Stoichiometery
... I have 1.6 mol of hydrogen. How much water can I make? A. 1.6 mol H2O B. 0.8 mol etc. C. 3.2 mol D. 4.8 mol E. None of the above ...
... I have 1.6 mol of hydrogen. How much water can I make? A. 1.6 mol H2O B. 0.8 mol etc. C. 3.2 mol D. 4.8 mol E. None of the above ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Chemical Reactions
... particles. We need some way of bridging the gulf between the “real world” of our ability to manipulate and measure materials, and the “atomic/molecular world” where small particles interact as described ...
... particles. We need some way of bridging the gulf between the “real world” of our ability to manipulate and measure materials, and the “atomic/molecular world” where small particles interact as described ...
Chemistry Bridging Work
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
Chapter 17: Reaction Energy and Reaction Kinetics
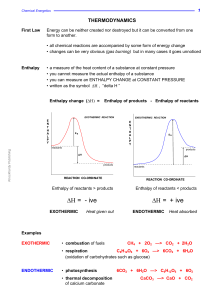
... compound has a high negative heat of formation. Such compounds are very stable. Once they start, the reactions forming them usually proceed vigorously and without outside assistance. Elements in their standard states are defined as having ∆H 0f = 0. The ∆H 0f of carbon dioxide is −393.5 kJ/mol of ga ...
... compound has a high negative heat of formation. Such compounds are very stable. Once they start, the reactions forming them usually proceed vigorously and without outside assistance. Elements in their standard states are defined as having ∆H 0f = 0. The ∆H 0f of carbon dioxide is −393.5 kJ/mol of ga ...
Structural determination of organic compounds
... steady, the vapour with the lowest boiling point firstly comes out from the top of the column ...
... steady, the vapour with the lowest boiling point firstly comes out from the top of the column ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... 3. The reaction: 2S(s) + 3O2 (g) ↔ 2SO3(g) + 800 kJ has reached the equilibrium in a closed container. Which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? A. adding a catalyst without changing the temperature or pressure B. increasing the pressure by reducing the volume C. increasing the temperatu ...
... 3. The reaction: 2S(s) + 3O2 (g) ↔ 2SO3(g) + 800 kJ has reached the equilibrium in a closed container. Which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? A. adding a catalyst without changing the temperature or pressure B. increasing the pressure by reducing the volume C. increasing the temperatu ...
Student Study Guide Chemistry 534
... perfume released into the corner of a room can, in time, be detected all over the room even if the air is still. Gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur oxides (SO2 and SO3) and nitrogen oxides (NO and NO2) have always been present in the atmosphere along with nitrogen gas (N2), oxygen gas (O2), ...
... perfume released into the corner of a room can, in time, be detected all over the room even if the air is still. Gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur oxides (SO2 and SO3) and nitrogen oxides (NO and NO2) have always been present in the atmosphere along with nitrogen gas (N2), oxygen gas (O2), ...
Chapter 19
... Redox and Electronegativity The chemistry of oxidation-reduction reactions is not limited to atoms of an element changing to ions or the reverse. Some redox reactions involve changes in molecular substances or polyatomic ions in which atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the fol ...
... Redox and Electronegativity The chemistry of oxidation-reduction reactions is not limited to atoms of an element changing to ions or the reverse. Some redox reactions involve changes in molecular substances or polyatomic ions in which atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the fol ...
KHARKOV STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... Macroelements are elements found in almost all of Earth's living systems. There are 11 of them. Six are called organogens or major biogenic elements. Organogens are: C, O, H, N, P, S. The content of them is 97% in the organism. These elements have not very large atomic radii and intermediate values ...
... Macroelements are elements found in almost all of Earth's living systems. There are 11 of them. Six are called organogens or major biogenic elements. Organogens are: C, O, H, N, P, S. The content of them is 97% in the organism. These elements have not very large atomic radii and intermediate values ...
Unit 12: Electrochemistry
... 4. Converter: A device that takes AC commercial current and converts it to DC current at the step-down voltage required by the device. 5. Direct Current (DC): The current produced by generators and batteries, where electricity flows only from anode to cathode. DC current is used in battery-powered e ...
... 4. Converter: A device that takes AC commercial current and converts it to DC current at the step-down voltage required by the device. 5. Direct Current (DC): The current produced by generators and batteries, where electricity flows only from anode to cathode. DC current is used in battery-powered e ...
Exam Review
... hotter parts of the tower, whereas those with lower boiling points condense near the cooler top of the tower. At various levels in the tower, trays collect mixtures of substances as they condense, each mixture containing compounds with similar boiling points. These mixtures are called petroleum fra ...
... hotter parts of the tower, whereas those with lower boiling points condense near the cooler top of the tower. At various levels in the tower, trays collect mixtures of substances as they condense, each mixture containing compounds with similar boiling points. These mixtures are called petroleum fra ...
Isopropanol oxidation by pure metal oxide
... reduction of the metal oxide surface can usually take place. Other methods involve the adsorption of CO2 and NH3 . CO2 and NH3 do not measure all the surface sites. CO2 only adsorbs on basic OH groups on the surface and NH3 only adsorbs on Lewis and Bronsted acid sites. Furthermore, the above method ...
... reduction of the metal oxide surface can usually take place. Other methods involve the adsorption of CO2 and NH3 . CO2 and NH3 do not measure all the surface sites. CO2 only adsorbs on basic OH groups on the surface and NH3 only adsorbs on Lewis and Bronsted acid sites. Furthermore, the above method ...
Mineralization of Drugs in Aqueous Medium by Advanced Oxidation
... This procedure is known as anodic oxidation with H2O2 electrogeneration. The electro-Fenton process involves the enhancement of the oxidizing power of the above electrolytic system by adding small amounts of a catalyst like Fe2+, which reacts with electrogenerated H2O2 to yield •OH in solution from ...
... This procedure is known as anodic oxidation with H2O2 electrogeneration. The electro-Fenton process involves the enhancement of the oxidizing power of the above electrolytic system by adding small amounts of a catalyst like Fe2+, which reacts with electrogenerated H2O2 to yield •OH in solution from ...
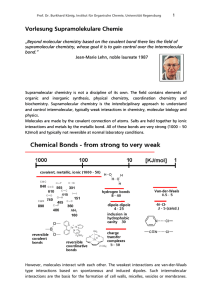
Vorlesung Supramolekulare Chemie
... directional and therefore of special importance in molecular recognition. The lengths, strengths and orientation of hydrogen bonds vary over a large range. In the solid state a single hydrogen bond can be sufficient to determine the structure; in solution or gas phase it may influence the aggregate ...
... directional and therefore of special importance in molecular recognition. The lengths, strengths and orientation of hydrogen bonds vary over a large range. In the solid state a single hydrogen bond can be sufficient to determine the structure; in solution or gas phase it may influence the aggregate ...
Chemistry - Benton Park School
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
File
... The colour before as well as after the test must be given in the answer. For example, bromine water changes from brown to colourless, not ‘is decolorised’, and acidified potassium dichromate(vi) goes from orange to green, not ‘goes green’. Gas evolved is not an observation (it is a deduction). Bubbl ...
... The colour before as well as after the test must be given in the answer. For example, bromine water changes from brown to colourless, not ‘is decolorised’, and acidified potassium dichromate(vi) goes from orange to green, not ‘goes green’. Gas evolved is not an observation (it is a deduction). Bubbl ...
Experimental and Computational Evidence of Metal‑O2 Activation
... serves as a fairly rigorous criterion for evaluating transition states. The Transition State Theory formalism in eq 4 requires isotopic imaginary modes to define the isotope effect on the reaction coordinate (18νRC) and 3N-6 stable isotopic vibrations to define the isotope effect on the pseudoequilibriu ...
... serves as a fairly rigorous criterion for evaluating transition states. The Transition State Theory formalism in eq 4 requires isotopic imaginary modes to define the isotope effect on the reaction coordinate (18νRC) and 3N-6 stable isotopic vibrations to define the isotope effect on the pseudoequilibriu ...
Η - Knockhardy
... 25cm3 of 2.0M HCl was added to 25cm3 of 2.0M NaOH in an insulated beaker. The initial temperature of both solutions was 20°C. The reaction mixture was stirred to ensure mixing and the highest temperature reached by the solution was 33°C. Calculate the Molar Enthalpy of Neutralisation. ...
... 25cm3 of 2.0M HCl was added to 25cm3 of 2.0M NaOH in an insulated beaker. The initial temperature of both solutions was 20°C. The reaction mixture was stirred to ensure mixing and the highest temperature reached by the solution was 33°C. Calculate the Molar Enthalpy of Neutralisation. ...
Support Material
... always contains the same elements in the same proportion by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay L ...
... always contains the same elements in the same proportion by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay L ...
Section 4.8
... results from the combustion of fossil fuels. • This is the balanced equation for the combustion of octane (gasoline) • 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) ...
... results from the combustion of fossil fuels. • This is the balanced equation for the combustion of octane (gasoline) • 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) ...
Review of N and Metal co-Doped TiO for Water Purification under
... various anthropogenic inputs. Despite their low concentration, the presence of these contaminants is still a major concern over public health and a major obstacle to water recycling due to their bio-recalcitrant and acute toxicity [2]. The method of “advanced oxidation processes” (AOPs) appears to b ...
... various anthropogenic inputs. Despite their low concentration, the presence of these contaminants is still a major concern over public health and a major obstacle to water recycling due to their bio-recalcitrant and acute toxicity [2]. The method of “advanced oxidation processes” (AOPs) appears to b ...
Stoichiometry
... formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. Example: I want to assemble a gadget that requires one nut, one bolt and two washers for every hole. I have in my garage a bucket filled with 12 washers, 4 bolts and five nuts. What is the LIMITING SMALL METAL ...
... formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. Example: I want to assemble a gadget that requires one nut, one bolt and two washers for every hole. I have in my garage a bucket filled with 12 washers, 4 bolts and five nuts. What is the LIMITING SMALL METAL ...
Chemical Equations
... Chemical Equations Identify the substances involved in a chemical process Distinguish between the reactants and products in a chemical process Allow easy determination of quantities of substances involved in chemical processes ...
... Chemical Equations Identify the substances involved in a chemical process Distinguish between the reactants and products in a chemical process Allow easy determination of quantities of substances involved in chemical processes ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.