Connect it in parallel (across) the resistor. Turn on the ammeter and adjust it to read 10 A. Place it in series with ...
Circuit Sums with ac
... DIFFERENCE between the voltage and current in each case ? (1 full cycle = 360 degree). If the circuit contains capacitance, the opposite effect happens; the current actually happens earlier than the voltage, or LEADS it as the saying goes. We often make use of that fact in practice to reduce the pha ...
... DIFFERENCE between the voltage and current in each case ? (1 full cycle = 360 degree). If the circuit contains capacitance, the opposite effect happens; the current actually happens earlier than the voltage, or LEADS it as the saying goes. We often make use of that fact in practice to reduce the pha ...
ELEC 5705 RF Systems Design: Assignment #1
... 3) Produce a plot of the output power of the IM3 products, and fundamental power versus input power for an input with two tones. Determine the 1dB compression point of the amplifier. ...
... 3) Produce a plot of the output power of the IM3 products, and fundamental power versus input power for an input with two tones. Determine the 1dB compression point of the amplifier. ...
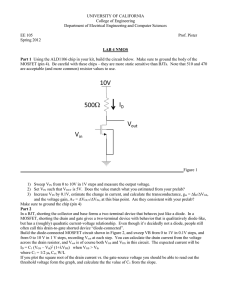
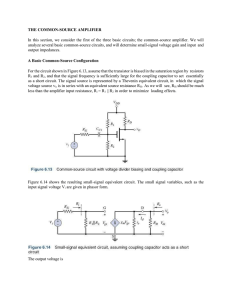
the common-source amplifier
... For the circuit shown in Figure 6.13, assume that the transistor is biased in the saturation region by resistors R1 and R2, and that the signal frequency is sufficiently large for the coupling capacitor to act essentially as a short circuit. The signal source is represented by a Thevenin equivalent ...
... For the circuit shown in Figure 6.13, assume that the transistor is biased in the saturation region by resistors R1 and R2, and that the signal frequency is sufficiently large for the coupling capacitor to act essentially as a short circuit. The signal source is represented by a Thevenin equivalent ...
Power, Energy and Delay
... • Part of this energy is dissipated in the pMOS device while the remainder is stored on the load capacitor. • When the output capacitance CL is discharge the stored energy is dissipated in the nMOS device. • The energy taken from the supply during a low-to-high transition can be determined precisely ...
... • Part of this energy is dissipated in the pMOS device while the remainder is stored on the load capacitor. • When the output capacitance CL is discharge the stored energy is dissipated in the nMOS device. • The energy taken from the supply during a low-to-high transition can be determined precisely ...
series mc - Gamma High Voltage
... isolation allows the user to select an output of either polarity on Models up to 5KV. *15 VDC input is required for output voltage of 15KVDC, 24VDC input is required for output voltage of 20KVDC. 10KV, 15KV and 20KV units have a fixed polarity, either Positive or Negative. The compact size of the GA ...
... isolation allows the user to select an output of either polarity on Models up to 5KV. *15 VDC input is required for output voltage of 15KVDC, 24VDC input is required for output voltage of 20KVDC. 10KV, 15KV and 20KV units have a fixed polarity, either Positive or Negative. The compact size of the GA ...
The HV 2/4 high-voltage power supply module
... (and A’ output) is increased by (for example) 100V, B’ output will also be increased (or reduced) by 100V, as if operating with a floating power supply. Changes of setting on B will only affect voltage output B’. However, it is to note that the high voltage outputs of the HV2/4PF are not floating, o ...
... (and A’ output) is increased by (for example) 100V, B’ output will also be increased (or reduced) by 100V, as if operating with a floating power supply. Changes of setting on B will only affect voltage output B’. However, it is to note that the high voltage outputs of the HV2/4PF are not floating, o ...
Solid State Lighting for the Developing World
... need to be smoothed, capacitors can be used as filters – Capacitors store electrical charge, like a bucket stores water – Electrons are brought to the capacitor by input current, like drops of water into a bucket – When needed, capacitor outputs current like the water bucket’s ...
... need to be smoothed, capacitors can be used as filters – Capacitors store electrical charge, like a bucket stores water – Electrons are brought to the capacitor by input current, like drops of water into a bucket – When needed, capacitor outputs current like the water bucket’s ...
Power electronics

Power electronics is the application of solid-state electronics to the control and conversion of electric power. It also refers to a subject of research in electronic and electrical engineering which deals with the design, control, computation and integration of nonlinear, time-varying energy-processing electronic systems with fast dynamics.The first high power electronic devices were mercury-arc valves. In modern systems the conversion is performed with semiconductor switching devices such as diodes, thyristors and transistors, pioneered by R. D. Middlebrook and others beginning in the 1950s. In contrast to electronic systems concerned with transmission and processing of signals and data, in power electronics substantial amounts of electrical energy are processed. An AC/DC converter (rectifier) is the most typical power electronics device found in many consumer electronic devices, e.g. television sets, personal computers, battery chargers, etc. The power range is typically from tens of watts to several hundred watts. In industry a common application is the variable speed drive (VSD) that is used to control an induction motor. The power range of VSDs start from a few hundred watts and end at tens of megawatts.The power conversion systems can be classified according to the type of the input and output power AC to DC (rectifier) DC to AC (inverter) DC to DC (DC-to-DC converter) AC to AC (AC-to-AC converter)