DSS2x101-015A
... Schottky Diode High Performance Schottky Diode Low Loss and Soft Recovery Parallel legs Part number ...
... Schottky Diode High Performance Schottky Diode Low Loss and Soft Recovery Parallel legs Part number ...
Addressable Input/Output Module I-9301 / I-9303
... Loop :::::: 1mA Power:::::: 2mA Loop :::::: 3mA Power:::::: 15mA capacity Output contact is 24VDC/5A is Voltage capacity output 24VDC/1A Dry contact output Electronically addressed ...
... Loop :::::: 1mA Power:::::: 2mA Loop :::::: 3mA Power:::::: 15mA capacity Output contact is 24VDC/5A is Voltage capacity output 24VDC/1A Dry contact output Electronically addressed ...
24_Banach_newp - Instytut Maszyn, Napędów i Pomiarów
... – difficulty to find the minimum of the input power while the load and the supply voltage are changing. The major advantage is, that a search controller does not require knowledge of any motor parameters. In consideration of these disadvantages, will be often used a control strategy based on the los ...
... – difficulty to find the minimum of the input power while the load and the supply voltage are changing. The major advantage is, that a search controller does not require knowledge of any motor parameters. In consideration of these disadvantages, will be often used a control strategy based on the los ...
Name: Record Responses in med blue bold font Module 8 Lesson 2
... 1. Current and Voltage Difference The net movement of electric charges in a single direction is an ______. In a metal wire, or any material, electrons are in ______ _______in all directions. As a result, there is no net movement of electrons in one direction. When an electric current flows in the wi ...
... 1. Current and Voltage Difference The net movement of electric charges in a single direction is an ______. In a metal wire, or any material, electrons are in ______ _______in all directions. As a result, there is no net movement of electrons in one direction. When an electric current flows in the wi ...
equipment in power distribution
... Losses due to Harmonics Losses due to low power factor Miscellaneous losses ...
... Losses due to Harmonics Losses due to low power factor Miscellaneous losses ...
Slide 1
... In a bridge circuit the voltage difference between the two parallel branches is used to indicate the potential difference between the two points. ...
... In a bridge circuit the voltage difference between the two parallel branches is used to indicate the potential difference between the two points. ...
L6375D
... The supply voltage is expected to range from 8 to 35 V. In this range the device operates correctly. To avoid any malfunctioning the supply voltage is continuously monitored to provide an undervoltage protection. As VS falls below Vsth-Vshys (typically 7.5 V, see Figure 1) the output Power MOSFET is ...
... The supply voltage is expected to range from 8 to 35 V. In this range the device operates correctly. To avoid any malfunctioning the supply voltage is continuously monitored to provide an undervoltage protection. As VS falls below Vsth-Vshys (typically 7.5 V, see Figure 1) the output Power MOSFET is ...
CB61F
... The only controlled copy of this Data Sheet is the electronic read-only version located on the Cooper Bussmann Network Drive. All other copies of this document are by definition uncontrolled. This bulletin is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information th ...
... The only controlled copy of this Data Sheet is the electronic read-only version located on the Cooper Bussmann Network Drive. All other copies of this document are by definition uncontrolled. This bulletin is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information th ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (b) Solve the following differential equation using operational amplifier. ...
... (b) Solve the following differential equation using operational amplifier. ...
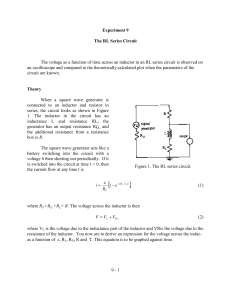
Theory
... an oscilloscope and compared to the theoretically calculated plot when the parameters of the circuit are known. ...
... an oscilloscope and compared to the theoretically calculated plot when the parameters of the circuit are known. ...
Low-Power and High Speed High-to-Low Level Shifter
... As channel width of PMOS transistor should be approximately three times larger than of NMOS, it leads to the unacceptable increase of occupied area. In case when signals at the input for second stage have high frequencies and high voltage levels, the output signal level which drives the third stage ...
... As channel width of PMOS transistor should be approximately three times larger than of NMOS, it leads to the unacceptable increase of occupied area. In case when signals at the input for second stage have high frequencies and high voltage levels, the output signal level which drives the third stage ...
Direct current (DC) supply grids for LED-Lighting
... Figure 6: Loss comparison of AC grid (a) and DC grid (b) with photovoltaic and battery storage operation. 3. Voltage selection The supply voltage of the DC grid also has an influence on the losses. Low voltages like 24 V or 48 V have as advantages that they are save to touch and commercially availab ...
... Figure 6: Loss comparison of AC grid (a) and DC grid (b) with photovoltaic and battery storage operation. 3. Voltage selection The supply voltage of the DC grid also has an influence on the losses. Low voltages like 24 V or 48 V have as advantages that they are save to touch and commercially availab ...
Examination of advanced differential pairs
... current through: M5, M6, M1, M2, M3, M4 and RL. Using the graphical results explain and prove the behavior of the circuit. Instructions: The figure shows current differential amplifier implemented with M1, M2, M3 and M4). The circuit has differential current inputs Iin1 and Iin2. Simple differential ...
... current through: M5, M6, M1, M2, M3, M4 and RL. Using the graphical results explain and prove the behavior of the circuit. Instructions: The figure shows current differential amplifier implemented with M1, M2, M3 and M4). The circuit has differential current inputs Iin1 and Iin2. Simple differential ...
College of Micronesia-FSM
... a. Why current is the same in all parts of a series circuit. 9 hrs b. Calculating total resistance, current, the voltage drops, and total power. c. Series aiding and series opposing voltages d. Analyzing series circuit e. Effect of an open circuit in a series path f. Switches represent the AND logic ...
... a. Why current is the same in all parts of a series circuit. 9 hrs b. Calculating total resistance, current, the voltage drops, and total power. c. Series aiding and series opposing voltages d. Analyzing series circuit e. Effect of an open circuit in a series path f. Switches represent the AND logic ...
What is power electronics? - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
... • When the diode is forward biased it begins to conduct with only a small voltage across it. • When the diode is reversed biased only a negligibly small leakage current flow through the device until the reverse breakdown voltage is reached. • In normal operation reverse bias voltage should not reach ...
... • When the diode is forward biased it begins to conduct with only a small voltage across it. • When the diode is reversed biased only a negligibly small leakage current flow through the device until the reverse breakdown voltage is reached. • In normal operation reverse bias voltage should not reach ...
Power electronics

Power electronics is the application of solid-state electronics to the control and conversion of electric power. It also refers to a subject of research in electronic and electrical engineering which deals with the design, control, computation and integration of nonlinear, time-varying energy-processing electronic systems with fast dynamics.The first high power electronic devices were mercury-arc valves. In modern systems the conversion is performed with semiconductor switching devices such as diodes, thyristors and transistors, pioneered by R. D. Middlebrook and others beginning in the 1950s. In contrast to electronic systems concerned with transmission and processing of signals and data, in power electronics substantial amounts of electrical energy are processed. An AC/DC converter (rectifier) is the most typical power electronics device found in many consumer electronic devices, e.g. television sets, personal computers, battery chargers, etc. The power range is typically from tens of watts to several hundred watts. In industry a common application is the variable speed drive (VSD) that is used to control an induction motor. The power range of VSDs start from a few hundred watts and end at tens of megawatts.The power conversion systems can be classified according to the type of the input and output power AC to DC (rectifier) DC to AC (inverter) DC to DC (DC-to-DC converter) AC to AC (AC-to-AC converter)